Artículos SCI
2015
2015
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Fine Tuning the Emission Properties of Nanoemitters in Multilayered Structures by Deterministic Control of their Local Photonic Environment
Alberto Jiménez-Solano, Juan Francisco Galisteo-López and Hernán MíguezSmall, 11 (2015) 2727-2732
Show abstract ▽
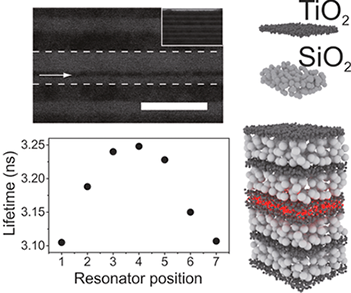
Deterministic control on the dynamics of organic nanoemitters is achieved through precise control of its photonic environment. Resonators are fabricated by a combination of spin- and dip-coating techniques, which allows placement of the emitters at different positions within the sample, thus acting as a probe of the local density of states.
Junio, 2015 | DOI: 10.1002/smll.201402898
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
H-2 oxidation as criterion for PrOx catalyst selection: Examples based on Au-Co-O-x-supported systems
Reina, TR; Megias-Sayago, C; Florez, AP; Ivanova, S; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAJournal of Catalysis, 326 (2015) 161-171
Show abstract ▽
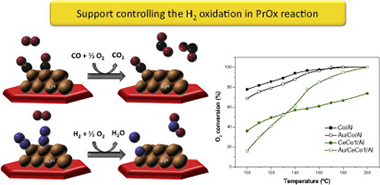
A new approach for understanding PrOx reaction over gold catalysts is proposed in this work. The competition between H-2 and CO oxidation has been studied over a series of Au/MOx/Al2O3 (M = Ce and Co) catalysts in simulated post-reforming gas stream, containing H2O and CO2 for H-2 cleanup goals. The catalysts' behavior is correlated to their oxygen storage capacity, redox behavior, and oxidation ability. The estimation of the reaction rates reveals that in these solids the H-2 combustion, the selectivity limiting factor in the PrOx process, is mainly controlled by the support and not by the gold presence. The possible use of the hydrogen oxidation reaction as a catalyst selection criterion is discussed.
Junio, 2015 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jcat.2015.03.015
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Porous, robust highly conducting Ni-YSZ thin film anodes prepared by magnetron sputtering at oblique angles for application as anodes and buffer layers in solid oxide fuel cells
Garcia-Garcia, Francisco J.; Yubero, Francisco; Gonzalez-Elipe, Agustin R.; Balomenou, Stella P.; Tsiplakides, Dimitris; Petrakopoulou, Ioanna; Lambert, Richard M.Inernational Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 40 (2015) 7382-7387
Show abstract ▽
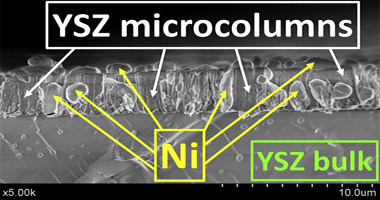
Uniform, highly porous, columnar thin films incorporating YSZ and NiO prepared by magnetron sputtering with deposition at glancing incidence exhibited stoichiometries close to that of the Y-Zr-Ni sputter target. Characterization by means of SEM, XRD, XPS and RBS revealed that the uniformly distributed nickel component in the as-deposited films consisted of NiO, and that the YSZ component was essentially amorphous. Annealing such films at 850 degrees C in hydrogen resulted in crystallization of the YSZ phase with preservation of the columnar morphology, while the NiO underwent reduction to metallic Ni, which partially segregated to the film surface. The hydrogen-annealed thin film anodes exhibited high conductivity, comparable to that of conventionally-prepared anodes, in both hydrogen and hydrogen/water mixtures at temperatures relevant to SOFC operation. They were also robust against strain-induced separation from the substrate under limited thermal cycling in both oxidizing and reducing atmospheres and are promising candidates for use as anodes in their own right and as strain-accommodating buffer layers between conventional anodes and the electrolyte for use in SOFC applications.
Junio, 2015 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2015.04.001
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Uranium immobilization by FEBEX bentonite and steel barriers in hydrothermal conditions
Villa-Alfageme, M; Hurtado, S; El Mrabet, S; Pazos, MC; Castro, MA; Alba, MDChemical Engineering Journal, 269 (2015) 279-287
Show abstract ▽
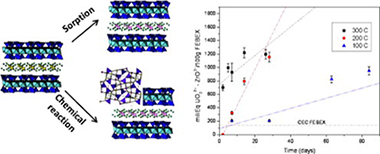
FEBEX clay is considered a reference material in engineered barriers for safe storage of nuclear waste and uranium is a minor component of high-level radioactive waste (HLRW) and a main component of the spent nuclear fuel (SNF). Here, the kinetics of reaction of uranium with FEBEX was investigated in addition to the uranium immobilisation ability and the structural analysis of the reaction products. Hydrothermal treatments were accomplished with UO22+ and tetravalent actinide simulator ZrO2+, also present in HLRW. The quantification of the reaction was performed through gamma spectrometry of uranium. Two mechanisms for UO22+ retention by FEBEX were detected: adsorption and formation of stable and insoluble new phases. The structural analyses performed using ZrO2+, confirmed the uranium adsorption and the presence of new phases, ZrO2 and Zr(SiO4), that emphasise the existence of a chemical reaction with the bentonite. The analysis of the velocity of reaction uranium-clay minerals revealed temperature dependence. An exponential fitting suggested that the removal of uranium from solution at temperatures over 200 °C could be completed in less than a year. For lower temperatures, several years are needed. Milliequivalents of UO22+ immobilised by the clay depended on temperature and time and were over cation exchange capacity (CEC) of FEBEX even at 100 °C (reaching 600% of CEC). The reaction with steel, also temperature dependent, was finally analysed. At 200 °C 40–70% of uranium reacted with steel. But only 30–15% reacted at 300 °C and 100 °C. The reactions provide a stable immobilisation mechanism for uranium even when its sorption and swelling capacities fail. Our experiments will be of particular interest for very deep borehole disposals were higher temperatures and pressures are expected.
Junio, 2015 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.01.134
Reactividad de Sólidos
In Situ Synthesis of a ZrB2-Based Composite Powder Using a Mechanochemical Reaction for the Zircon/Magnesium/Boron Oxide/Graphite System
Jalaly, M; Bafghi, MSS; Tamizifar, M; Gotor, FJInternational Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 12 (2015) 551-559
Show abstract ▽
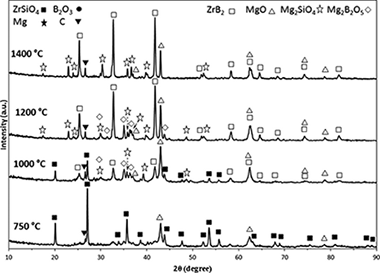
A ZrSiO4/B2O3/Mg/C system was used to synthesize a ZrB2-based composite through a high-energy ball milling process. As a result of the milling process, a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction (MSR) was achieved in this system. A composite powder of ZrB2-SiC-ZrC was prepared in situ by a magnesiothermic reduction with an ignition time of approximately 6min. The mechanism for the formation of the product was investigated by studying the relevant subreactions, the stoichiometric amount of B2O3, and thermal analysis.
Mayo, 2015 | DOI: 10.1111/ijac.12202
- ‹ anterior
- 248 of 420
- siguiente ›














