Artículos SCI
2015
2015
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Anisotropic In-Plane Conductivity and Dichroic Gold Plasmon Resonance in Plasma-Assisted ITO Thin Films e-Beam-Evaporated at Oblique Angles
Parra-Barranco, Julian; Garcia-Garcia, Francisco J.; Rico, Victor; Borras, Ana; Lopez-Santos, Carmen; Frutos, Fabian; Barranco, Angel; Gonzalez-Elipe, Agustin R.ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 7 (2015) 10993-11001
Show abstract ▽
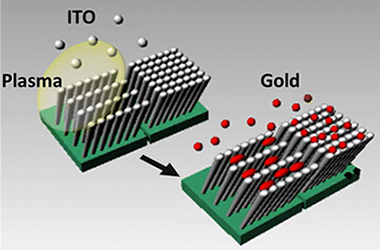
ITO thin films have been prepared by electron beam evaporation at oblique angles (OA), directly and while assisting their growth with a downstream plasma. The films microstructure, characterized by scanning electron microscopy, atomic force microscopy, and glancing incidence small-angle X-ray scattering, consisted of tilted and separated nanostructures. In the plasma assisted films, the tilting angle decreased and the nanocolumns became associated in the form of bundles along the direction perpendicular to the flux of evaporated material. The annealed films presented different in-depth and sheet resistivity as confirmed by scanning conductivity measurements taken for the individual nanocolumns. In addition, for the plasma-assisted thin films, two different sheet resistance values were determined by measuring along the nanocolumn bundles or the perpendicular to it. This in-plane anisotropy induces the electrochemical deposition of elongated gold nanostructures. The obtained Au-ITO composite thin films were characterized by anisotropic plasmon resonance absorption and a dichroic behavior when examined with linearly polarized light.
Mayo, 2015 | DOI: 10.1021/acsami.5b02197
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Electrochemical activation of an oblique angle deposited Cu catalyst film for H-2 production
Gonzalez-Cobos, J; Rico, VJ; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Valverde, JL; de Lucas-Consuegra, ACatalysis Science & Technology, 5 (2015) 2203-2214
Show abstract ▽
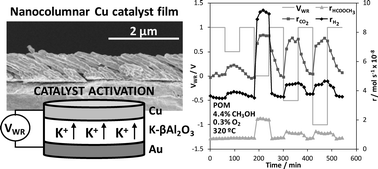
A novel Cu catalyst film was prepared by oblique angle physical vapour deposition (OAD) on a K-βAl2O3 solid electrolyte (alkaline ionic conductor) for catalytic/electrocatalytic purposes. This technique allowed us to obtain a highly porous and electrically conductive Cu catalyst electrode which was tested in the partial oxidation of methanol (POM) reaction for H2 production and its catalytic activity was in situ enhanced via electrochemical promotion of catalysis (EPOC). The electropromotional effect was reversible and reproducible, and allowed us to increase both hydrogen and methyl formate production rates by almost three times under optimal promotion conditions (320 °C, 2.2 × 10−7 mol of K+ transferred). The observed promotional effect was attributed to a decrease in the Cu catalyst work function as a consequence of the controlled migration of electropositive K+ ions which favoured the chemisorption of electron acceptor molecules (O2) at the expense of the electron donor ones (CH3OH). Under the reaction conditions these ions formed some kinds of potassium surface compounds as demonstrated by SEM, EDX and XPS post-reaction characterization analyses. The obtained results demonstrate the interest of the used catalyst-electrode preparation technique for the electrochemical activation of non-noble metal catalyst films.
Mayo, 2015 | DOI: 10.1039/c4cy01524j
Reactividad de Sólidos
In Situ Synthesis of a ZrB2-Based Composite Powder Using a Mechanochemical Reaction for the Zircon/Magnesium/Boron Oxide/Graphite System
Jalaly, M; Bafghi, MSS; Tamizifar, M; Gotor, FJInternational Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology, 12 (2015) 551-559
Show abstract ▽
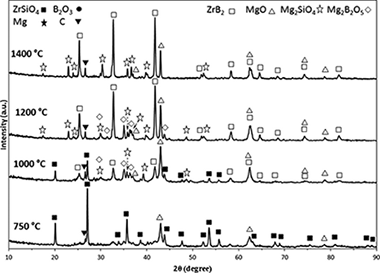
A ZrSiO4/B2O3/Mg/C system was used to synthesize a ZrB2-based composite through a high-energy ball milling process. As a result of the milling process, a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction (MSR) was achieved in this system. A composite powder of ZrB2-SiC-ZrC was prepared in situ by a magnesiothermic reduction with an ignition time of approximately 6min. The mechanism for the formation of the product was investigated by studying the relevant subreactions, the stoichiometric amount of B2O3, and thermal analysis.
Mayo, 2015 | DOI: 10.1111/ijac.12202
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Free-Base Carboxyphenyl Porphyrin Films Using a TiO2 Columnar Matrix: Characterization and Application as NO2 Sensors
Roales, Javier; Pedrosa, Jose M.; Guillen, Maria G.; Lopes-Costa, Tania; Castillero, Pedro; Barranco, Angel; Gonzalez-Elipe, Agustin R.Sensors, 15 (2015) 11118-11132
Show abstract ▽
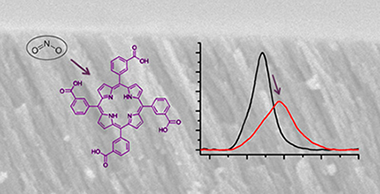
The anchoring effect on free-base carboxyphenyl porphyrin films using TiO2 microstructured columns as a host matrix and its influence on NO2 sensing have been studied in this work. Three porphyrins have been used: 5-(4-carboxyphenyl)10,15,20-triphenyl-21H,23H-porphyrin (MCTPP); 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(4-carboxyphenyl)-21H,23H-porphyrin (p-TCPP); and 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(3-carboxyphenyl)-21H,23H-porphyrin (m-TCPP). The analysis of UV-Vis spectra of MCTPP/TiO2, p-TCPP/TiO2 and m-TCPP/TiO2 composite films has revealed that m-TCPP/TiO2 films are the most stable, showing less aggregation than the other porphyrins. IR spectroscopy has shown that m-TCPP is bound to TiO2 through its four carboxylic acid groups, while p-TCPP is anchored by only one or two of these groups. MCTPP can only be bound by one carboxylic acid. Consequently, the binding of p-TCPP and MCTPP to the substrate allows them to form aggregates, whereas the more fixed anchoring of m-TCPP reduces this effect. The exposure of MCTPP/TiO2, p-TCPP/TiO2 and m-TCPP/TiO2 films to NO2 has resulted in important changes in their UV-Vis spectra, revealing good sensing capabilities in all cases. The improved stability of films made with m-TCPP suggests this molecule as the best candidate among our set of porphyrins for the fabrication of NO2 sensors. Moreover, their concentration-dependent responses upon exposure to low concentrations of NO2 confirm the potential of m-TCPP as a NO2 sensor.
Mayo, 2015 | DOI: 10.3390/s150511118
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Mono and bimetallic Cu-Ni structured catalysts for the water gas shift reaction
O. Arbeláez, T.R. Reina, S. Ivanova, F. Bustamante, A.L. Villa, M.A. Centeno, J.A. OdriozolaApplied Catalysis A-General, 497 (2015) 1-9
Show abstract ▽
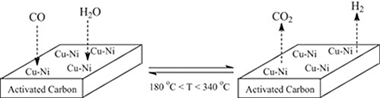
The water-gas shift (WGS) reaction over structured Cu, Ni, and bimetallic Cu-Ni supported on active carbon (AC) catalysts was investigated. The structured catalysts were prepared in pellets form and applied in the medium range WGS reaction. A good activity in the 180–350 °C temperature range was registered being the bimetallic Cu-Ni:2-1/AC catalyst the best catalyst. The presence of Cu mitigates the methanation activity of Ni favoring the shift process. In addition the active carbon gasification reaction was not observed for the Cu-containing catalyst converting the active carbon in a very convenient support for the WGS reaction. The stability of the bimetallic Cu-Ni:2-1/AC catalyst under continuous operation conditions, as well as its tolerance towards start/stop cycles was also evaluated.
Mayo, 2015 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2015.02.041
- ‹ anterior
- 249 of 420
- siguiente ›














