Artículos SCI
2015
2015
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Nanocolumnar 1-dimensional TiO2 photoanodes deposited by PVD-OAD for perovskite solar cell fabrication
Javier Ramos, F.; Oliva-Ramirez, Manuel; Nazeeruddin, Mohammad Khaja; Graetzel, Michael; Gonzalez-Elipe, Agustin R.; Ahmad, ShahzadaJournal of Materials Chemistry A, 3 (2015) 13291-13298
Show abstract ▽
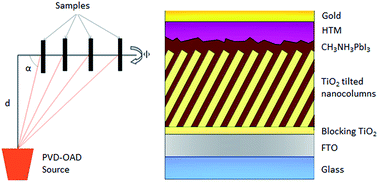
Perovskite solar cells have attracted increasing interest among the photovoltaic community in the last few years owing to their unique properties and high efficiency. In the present work, we report the fabrication of perovskite solar cells based on highly ordered 1-dimensional porous TiO2 photoanodes, which are uniform on a large area. These nanocolumnar porous TiO2 photoanodes were deposited by physical vapor deposition in an oblique angle configuration (PVD-OAD) by varying the zenithal angle between the target and the substrate normal. Perovskite infiltration into these 1-dimensional nanocolumnar structures was homogeneous through the entire thickness of the porous layer as revealed by secondary ion mass spectroscopy studies. The fabricated solar cells, with an optimized thickness of the photoanode and with industrially accepted methods, will pave the way for easy implementation on a large scale.
Julio, 2015 | DOI: 10.1039/c5ta02238j
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Island-type growth of Au–Pt heterodimers: direct visualization of misfit dislocations and strain-relief mechanisms
Garcia-Negrete, CA; Knappett, BR; Schmidt, FP; Rojas, TC; Wheatley, AEH; Hofer, F; Fernandez, ARSC Advances, 5 (2015) 55262-55268
Show abstract ▽
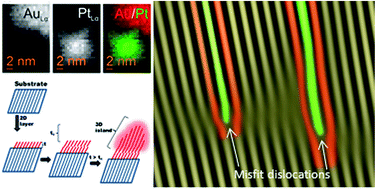
Structural and analytical characterization related to the formation mechanism of Au–Pt heterodimers from polyhedral Pt nanocrystals is reported. The observation of specific lattice strain effects and the emergence of misfit dislocations point to the relevance of the Stranski–Krastanov growth mode as a means of explaining the previously reported dimerisation reaction between Au and Pt. Two size-dependent strain relief mechanisms were identified. For dimers grown from 4.7 nm seeds, the mechanism is related to bulk lattice strain accumulation at {111} planes along with lattice relaxation effects on other crystalline planes. However, for dimers grown from 11.2 nm seed sizes, the formation of misfit dislocations proved to be a highly efficient mechanism by which to release interface mismatch strain. Nanoscale chemical mapping at Au–Pt interfaces also revealed Au–Pt alloying to be unlikely under the mild temperature conditions employed in this work for Au–Pt heterodimer synthesis.
Junio, 2015 | DOI: 10.1039/C5RA09808D
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Environmental Effects on the Photophysics of Organic-Inorganic Halide Perovskites
Galisteo-Lopez, JF; Anaya, M; Calvo, ME; Miguez, HJournal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 6 (2015) 2200-2205
Show abstract ▽
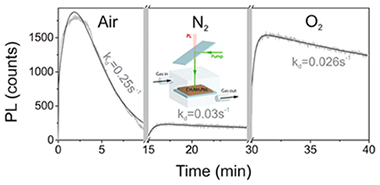
The photophysical properties of films of organic-inorganic lead halide perovskites under different ambient conditions are herein reported. We demonstrate that their luminescent properties are determined by the interplay between photoinduced activation and darkening processes, which strongly depend on the atmosphere surrounding the samples. We have isolated oxygen and moisture as the key elements in each process, activation and darkening, both of which involve the interaction with photogenerated carriers. These findings show that environmental factors play a key role in the performance of lead halide perovskites as efficient luminescent materials.
Junio, 2015 | DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.5b00785
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Core-shell polydopamine magnetic nanoparticles as sorbent in micro-dispersive solid-phase extraction for the determination of estrogenic compounds in water samples prior to high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis
Socas-Rodriguez, B; Hernandez-Borges, J; Salazar, P; Martin, M; Rodriguez-Delgado, MAJournal of Chromatography A, 1397 (2015) 1-10
Show abstract ▽

In this work, core-shell Fe3O4@poly(dopamine) magnetic nanoparticles (m-NPs) were prepared and characterized in our laboratory and applied as sorbents for the magnetic-micro solid phase extraction (m-mu SPE) of twelve estrogenic compounds of interest (i.e. 17 alpha-estradiol, 17 beta-estradiol, estrone, hexestrol, 17 alpha-ethynylestradiol, diethylstibestrol, dienestrol, zearalenone, alpha-zearalanol,beta-zearalanol, alpha-zearalenol and beta-zearalenol) from different water samples. Separation, determination and quantification were achieved by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled to ion trap mass spectrometry with electrospray ionization. NPs@poly(dopamine) were synthesized by a chemical coprecipitation procedure and characterized by different surface characterization techniques (X-ray diffraction, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, thermogravimetric analysis, transmission and scanning electron microscopy, infrared and Raman spectroscopy, vibrating sample magnetometry, microelectrophoresis and adsorption/desorption isotherms). Parameters affecting the extraction efficiency of m-mu SPE (i.e. polymerization time, pH of the sample, extraction and elution conditions) were studied and optimized. The methodology was validated for Milli-Q, mineral, tap and wastewater using 2-methoxyestradiol as internal standard, obtaining recoveries ranging from 70 to 119% with relative standard deviation values lower than 20% and limits of quantification in the range 0.02-1.1 mu g/L.
Junio, 2015 | DOI: 10.1016/j.chroma.2015.04.010
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
A novel two-steps solvothermal synthesis of nanosized BiPO4 with enhanced photocatalytic activity
Zhang, YF; Sillanpaa, M; Obregon, S; Colon, GJournal of Molecular Catalysis A-Chemical, 402 (2015) 92-99
Show abstract ▽
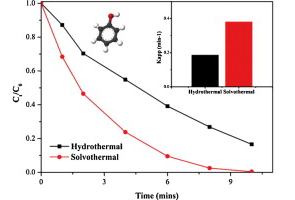
Nano-sized BiPO4 has been successfully synthesized via a novel designed two-steps solvothermal route using ethylene glycol as solvent. Comparing with traditional hydrothermal method, the novel approach could readily prepare BiPO4 with shorter time. The photocatalytic activity of prepared BiPO4 has been tested via degradation of methylene blue (MB) under light irradiation. The experimental results show that the BiPO4 prepared by novel route had enhanced photocatalytic activity and the synthetic parameters also impact the reaction rate meaningfully. Finally, the obtained samples have been widely characterized by means of powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) surface area, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), UV–vis diffuse reflectance spectra (DRS) and Fourier transformed infrared (FTIR) spectra. BiPO4 prepared by this novel approach have a particles size below 100 nm, which is a big improvement by comparing with previous works (few micrometer). The effect of EG during the formation of BiPO4 has been discussed and a possible formation mechanism is proposed.
Junio, 2015 | DOI: 10.1016/j.molcata.2015.03.011
- ‹ anterior
- 247 of 420
- siguiente ›














