Artículos SCI
2014
2014
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Understanding the Role of the Cosolvent in the Zeolite Template Function of Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquid
Ayala, R; Ivanova, S; Blanes, JMM; Romero-Sarria, F; Odriozola, JAJournal of Physical Chemistry B, 118 (2014) 3650–3660 DOI: 10.1021/jp410260g
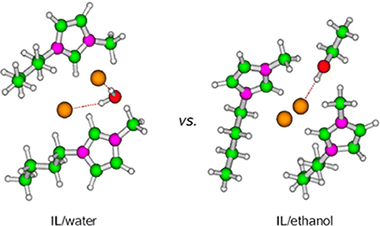
Abstract
In this work, a study for understanding the role played by [ClBmim], [BF4Bmim], [PF6Bmim], and [CH3SO3Bmim] ionic liquids (ILs) in the synthesis of zeolites is presented. The use of [ClBmim] and [CH3SO3Bmim] ILs, as reported earlier [ Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 2122] led to the formation of MFI or BEA type zeolites. Contrary, [BF4Bmim] and [PF6Bmim] ILs did not succeed in organizing the Si–Al network into a zeolite structure. To try to explain these results, a series of quantum mechanical calculations considering monomers ([XBmim]) and dimers ([XBmim]2) by themselves and plus cosolvent (water or ethanol) were carried out, where X ≡ Cl–, BF4–, PF6–, or CH3SO3–. Our attention was focused on the similarities and differences among the two types of cosolvents and the relation between the structure and the multiple factors defining the interactions among the ILs and the cosolvent. Although a specific pattern based on local structures explaining the different behavior of these ILs as a zeolite structuring template was not found, the calculated interaction energies involving the Cl– and CH3SO3– anions were very close and larger than those for BF4– and PF6– species. These differences in energy can be used as an argument to describe their different behavior as structure directing agents. Moreover, the topology of the cosolvent is also an ingredient to take into account for a proper understanding of the results.
Abril, 2014 · DOI: 10.1021/jp410260g
Reactividad de Sólidos
Nanosilica supported CaO: A regenerable and mechanically hard CO2 sorbent at Ca-looping conditions
Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Valverde, JMApplied Energy, 118 (2014) 92-99 DOI: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2013.12.024
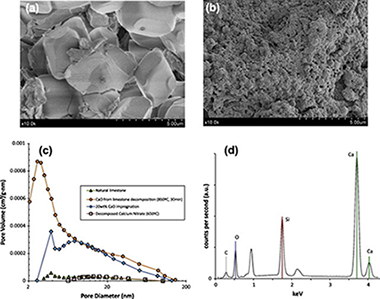
Abstract
This work presents a CO2 sorbent that may be synthesized from low-cost and widely available materials following a simple method basically consisting of impregnation of a nanostructured silica support with a saturated solution of calcium nitrate. In a first impregnation stage, the use of a stoichiometric CaO/SiO2 ratio serves to produce a calcium silicate matrix after calcination. This calcium silicate matrix acts as a thermally stable and mechanically hard support for CaO deposited on it by further impregnation. The CaO-impregnated sorbent exhibits a stable CaO conversion at Ca-looping conditions whose value depends on the CaO wt% deposited on the calcium silicate matrix, which can be increased by successive reimpregnations. A 10 wt% CaO impregnated sorbent reaches a stable conversion above 0.6 whereas the stable conversion of a 30 wt% CaO impregnated sorbent is around 0.3, which is much larger than the residual conversion of CaO derived from natural limestone (between 0.07 and 0.08). Moreover, particle size distribution measurements of samples predispersed in a liquid and subjected to high energy ultrasonic waves indicate that the CaO-impregnated sorbent has a relatively high mechanical strength as compared to limestone derived CaO.
Abril, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2013.12.024
Reactividad de Sólidos
Comparison of thermal behavior of natural and hot-washed sisal fibers based on their main components: Cellulose, xylan and lignin. TG-FTIR analysis of volatile products
Benitez-Guerrero, M; Lopez-Beceiro, J; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Pascual-Cosp, JThermochimica Acta, 581 (2014) 70-86 DOI: 10.1016/j.tca.2014.02.013
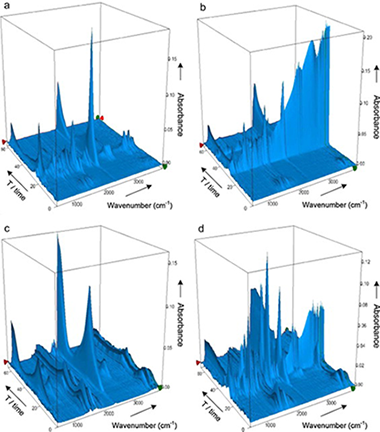
Abstract
This paper presents in a comprehensive way the thermal behavior of natural and hot-washed sisal fibers, based on the fundamental components of lignocellulosic materials: cellulose, xylan and lignin. The research highlights the influence exerted on the thermal stability of sisal fibers by other constituents such as non-cellulosic polysaccharides (NCP) and mineral matter.
Thermal changes were investigated by thermal X-ray diffraction (TXRD), analyzing the crystallinity index (%Ic) of cellulosic samples, and by simultaneous thermogravimetric and differential thermal analysis coupled with Fourier-transformed infrared spectrometry (TG/DTA-FTIR), which allowed to examine the evolution of the main volatile compounds evolved during the degradation under inert and oxidizing atmospheres. The work demonstrates the potential of this technique to elucidate different steps during the thermal decomposition of sisal, providing extensible results to other lignocellulosic fibers, through the analysis of the evolution of CO2, CO, H2O, CH4, acetic acid, formic acid, methanol, formaldehyde and 2-butanone, and comparing it with the volatile products from pyrolysis of the biomass components. The hydroxyacetaldehyde detected during pyrolysis of sisal is indicative of an alternative route to that of levoglucosan, generated during cellulose pyrolysis.
Hot-washing at 75 °C mostly extracts non-cellulosic components of low decomposition temperature, and reduces the range of temperature in which sisal decomposition occurs, causing a retard in the pyrolysis stage and increasing TbNCP and TbCEL, temperatures at the maximum mass loss rate of non-cellulosic polysaccharides and cellulose decompositions, respectively. However, enriching sisal fibers in cellulose produces a decrease of TbCEL under an oxidizing atmosphere, and furthermore, a delay of the combustion process, displacing TbCOM to higher temperatures.
The results and findings of the paper would help further understanding of thermal processes where Agave fibers are involved, as the decomposition of their composites.
Abril, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.tca.2014.02.013
Reactividad de Sólidos
The effect of polymer matrices on the thermal hazard properties of RDX-based PBXs by using model-free and combined kinetic analysis
Yan, QL; Zeman, S; Jimenez, PES; Zhao, FQ; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Malek, JJournal of Hazardous Materials, 271 (2014) 185-195 DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.02:019
Abstract
In this paper, the decomposition reaction models and thermal hazard properties of 1,3,5-trinitro-1,3,5-triazinane (RDX) and its PBXs bonded by Formex P1, Semtex 1A, C4, Viton A and Fluorel polymer matrices have been investigated based on isoconversional and combined kinetic analysis methods. The established kinetic triplets are used to predict the constant decomposition rate temperature profiles, the critical radius for thermal explosion and isothermal behavior at a temperature of 82 C. It has been found that the effect of the polymer matrices on the decomposition mechanism of RDX is significant resulting in very different reaction models. The Formex P1, Semtex and C4 could make decomposition process of RDX follow a phase boundary controlled reaction mechanism, whereas the Viton A and Fluorel make its reaction model shifts to a two dimensional Avrami-Erofeev nucleation and growth model. According to isothermal simulations, the threshold cook-off time until loss of functionality at 82 degrees C for RDX-C4 and RDX-FM is less than 500 days, while it is more than 700 days for the others. Unlike simulated isothermal curves, when considering the charge properties and heat of decomposition, RDX-FM and RDX-C4 are better than RDX-SE in storage safety at arbitrary surrounding temperature.
Abril, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.02:019
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Influence of the acid–base properties over NiSn/MgO–Al2O3 catalysts in the hydrogen production from glycerol steam reforming
Bobadilla, LF; Penkova, A; Romero-Sarria, F; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAInternational Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 39 (2014) 5704-5712 DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2014.01.136
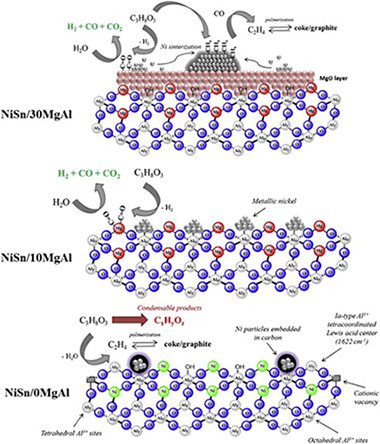
Abstract
In this work we have investigated the hydrogen production from glycerol steam reforming. The effect of the acid-base properties was evaluated using four catalysts based in an alloy Ni-Sn as active phase supported over (Upsilon)-Al2O3 with different content in MgO, varying between 0 and 30 wt.% The incorporation of MgO results in the formation of MgAl2O4 spinel, which modifies the acid-base properties of the catalyst. Addition of MgO favored the glycerol conversion into gas, and the catalyst loaded with 10 wt.% MgO exhibited better catalytic performance and higher stability. A blank test with quartz was performed indicating that pyrolysis of glycerol takes place in the quartz.
Abril, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2014.01.136
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Perovskite Solar Cells Based on Nanocolumnar PlasmaDeposited ZnO Thin Films
Ramos, FJ; Lopez-Santos, MC; Guillen, E; Nazeeruddin, MK; Gratzel, M; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Ahmad, SChemphyschem, 15 (2014) 1148-1153 DOI: 10.1002/cphc.201301215
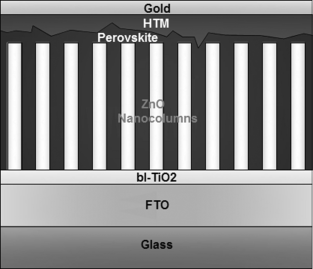
Abstract
ZnO thin films having a nanocolumnar microstructure are grown by plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition at 423 K on pre-treated fluorine-doped tin oxide (FTO) substrates. The films consist of c-axis-oriented wurtzite ZnO nanocolumns with well-defined microstructure and crystallinity. By sensitizing CH3NH3PbI3 on these photoanodes a power conversion of 4.8 % is obtained for solid-state solar cells. Poly(triarylamine) is found to be less effective when used as the hole-transport material, compared to 2,2′,7,7′-tetrakis(N,N-di-p-methoxyphenylamine)-9,9′-spirobifluorene (spiro-OMeTAD), while the higher annealing temperature of the perovskite leads to a better infiltration in the nanocolumnar structure and an enhancement of the cell efficiency.
Abril, 2014 · DOI: 10.1002/cphc.201301215
Reactividad de Sólidos
Self-propagating combustion synthesis via an MSR process: An efficient and simple method to prepare (Ti, Zr, Hf)B2–Al2O3 powder nanocomposites
Sayagues, MJ; Aviles, MA; Cordoba, JM; Gotor, FJPowder Technology, 256 (2014) 244-250 DOI: 10.1016/j.powtec.2014.02.031
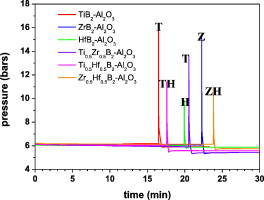
Abstract
The synthesis of (Ti1 − xZrx)B2–Al2O3, (Ti1 − xHfx)B2–Al2O3 and (Zr1 − xHfx)B2–Al2O3 (x = 0, 0.5 and 1) powder nanocomposites via a mechanochemical method using TiO2, ZrO2, HfO2, HBO2 and Al as the raw materials was investigated. The formation of the nanocomposites proceeds via a mechanically-induced self-sustaining reaction (MSR) process that involves several simultaneous reactions. The aluminothermic reductions of the TMO2 and HBO2 produce Al2O3 and transition metal and boron elements, which in turn react to yield the diboride phase. The ignition of the complex combustion reaction occurred after a short milling time (15–30 min), instantly transforming most of the reactants into products. The sample composition was marked by the stoichiometry of the combustion reaction, and the resulting nanocomposites were analysed using XRD, ED, SEM, TEM and EDX techniques. The X-ray results confirmed the biphasic character of the prepared composite powder (TMB2 and Al2O3 structures); minor amounts of the Zr and Hf oxides were also observed. The achieved microstructure was characterised by the agglomeration of Al2O3 nanocrystallites and diboride crystals with a diffraction domain size ranging between 100 and 300 nm.
Abril, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.powtec.2014.02.031
Propiedades mecánicas, modelización y caracterización de cerámicos avanzados
Additive-free superhard B4C with ultrafine-grained dense microstructures
Moshtaghioun, BM; Cumbrera, FL; Ortiz, AL; Castillo-Rodriguez, M; Gomez-Garcia, DJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 34 (2014) 841-848 DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2013.10.006

Abstract
A unique combination of high-energy ball-milling, annealing, and spark-plasma sintering has been used to process superhard B4C ceramics with ultrafine-grained, dense microstructures from commercially available powders, without sintering additives. It was found that the ultrafine powder prepared by high-energy ball-milling is hardly at all sinterable, but that B2O3 removal by gentle annealing in Ar provides the desired sinterability. A parametric study was also conducted to elucidate the role of the temperature (1600–1800 °C), time (1–9 min), and heating ramp (100 or 200 °C/min) in the densification and grain growth, and thus to identify optimal spark-plasma sintering conditions (i.e., 1700 °C for 3 min with 100 °C/min) to densify completely (>98.5%) the B4C ceramics with retention of ultrafine grains (∼370 nm). Super-high hardness of ∼38 GPa without relevant loss of toughness (∼3 MPa m1/2) was thus achieved, attributable to the smaller grain size and to the transgranular fracture mode of the B4C ceramics.
Marzo, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2013.10.006
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
A new route of synthesis of Na-Mica-4 from sodalite
Naranjo, M; Castro, MA; Cota, A; Pavon, E; Pazos, MC; Alba, MDMicroporous and Mesoporous Materials, 188 (2014) 176-180 DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2013.12.004
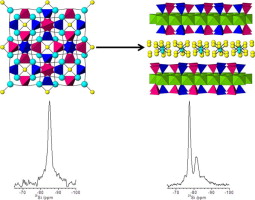
Abstract
Synthesis of Na-Mica-4 has been achieved by a “mix and calcine” method using sodalite and magnesium fluoride as the only precursors. Previous research found sodalite as a key intermediate reaction product in the formation of Na-Mica-4 when the NaCl melt method was employed. Similarities in structure, chemical composition and cation distribution in products using the proposed method and the NaCl melt method are described and suggest that Na-Mica-4 is a very stable product. The use of sodalite as precursor provokes microporous formation in the final mica. The absence of excess Na leads to a lower particle size and to the presence of less impurity in the calcined product. Different sodalites could be used in the synthesis of different Na-Mica-4 with presumably different physicochemical properties.
Marzo, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2013.12.004
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Long-term high temperature oxidation of CrAl(Y)N coatings in steam atmosphere
Mato, S; Alcala, G; Brizuela, M; Galindo, RE; Perez, FJ; Sanchez-Lopez, JCCorrosion Science, 80 (2014) 453-460 DOI: 10.1016/j.corsci.2013.11.066
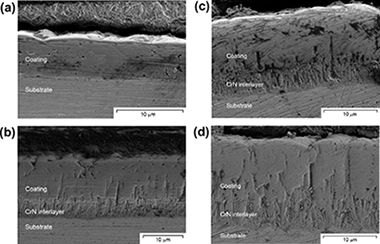
Abstract
The oxidation resistance of CrAl(Y)N coatings deposited by reactive magnetron sputtering on P92 steel substrates was tested at 650 °C in 100% steam atmosphere up to 2000 h of oxidation. Mass gain measurements and characterisation of coatings and scales after oxidation show the enhanced oxidation resistance provided by the coatings with respect to that of the substrate. The dominant influence of the film microstructure developed due to the presence of an adhesion interlayer of CrN at the coating/substrate interface over Y additions is evidenced. The best performance is achieved by a CrAlN dense coating of around 6 μm without adhesion interlayer.
Marzo, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.corsci.2013.11.066
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Mechanical and phase stability of TiBC coatings up to 1000 degrees C
Abad, MD; Veldhuis, SC; Endrino, JL; Beake, BD; Garcia-Luis, A; Brizuela, M; Sanchez-Lopez, JCJournal of Vacuum Science & Technology A, 32 (2014) 021508 DOI: 10.1116/1.4861365
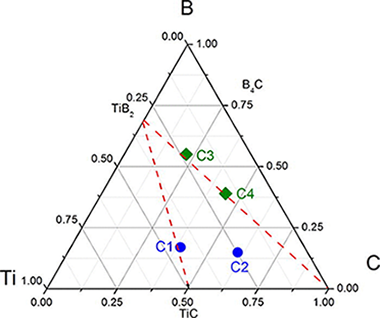
Abstract
TiBC coatings with different phase compositions (nanocrystalline TiBxCy or TiB2 phases mixed or not with amorphous carbon, a-C) were prepared by magnetron sputtering. These coatings were comparatively studied in terms of phase stability after thermal annealing at 250, 500, 750, and 1000 °C in argon using Raman and x-ray absorption near-edge spectroscopy techniques. The main differences were observed at temperatures above 500 °C when oxidation processes occur and the mechanical properties deteriorate. At 1000 °C, the samples were fully oxidized forming a-C, TiO2, and B2O3 as final products. Higher hardness and reduced indentation modulus values and better tribological properties were observed at 750 °C for nanocomposite structures including amorphous carbon and ternary TiBxCy phases. This behavior is attributed to a protective effect associated with the a-C phase which is achieved by the encapsulation of the nanocrystals in the coating and the better hard/lubricant phase ratio associated with this type of coating.
Marzo, 2014 · DOI: 10.1116/1.4861365
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Osteoblasts Interaction with PLGA Membranes Functionalized with Titanium Film Nanolayer by PECVD. In vitro Assessment of Surface Influence on Cell Adhesion during Initial Cell to Material Interaction
Terriza, A; Vilches-Perez, JI; Gonzalez-Caballero, JL; de la Orden, E; Yubero, F; Barranco, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Vilches, J; Salido, MMaterials, 7(3) (2014) 1687-1708 DOI: 10.3390/ma7031687
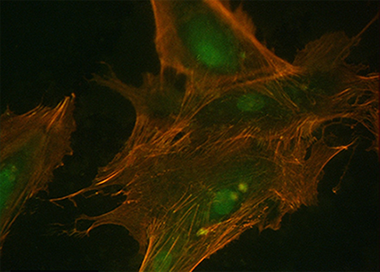
Abstract
New biomaterials for Guided Bone Regeneration (GBR), both resorbable and non-resorbable, are being developed to stimulate bone tissue formation. Thus, the in vitro study of cell behavior towards material surface properties turns a prerequisite to assess both biocompatibility and bioactivity of any material intended to be used for clinical purposes. For this purpose, we have developed in vitro studies on normal human osteoblasts (HOB®) HOB® osteoblasts grown on a resorbable Poly (lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) membrane foil functionalized by a very thin film (around 15 nm) of TiO2 (i.e., TiO2/PLGA membranes), designed to be used as barrier membrane. To avoid any alteration of the membranes, the titanium films were deposited at room temperature in one step by plasma enhanced chemical vapour deposition. Characterization of the functionalized membranes proved that the thin titanium layer completely covers the PLGA foils that remains practically unmodified in their interior after the deposition process and stands the standard sterilization protocols. Both morphological changes and cytoskeletal reorganization, together with the focal adhesion development observed in HOB osteoblasts, significantly related to TiO2 treated PLGA in which the Ti deposition method described has revealed to be a valuable tool to increase bioactivity of PLGA membranes, by combining cell nanotopography cues with the incorporation of bioactive factors.
Marzo, 2014 · DOI: 10.3390/ma7031687
Reactividad de Sólidos
Analysis on the mechanical strength of WC-Co cemented carbides under uniaxial and biaxial bending
Torres, Y; Bermejo, R; Gotor, FJ; Chicardi, E; Llanes, LMaterials & Design, 55 (2014) 851-856 DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2013.10.051
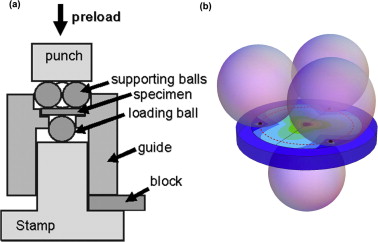
Abstract
The mechanical strength of three WC-Co grades was determined and compared under uniaxial and biaxial bending. Uniaxial four-point bending was conducted on bar-shaped specimens; biaxial testing was performed on discs using the ball-on-three-balls (B3B) method. Strength results were analysed within the frame of the Weibull theory. Differences in characteristic strength between uniaxial and biaxial bending were explained as an effect of the effective surface tested in each case. A higher Weibull modulus was obtained in one grade, independent of the testing method, which was related to its higher fracture toughness. The use and validity of the B3B biaxial test to determine the strength distribution of cemented carbides is discussed.
Marzo, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2013.10.051
Reactividad de Sólidos
Enhanced general analytical equation for the kinetics of the thermal degradation of poly(lactic acid)/montmorillonite nanocomposites driven by random scission
Carrasco, F; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Santana, OO; Maspoch, MLPolymer Degradation and Stability, 101 (2014) 52-59 DOI: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2014.01.014
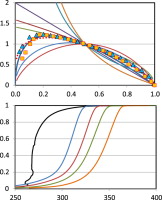
Abstract
An enhanced general analytical equation has been developed in order to evaluate the kinetic parameters of the thermal degradation of nanocomposites, composed of poly(lactic acid) (PLA) and organo-modified montmorillonite (OMMT) nanoparticles. This improvement has consisted of replacing the n-order conversion function by a modified form of the Sestak–Berggren equation f(α) = c (1 − α)nαm that led to a better adjustment of experimental data and also adequately represented the conventional mechanisms for solid-state processes. The kinetic parameters so obtained have been compared to those determined by conventional differential and isoconversional methods. Given that the thermal degradation of PLA has been argued to be caused by random chain scission reactions of ester groups, the conversion function f(α) = L (L − 1)x(1 − x)L−1, corresponding to a random scission mechanism, has been tested. Once optimized the kinetic model, the thermal degradation kinetics of nanocomposites (0.5 and 2.5% of OMMT) was compared to that of the polymer matrix. Moreover, the thermal stability of nanocomposites was tested and compared to that of the polymer matrix.
Marzo, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2014.01.014
Mineralogical Characterization of the Polychrome in Cultural Heritage Artifacts (Antiquity to Date) from Southern Spain Using Micro-Raman Spectroscopy and Complementary Techniques
Perez-Rodriguez, JL; Duran, ASpectroscopy Letters: An International Journal for Rapid Communication, 47 (2014) 223-237 DOI: 10.1080/00387010.2013.791857
Abstract
This work reports on the use of micro-Raman spectroscopy for the characterization of materials used for producing the polychrome in cultural heritage artifacts from southern Spain. The micro-Raman technique was applied for the characterization of several types of artworks or for cross-sections from these works, which were produced along different historical epochs. This technique was demonstrated to be valuable for the characterization of compounds, which were all detected within the artworks studied. The identification of all of these compounds by micro-Raman was confirmed by other complementary techniques, such as micro-X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopy coupled with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy.
Marzo, 2014 · DOI: 10.1080/00387010.2013.791857
Reactividad de Sólidos
An investigation on the formation mechanism of nano ZrB2 powder by a magnesiothermic reaction
Jalaly, M; Bafghi, MS; Tamizifar, M; Gotor, FJJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 588 (2014) 36-41 DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.11.050
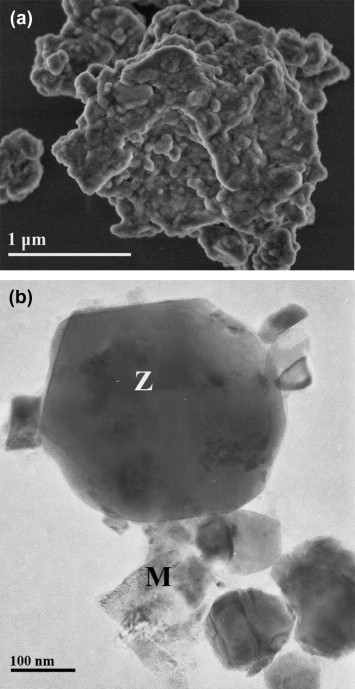
Abstract
Nanocrystalline zirconium diboride (ZrB2) powder was produced by mechanochemistry from the magnesiothermic reduction in the Mg/ZrO2/B2O3 system. The use of high-energy milling conditions was essential to induce a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction (MSR) and significantly reduce the milling time required for complete conversion. Under these conditions, it was found that the ignition time for ZrB2 formation was only about a few minutes. In this study, the mechanism for the formation of ZrB2 in this system was determined by studying the relevant sub-reactions, the effect of stoichiometry, and the thermal behavior of the system.
Marzo, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.11.050
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Effect of carbonization temperature on the microplasticity of wood-derived biocarbon
Shpeizman, VV; Orlova, TS; Kardashev, BK; Smirnov, BI; Gutierrez-Pardo, A; Ramirez-Rico, JPhysics of the Solid State, 56 (2014) 538-545 DOI: 10.1134/S1063783414030305
Abstract
The uniaxial compression strength under stepped loading and the 325-nm-stepped deformation rate of biocarbon samples obtained by carbonization of beech wood at different temperatures in the 600–1600°C range have been measured using high-precision interferometry. It has been shown that the strength depends on the content of nanocrystalline phase in biocarbon. The magnitude of deformation jumps at micro- and nanometer levels and their variation with a change in the structure of the material and loading time have been determined. For micro- and nanometer-scale jumps, standard deviations of the differences between the experimentally measured deformation rate at loading steps and its magnitude at the smoothed fitting curve have been calculated, and the correlation of the error with the deformation prior to destruction has been shown. The results obtained have been compared with the previously published data on measurements of the elastic properties and internal friction of these materials.
Marzo, 2014 · DOI: 10.1134/S1063783414030305
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
c- C4F8 Plasmas for the Deposition of Fluorinated Carbon Films
Terriza, A; Macias-Montero, M; Lopez-Santos, MC; Yubero, F; Cotrino, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARPlasma Processes and Polymers, 11 (2014) 289-299 DOI: 10.1002/ppap.201300129
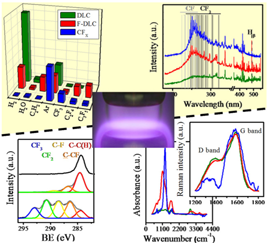
Abstract
Highly fluorinated polymeric (CFX), fluorine containing diamond-like carbon (F-DLC) and, for comparison, diamond-like carbon (DLC) films have been plasma deposited in a RF parallel plate reactor by using c-C4F8 as fluorine precursor and different mixtures of argon, C2H2, and H2. Plasmas have been characterized by optical emission spectroscopy, mass spectrometry, and Langmuir probe measurements. Differences in the film composition and structure have been related with the type of species formed in the plasma and with the self-bias potential developed at the deposition electrode. Additional experiments using CF4 have confirmed that the formation in the plasmas of neutral or ionized CxFy species with x > 2 is a critical factor for the synthesis of fluorine rich films.
Marzo, 2014 · DOI: 10.1002/ppap.201300129
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Comparative Study of Micro- and Nano-structured Coatings for High-Temperature Oxidation in Steam Atmospheres
Perez, FJ; Castaneda, SI; Hierro, MP; Galindo, RE; Sanchez-Lopez, JC; Mato, SOxidation of Metals, 81 (2014) 227-236 DOI: 10.1007/s11085-013-9447-2
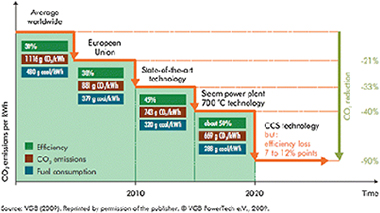
Abstract
For many high-temperature applications, coatings are applied in order to protect structural materials against a wide range of different environments: oxidation, metal dusting, sulphidation, molten salts, steam, etc. The resistance achieved by the use of different kind of coatings, such as functionally graded material coatings, has been optimized with the latest designs. In the case of supercritical steam turbines, many attempts have been made in terms of micro-structural coatings design, mainly based on aluminides, and other diffusion coating systems in order to consider alternatives, nano-structured coatings based on Cr and Al compositions and deposited by a physical vapor deposition technique, were assessed to high-temperature oxidation resistance in steam environments. The oxidation kinetics where analyzed for up to 2,000 h at 650 °C by means of gravimetric measurements. The evaporation behavior was also analyzed by thermogravimetric-mass spectrometry. Excellent results where observed for some of the nano-structured coatings tested. Those results where compared to results obtained for micro-structured coatings. Based on that comparison, it was deduced that the nano-structured coatings have a potential application as protective systems in high-temperature steam environments.
Febrero, 2014 · DOI: 10.1007/s11085-013-9447-2
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Promoting effect of Ce and Mg cations in Ni/Al catalysts prepared from hydrotalcites for the dry reforming of methane
Djebarri, B; Gonzalez-Delacruz, VM; Halliche, D; Bachari, K; Saadi, A; Caballero, A; Holgado, JP; Cherifi, OReaction Kinetics, Mechanisms and Catalysis, 111 (2014) 259-275 DOI: 10.1007/s11144-013-0646-2
Abstract
Several catalytic systems containing Ni/Mg/Al/Ce were synthesized from nitrates of Ni2+, Mg2+, Al3+ and Ce3+ cations with M2+/M3+ = 2 ratios by means of the carbonate co-precipitation method and subsequent calcination at 800 A degrees C. Atomic absorption spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD), FT-IR spectroscopy, BET, temperature programmed reduction and scanning electron microscopy were used in order to describe the structural, morphological and surface characteristics of the solids completely. The effect of substitution/incorporation of Al by Ce and/or Mg on NiAl sample was studied. XRD analyses confirm that on Al-containing samples (NiAl, NiMgAl), the formation of the precursors layered double hydroxide structure. On the other hand, on cerium containing samples (NiCe, NiMgCe), poorly resolved diffractograms were observed what can be explained by the large radius of cerium. The catalysts were evaluated in the reaction of CO2 reforming of methane at 750 A degrees C. NiCe and NiMgAl catalysts exhibit higher activity and a H-2/CO ratio of almost 1. NiAl and NiMgCe samples showed lower conversions and a CH4/CO2 ratio < 1, indicating the occurrence of reverse water gas shift reaction.
Febrero, 2014 · DOI: 10.1007/s11144-013-0646-2
Study and restoration of the Seville City Hall facade
Robador, MD; Arroyo, F; Perez-Rodriguez, JLConstruction and Building Materials, 53 (2014) 370-380 DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2013.11.088
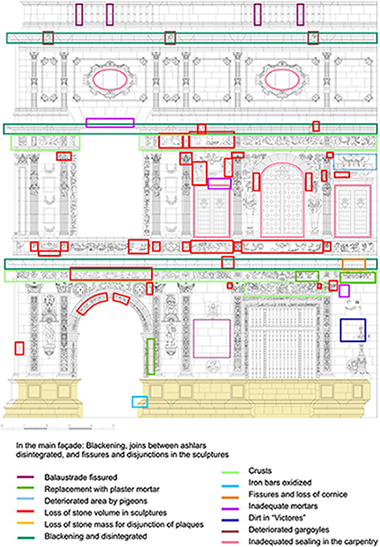
Abstract
Before restoring the Seville City Hall façade, a study of the original materials and the compounds added or formed was performed. The stone is fine-grained carbonate rock. Gypsum and mortars were used to restore stone fragments. A black crust was also found the wall was covered with an acrylic resin. A layer of lime on the surface was also detected. The restoration was intended to preserve the artistic quality and uniqueness of this building. The cleaning, reinforcing and innovatively consolidating and protecting the stone using suitable materials similar to those used in the original construction are described in this study.
Febrero, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2013.11.088
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
A Nanoscale Characterization with Electron Microscopy of Multilayered CrAlYN Coatings: A Singular Functional Nanostructure
Rojas, TC; Dominguez-Meister, S; Brizuela, M; Garcia-Luis, A; Fernandez, A; Sanchez-Lopez, JCMicroscoy and Microanalysis, 20 (2014) 14-24 DOI: 10.1017/S1431927613013962
Abstract
A combination of transmission electron microscopy techniques and spatially resolved microanalysis is used to investigate the nanostructure, constituting phases, and chemical elemental distribution in CrAlYN multilayered coatings. The location of the metallic elements and their chemical state are needed to understand their functional properties. Samples were prepared with variable Al (4-12 at%) and Y (2-5 at%) contents by direct current reactive magnetron sputtering on silicon substrates using metallic targets and Ar/N-2 mixtures under different deposition parameters (power applied to the target and rotation speed of the sample holder). The changes produced in the nanostructure and chemical distribution were investigated. Nanoscale resolution electron microscopy analysis has shown that these coatings present a singular nanostructure formed by multilayers containing at a certain periodicity nanovoids filled with molecular nitrogen. Spatially resolved energy dispersive spectroscopy and electron energy loss elemental mappings and profiles showed that the chromium, aluminum, and yttrium atoms are distributed in a sequential way following the position of the targets inside the deposition chamber. Analysis of the different atomic distribution and phases formed at the nanoscale is discussed depending on the deposition parameters.
Febrero, 2014 · DOI: 10.1017/S1431927613013962
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Wall paintings studied using Raman spectroscopy: A comparative study between various assays of cross sections and external layers
Perez-Rodriguez, JL; Robador, MD; Centeno, MA; Siguenza, B; Duran, ASpectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 120 (2014) 602-609 DOI: 10.1016/j.saa.2013.10.052

Abstract
This work describes a comparative study between in situ applications of portable Raman spectroscopy and direct laboratory measurements using micro-Raman spectroscopy on the surface of small samples and of cross sections. The study was performed using wall paintings from different sites of the Alcazar of Seville.
Little information was obtained using a portable Raman spectrometer due to the presence of an acrylic polymer, calcium oxalate, calcite and gypsum that was formed or deposited on the surface. The pigments responsible for different colours, except cinnabar, were not detected by the micro-Raman spectroscopy study of the surface of small samples taken from the wall paintings due to the presence of surface contaminants.
The pigments and plaster were characterised using cross sections. The black colour consisted of carbon black. The red layers were formed by cinnabar and white lead or by iron oxides. The green and white colours were composed of green emerald or atacamite and calcite, respectively. Pb3O4 has also been characterised. The white layers (plaster) located under the colour layers consisted of calcite, quartz and feldspars. The fresco technique was used to create the wall paintings.
A wall painting located on a gypsum layer was also studied. The Naples yellow in this wall painting was not characterised due to the presence of glue and oils.
This study showed the advantage of studying cross sections to completely characterise the pigments and plaster in the studied wall paintings.
Febrero, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.saa.2013.10.052
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Plasma Deposition of Superhydrophobic Ag@ TiO2 Core@ shell Nanorods on Processable Substrates
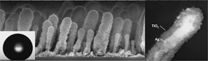
Macias-Montero, M; Borras, A; Romero-Gomez, P; Cotrino, J; Frutos, F; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARPlasma Process and Polymers, 11 (2014) 164-174 DOI: 10.1002/ppap.201300112
Abstract
This work reports the low temperature plasma formation of Ag@TiO2 nanorods (NRs) on processable substrates. The layers have been analyzed by electron microscopy and secondary ion mass spectroscopy. The NRs morphologies suggest that the plasma sheath, the high mobility of the silver and the incoming direction of the precursor moieties are key factors determining their shape, dimensions, and tilting orientation. Both amorphous and anatase Ag@TiO2 NRs surfaces are superhydrophobic, and turn into superhydrophilic by irradiation with UV light. This wetting behavior is discussed by considering the water penetration in the inter-NR space during the light-mediated transformation.
Febrero, 2014 · DOI: 10.1002/ppap.201300112
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Fully stable numerical calculations for finite one-dimensional structures: Mapping the transfer matrix method
Luque-Raigon, JM; Halme, J; Miguez, HJournal of Quantitative Spectroscopy and Radiative Transfer, 134 (2014) 9-20 DOI: 10.1016/j.jqsrt.2013.10.007
Abstract
We design a fully stable numerical solution of the Maxwell's equations with the transfer matrix method (TMM) to understand the interaction between an electromagnetic field and a finite, one-dimensional, non-periodic structure. Such an exact solution can be tailored from a conventional solution by choosing an adequate transformation between its reference systems, which induces a mapping between its associated TMMs. The paper demonstrates theoretically the numerical stability of the TMM for the exact solution within the framework of Maxwell's equations, but the same formalism can efficiently be applied to resolve other classical or quantum linear wave-propagation interaction in one, two, and three dimensions. This is because the formalism is exclusively built up for an in depth analysis of the TMM's symmetries.
Febrero, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jqsrt.2013.10.007
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Low Temperature Production of Formaldehyde from Carbon Dioxide and Ethane by Plasma-Assisted Catalysis in a Ferroelectrically Moderated Dielectric Barrier Discharge Reactor
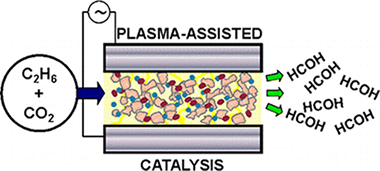
Gomez-Ramirez, A; Rico, VJ; Cotrino, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, A; Lambert, RMACS Catalysis, 4 (2014) 402-408 DOI: 10.1021/cs4008528
Abstract
Plasma-assisted catalysis of the reaction between CO2 and C2H6 in a single-pass, ferroelectrically moderated dielectric barrier discharge reactor has been studied at near ambient temperature as a function of physicochemical and electrical reaction variables. The presence of small amounts of a vanadia/alumina catalyst dispersed on the BaTiO3 ferroelectric markedly enhanced the production of formaldehyde, the focus of this work. A maximum HCOH selectivity of 11.4% (defined with respect to the number of ethane carbon atoms consumed) at 100% ethane conversion was achieved, the other products being CO, H2O, H2, CH4 and a small amount of C3H8. N2O was also an effective partial oxidant (HCOH selectivity 8.9%) whereas use of O2 led to complete combustion, behavior that may be rationalized in terms of the electron impact excitation cross sections of the three oxidants. Control experiments with the coproducts CH4 and C3H8 showed that these species were not intermediates in HCOH formation from C2H6. Analysis of reactor performance as a function of discharge characteristics revealed that formaldehyde formation was strongly favored at low frequencies where the zero-current fraction of the duty cycle was greatest, the implication being that plasma processes also acted to destroy previously formed products. A tentative reaction mechanism is proposed that accounts for the broad features of formaldehyde production.
Febrero, 2014 · DOI: 10.1021/cs4008528
Reactividad de Sólidos - Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Spinodal decomposition and precipitation in Cu–Cr nanocomposite
Sheibani, S; Heshmati-Manesh, S; Ataie, A; Caballero, A; Criado, JMJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 587 (2014) 670-676 DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.11.019

Abstract
In this study, spinodal decomposition and precipitation mechanism of mechanically alloyed supersaturated Cu–3wt.%Cr and Cu–5wt.%Cr solid solutions was investigated under nonisothermal aging. Decomposition mechanism and kinetics were studied using differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and X-ray diffraction (XRD) techniques. Also, the microstructure was characterized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Effect of Al2O3 reinforcement on the aging kinetics was also evaluated. It was found that Cu–3wt.%Cr and Cu–5wt.%Cr solid solutions undergo spinodal decomposition at initial stages of ageing. However, decomposition mechanism was changed to nucleation and growth by the aging progress. The aging kinetics for the Cu–Cr/Al2O3 composition appeared to be slightly faster than that for Cu–Cr, since the ageing activation energy is decreased in presence of Al2O3 nano-particles. This behavior is probably due to the higher dislocation density and other structural defects previously produced during ball milling. A detailed comparison of the DSC results with those obtained by TEM, showing good consistency, has been presented. The average size of Cr-rich precipitates was about 10 nm in the copper matrix.
Febrero, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.11.019
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Nanometer-Scale Precision Tuning of 3D Photonic Crystals Made Possible Using Polyelectrolytes with Controlled Short Chain Length and Narrow Polydispersity
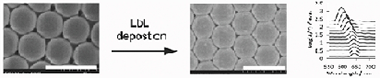
Wang, Z; Calvo, ME; Masson, G; Arsenault, AC; Peiris, F; Mamak, M; Miguez, H; Manners, I; Ozin, GAAdvanced Materials Interfaces, 1 (2014) Art. 1300051 DOI: 10.1002/admi.201300051
Abstract
Nanometer-scale tuning of the optical properties of prefabricated photonic crystals is achieved via layer-by-layer assembly of polyelectrolytes in the interstitial spaces of the photonic lattice. The key to the approach is using polyelectrolytes with controlled short chain lengths. This ensures they do not block the air voids, thereby maintaining uniform coating and thus precise and reproducible optical
Febrero, 2014 · DOI: 10.1002/admi.201300051
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Dye sensitized solar cells as optically random photovoltaic media
Galvez, FE; Barnes, PRF; Halme, J; Miguez, HEnergy & Environmental Science, 6 (2014) 1260-1266 DOI: 10.1039/C3EE42587H
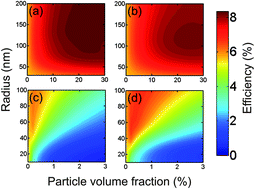
Abstract
In order to enhance optical absorption, light trapping by multiple scattering is commonly achieved in dye sensitized solar cells by adding particles of a different sort. Herein we propose a theoretical method to find the structural parameters (particle number density and size) that optimize the conversion efficiency of electrodes of different thicknesses containing spherical inclusions of diverse composition. Our work provides a theoretical framework in which the response of solar cells containing diffuse scattering particles can be rationalized. Optical simulations are performed by combining a Monte Carlo approach with Mie theory, in which the angular distribution of scattered light is accounted for. Several types of scattering centers, such as anatase, gold and silver particles, as well as cavities, are considered and their effect compared. Estimates of photovoltaic performance, insight into the physical mechanisms responsible for the observed enhancements, and guidelines to improve the cell design are provided. We discuss the results in terms of light transport in weakly disordered optical media and find that the observed variations between the optimum scattering configurations attained for different electrode thicknesses can be understood as the result of the randomization of the light propagation direction at different depths within the active layer. A primary conclusion of our study is that photovoltaic performance is optimised when the scattering properties of the film are adjusted so that the distance over which incident photons are randomized is comparable to the thickness of the film. This simple relationship could also be used as a design rule to attain the optimum optical design in other photovoltaic materials.
Febrero, 2014 · DOI: 10.1039/C3EE42587H
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Gold supported on CuOx/CeO2 catalyst for the purification of hydrogen by the CO preferential oxidation reaction (PROX)
Laguna, OH; Hernandez, WY; Arzamendi, G; Gandia, LM; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAFuel, 134 (2014) 9-20 DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2013.10.072
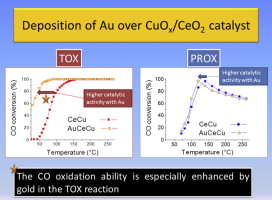
Abstract
Hydrogen produced from the conversion of hydrocarbons or alcohols contains variable amounts of CO that should be removed for some applications such as feeding low-temperature polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs). The CO preferential oxidation reaction (PROX) is particularly well-suited for hydrogen purification for portable and on-board applications. In this work, the synthesis and characterization by XRF, BET, XRD, Raman spectroscopy and H2-TPR of a gold catalyst supported on a copper−cerium mixed oxide (AuCeCu) for the PROX reaction are presented. The comparison of this catalyst with the copper–cerium mixed oxide (CeCu) revealed that the experimental procedure used for the deposition of gold gave rise to the loss of reducible material by copper lixiviation. However, the AuCeCu solid was more active for CO oxidation at low temperature. A kinetic study has been carried over the AuCeCu catalyst for the PROX reaction and compared with that of the CeCu catalyst. The main difference between the models affected the contribution of the CO adsorption term. This fact may be related to the surface electronic activity produced by the interaction of the cationic species in the AuCeCu solid, able to create more active sites for the CO adsorption and activation in the presence of gold.
Febrero, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2013.10.072
Reactividad de Sólidos
Characterization of thermally stable gamma alumina fibres biomimicking sisal
Benitez-Guerrero, M; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Pascual-Cosp, JMicroporous and Mesoporous Materials, 185 (2014) 167-178 DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2013.11.012
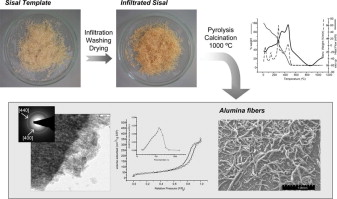
Abstract
Mesoporous gamma alumina fibres of high surface area, stable up to 1000 °C, were synthesized by bioreplica technique using sisal fibres as templates. Alumina formation during pyrolysis and calcination of fibres infiltrated with aluminium chloride solution has been studied, paying special attention to the interaction between the precursor and sisal fibres, using several experimental techniques such as ATR-FTIR, coupled TG-FTIR and thermo-XRD analysis. The morphology and microstructure of the resulting alumina fibres were characterized using SEM and TEM. The crystallographic analysis of the alumina sample performed by electron and X-ray diffraction suggests that fibres are constituted by η and γ-Al2O3 crystallites, whose chemical structure was confirmed by ATR-FTIR and Al27-MAS-NMR. The specific surface area and porosity of ceramic fibres were determined by N2 and CO2 adsorption–desorption measurements. Resulting alumina fibres retain high specific surface areas of 200 and 150 m2/g even after calcination at 1000 °C for 15 h in dry air and for 4 h in wet air, respectively.
Febrero, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2013.11.012
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
New Bio-Ceramization Processes Applied to Vegetable Hierarchical Structures for Bone Regeneration: An Experimental Model in Sheep
Filardo, G; Kon, E; Tampieri, A; Cabezas-Rodriguez, R; Di Martino, A; Fini, M; Giavaresi, G; Lelli, M; Martinez-Fernandez, J; Martini, L; Ramirez-Rico, J; Salamanna, F; Sandri, M; Sprio, S; Marcacci, MTissue Engineering Part A, 20 (2014) 763-773 DOI: 10.1089/ten.tea.2013.0108
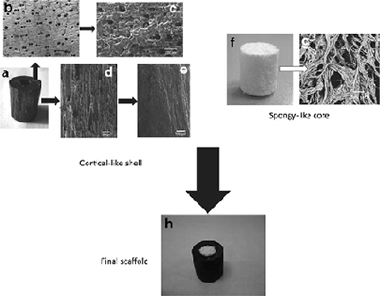
Abstract
Bone loss is still a major problem in orthopedics. The purpose of this experimental study is to evaluate the safety and regenerative potential of a new scaffold based on a bio-ceramization process for bone regeneration in long diaphyseal defects in a sheep model. The scaffold was obtained by transformation of wood pieces into porous biomorphic silicon carbide (BioSiC®). The process enabled the maintenance of the original wood microstructure, thus exhibiting hierarchically organized porosity and high mechanical strength. To improve cell adhesion and osseointegration, the external surface of the hollow cylinder was made more bioactive by electrodeposition of a uniform layer of collagen fibers that were mineralized with biomimetic hydroxyapatite, whereas the internal part was filled with a bio-hybrid HA/collagen composite. The final scaffold was then implanted in the metatarsus of 15 crossbred (Merinos-Sarda) adult sheep, divided into 3 groups: scaffold alone, scaffold with platelet-rich plasma (PRP) augmentation, and scaffold with bone marrow stromal cells (BMSCs) added during implantation. Radiological analysis was performed at 4, 8, 12 weeks, and 4 months, when animals were sacrificed for the final radiological, histological, and histomorphometric evaluation. In all tested treatments, these analyses highlighted the presence of newly formed bone at the bone scaffolds' interface. Although a lack of substantial effect of PRP was demonstrated, the scaffold+BMSC augmentation showed the highest value of bone-to-implant contact and new bone growth inside the scaffold. The findings of this study suggest the potential of bio-ceramization processes applied to vegetable hierarchical structures for the production of wood-derived bone scaffolds, and document a suitable augmentation procedure in enhancing bone regeneration, particularly when combined with BMSCs.
Febrero, 2014 · DOI: 10.1089/ten.tea.2013.0108
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Interaction of Hydrated Cations with Mica-n (n = 2, 3 and 4) Surface
Pavon, E; Castro, MA; Cota, A; Osuna, FJ; Pazos, MC; Alba, MDJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 118 (2014) 2115-2121 DOI: 10.1021/jp4110695

Abstract
High charged swelling micas, with layer charge between 2 and 4, have been found to readily swell with water, and complete cation exchange (CEC) can be achieved. Because of their high CEC, applications like radioactive cation fixation or removal of heavy metal cations from wastewater were proposed. Their applicability can be controlled by the location of the interlayer cation in a confined space with a high electric field. In synthetic brittle micas, the interlayer cation has a low water coordination number; therefore, their coordination sphere would be completed by the basal oxygen of the tetrahedral layer as inner-sphere complexes (ISC). However, no direct evidence of these complexes formation in brittle micas has been reported yet. In this contribution, we mainly focus on the understanding the mechanisms that provoke the formation of ISC in high charge swelling micas, Mica-n. A whole series of cations (X) were used to explore the influence of the charge and size of the interlayer cation. Three brittle swelling micas, Mica-n (n = 4, 3 and 2), were selected in order to analyze the influence of the layer charge in the formation of ISC. The contribution of the ISC has been analyzed thorough the evolution of the 060 reflection and the changes in the short-range order of the tetrahedral cations will be followed 29Si and 27Al MAS NMR. The results showed that ISC was favored in X-Mica-4 and that provoked a high distortion angle between the Si–Al tetrahedra. When the content of aluminum decreases, the electrostatic forces between the layers are relaxed, and the hydrated cations did not interact so strongly with the tetrahedral sheet, having the opportunity to complete their hydration sphere.
Enero, 2014 · DOI: 10.1021/jp4110695
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Panchromatic porous specular back reflectors for efficient transparent dye solar cells
Lopez-Lopez, C; Colodrero, S; Miguez, HPhysical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 16 (2014) 663-668 DOI: 10.1039/C3CP53939C
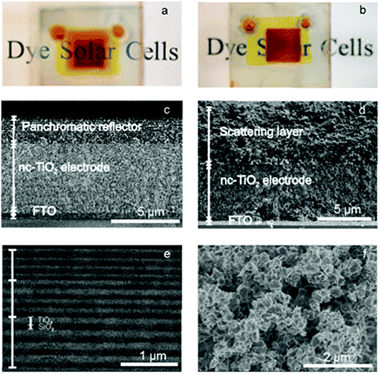
Abstract
A panchromatic specular reflector based dye solar cell is presented herein. Photovoltaic performance of this novel design is compared to that of cells in which standard diffuse scattering layers are integrated. The capability of the proposed multilayer structures to both emulate the broad band reflection of diffuse scattering layers of standard thickness (around 5 microns) and give rise to similarly high light harvesting and power conversion efficiencies, yet preserving the transparency of the device, is demonstrated. Such white light reflectors are comprised of stacks of different porous optical multilayers, each one displaying a strong reflection in a complementary spectral range, and are designed to leave transmittance unaltered in a narrow red-frequency range in which the sensitized electrode shows negligible absorption, thus allowing us to see through the cell. The reflectance bandwidth achieved is three times as broad as the largest bandwidth previously achieved using any photonic structure integrated into a dye solar cell.
Enero, 2014 · DOI: 10.1039/C3CP53939C
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
A ternary Er3+-BiVO4/TiO2 complex heterostructure with excellent photocatalytic performance
Obregon, S; Colon, GRSC Advances, 4 (2014) 20765-20771 DOI: 10.1039/C3RA46603E
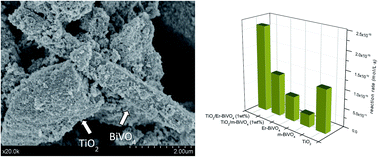
Abstract
Ternary erbium doped BiVO4/TiO2 complexes are synthesized by means of a simple impregnation method with good photoactivities under sun-like excitation for the degradation of phenol. From the structural and morphological characterization it has been stated that the presence of Er3+ induces a slight stabilization of the tetragonal phase probably due to its incorporation in the BiVO4 lattice. Therefore a ternary heterostructured material has been obtained. The best photocatalytic performance was attained for the samples with 1 wt% of Er3+-doped BiVO4 content with respect to TiO2. The occurrence of a complex structural mixture with the adequate band position leads to effective charge pair separation which induces higher photocatalytic activities.
Enero, 2014 · DOI: 10.1039/C3RA46603E
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Improved H2 production of Pt-TiO2/g-C3N4-MnOx composites by an efficient handling of photogenerated charge pairs
Obregon, S; Colon, GApplied Catalysis B: Environmental, 144 (2014) 775-782 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.07.034
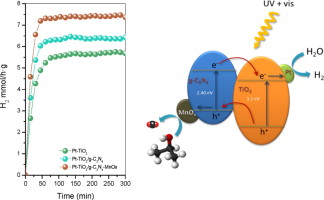
Abstract
Pt-TiO2/g-C3N4-MnOx hybrid structures are synthesized by means of a simple impregnation method of Pt-TiO2 and g-C3N4-MnOx. From the wide structural and surface characterization we have stated that TiO2/g-C3N4 composites are formed by an effective covering of g-C3N4 by TiO2. The modification of composite by Pt and/or MnOx leads to improved photoactivities for phenol degradation reaction. Moreover, enhanced photoactivities have been obtained for composites systems for H2 evolution reaction. The notably photocatalytic performance obtained was related with the efficient separation of charge pairs in this hybrid heterostructure.
Enero, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.07.034
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Competitive effect of the metallic canister and clay barrier on the sorption of Eu3+ under subcritical conditions
El Mrabet, S; Castro, MA; Hurtado, S; Orta, MM; Pazos, MC; Villa-Alfageme, M; Alba, MDApplied Geochemistry, 40 (2014) 25-31 DOI: j.apgeochem.2013.10.014
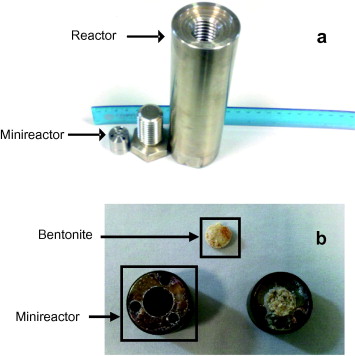
Abstract
An in depth knowledge and understanding of high activity radionuclide (HLRW) immobilization processes on the materials composing the engineered barrier (clay and metallic canister) is required to ensure the safety and the long-term performance of radioactive waste disposal procedures. Therefore, the aim of this study was to understand the mechanisms involved in the retention of Eu3+ by two components of the multibarrier system, the bentonite barrier and the canister. As such, a comparative study of the interaction of trivalent Eu3+, used to simulate trivalent actinides, with both bentonite and a metallic canister has been undertaken in this work. To this end, we designed a minireactor into which the bentonite was introduced and compacted. The minireactor-bentonite system was then submitted to a hydrothermal reaction with a 7.9 × 10−2 M solution of Eu3+ at 300 °C for 4.5 days. SEM and XRD results revealed that both bentonite and the container were involved in the immobilization of europium by the formation of insoluble europium silicate phases. The presence of europium silicate adsorbed on the surface of the metallic canister indicates the competitive effect of both components of the engineered barrier (bentonite and metallic canister) in HLRW immobilization. These results suggested that the canister could play a role in the HLRW immobilization even during its corrosion process.
Enero, 2014 · DOI: j.apgeochem.2013.10.014
Materiales Coloidales
Synthesis of antibacterial silver-based nanodisks and dendritic structures mediated by royal jelly
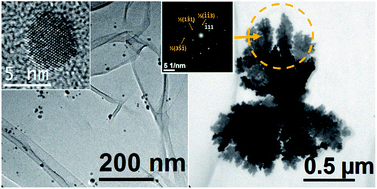
Mendoza-Resendez, R; Gomez-Trevino, A; Barriga-Castro, ED; Nunez, NO; Luna, CRSC Advances, 4 (2014) 1650-1658 DOI: 10.1039/C3RA45680C
Abstract
The one-step preparation of silver nanoparticles and dendritic structures mediated by aqueous royal jelly solutions has been investigated for the first time. It has been found that royal jelly (RJ) is a complex organic matrix that can be simultaneously used as a reducing and stabilizing agent in the chemical synthesis of colloidal silver-based nanostructures from aqueous AgNO3 solutions, without the requirement of additional reagents or heating sources to initiate the oxidation–reduction reactions. The resulting product consisted of very fine single-crystal disks of Ag and silver 4,4′-dimethyldiazoaminobenzene (a triazenic compound). Both kinds of particles tended to coalesce and form supramolecular dendritic structures, the AgNO3/RJ weight ratio chosen in the synthesis being a key parameter to control the crystal growth and the microstructural properties of the Ag nanodisks. Data obtained from Fourier transform infrared and Raman spectroscopy analysis indicated that these nanostructures are coated by RJ biomolecules (residues of proteins and carbohydrates). In vitro biological assays showed that these nanostructures exhibit a promising enhanced antibacterial activity against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
Enero, 2014 · DOI: 10.1039/C3RA45680C
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Anchoring effect on (tetra)carboxyphenyl porphyrin/TiO2 composite films for VOC optical detection
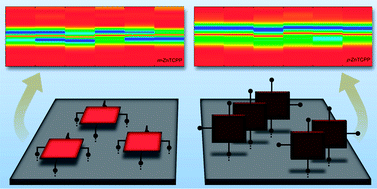
Roales, J; Pedrosa, JM; Cano, M; Guillen, MG; Lopes-Costa, T; Castillero, P; Barranco, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARRSC Advances, 4 (2014) 1974-1981 DOI: 10.1039/C3RA42443J
Abstract
The optical gas sensing properties of Zn-(II)-5,10,15,20-tetra(3-carboxyphenyl)porphyrin (m-ZnTCPP) and Zn-(II)-5,10,15,20-tetra(4-carboxyphenyl)porphyrin (p-ZnTCPP) bound to microcolumnar TiO2 thin films have been compared and explained in terms of their different molecular structure and anchoring to the titania surface. This different binding has been confirmed by specular reflectance FTIR revealing that m-ZnTCPP is bound by its four carboxylic groups in contrast to p-ZnTCPP where two or three of these groups remain unanchored. As a consequence, the Soret band of the para derivative is blue shifted with respect to the solution, indicating H aggregation, while m-ZnTCPP remained in its monomeric form due to the planar anchoring by the four COOH groups to the titania matrix that would avoid porphyrin aggregation. The sensing performance of the two systems has been assessed by analyzing the spectral changes in their UV-visible spectra under exposure to six volatile organic compounds. Although the highly porous and non-dispersive TiO2 matrix allow good sensing ability in both cases, the response of the m-ZnTCPP/TiO2 composite has been found to be more intense and faster than that of p-ZnTCPP. Moreover, the use of identification patterns also indicates that the meta derivative achieves a more selective recognition of the selected analytes. This improvement in the sensing capabilities of m-ZnTCPP has been attributed to the absence of aggregation between adjacent macrocycles.
Enero, 2014 · DOI: 10.1039/C3RA42443J
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Tribological behaviour at high temperature of hard CrAlN coatings doped with Y or Zr
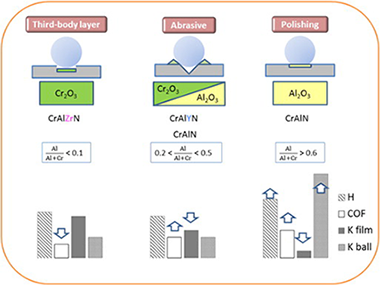
Sanchez-Lopez, JC; Contreras, A; Dominguez-Meister, S; Garcia-Luis, A; Brizuela, MThin Solid Films, 550 (2014) 413-420 DOI: 10.1016/j.tsf.2013.10.041
Abstract
The tribological properties of CrAlN, CrAlYN and CrAlZrN coatings deposited by direct current reactive magnetron sputtering are studied by means of pin-on-disc experiments at room temperature, 300, 500 and 650 °C using alumina balls as counterparts. The influence of the metallic composition (Al, Y and Zr) on the friction, wear properties and oxidation resistance is studied by means of scanning electron microscopy, energy dispersive X-ray analysis and Raman analysis of the contact region after the friction tests. The results obtained allow us to classify the tribological behaviour of the CrAl(Y,Zr)N coatings into three groups according to the nature of the dopant and aluminium content. The sliding wear mechanism is characterized by the formation of an overcoat rich in chromium and aluminium oxides whose particular composition is determined by the initial chemical characteristics of the coating and the testing temperature. The fraction of Cr2O3 becomes more significant as the Al content decreases and the temperature increases. The addition of Y, and particularly Zr, favours the preferential formation of Cr2O3 versus CrO2 leading to a reduction of friction and wear of the counterpart. Conversely, the tribological behaviour of pure CrAlN coatings is characterized by higher friction but lower film wear rates as a result of higher hardness and major presence of aluminium oxides on the coating surface.
Enero, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.tsf.2013.10.041
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Nanoindentation of nanocolumnar TiO2 thin films with single and stacked zig-zag layers
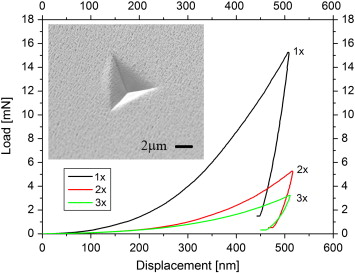
Jimenez-Pique, E; Gonzalez-Garcia, L; Rico, VJ; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARThin Solid Films, 550 (2014) 444-449 DOI: 10.1016/j.tsf.2013.10.022
Abstract
This paper reports a systematic analysis of the mechanical properties of nanocolumnar TiO2 thin films prepared by evaporation at a glancing geometry. A systematic study of the mechanical properties is carried out by comparing the hardness and the Young's modulus determined by nanoindentation for thin films prepared at different deposition angles and characterized by a tilted nanocolumnar structure and others where the nanocolumns are perpendicular to the substrate or are arranged as zig-zag stacked layers. A correlation between mechanical properties and glazing angle geometry is proposed. Differences in the results are discussed in view of the cross section images obtained by focused ion beam and of the deformed areas. Zig-zagged layers present lower values of hardness and Young's modulus due to the collapse of the angles of the columns, but at the same time this configuration impedes the appearance of fracture or delamination, as observed for tilted columns.
Enero, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.tsf.2013.10.022
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Exalted photocatalytic activity of tetragonal BiVO4 by Er3+ doping through a luminescence cooperative mechanism
Obregon, S; Lee, SW; Colon, GDalton Transactions, 43 (2014) 311-316 DOI: 10.1039/C3DT51923F
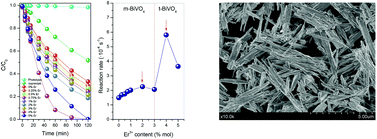
Abstract
Er-doped BiVO4 are synthesized by means of a surfactant free microwave assisted hydrothermal method having good photoactivities under sun-like excitation for the degradation of methylene blue. From the structural and morphological characterization, it has been stated that the presence of Er3+ induces a slight stabilization of the tetragonal phase, probably due to its incorporation in the BiVO4 lattice. The best photocatalytic performances were attained for the samples with Er3+ content higher than 3 at%. The occurrence of the Er3+ doped tetragonal BiVO4 clearly induces higher photocatalytic activities. The existence of a luminescence process has been related with the enhanced photoactivity observed.
Enero, 2014 · DOI: 10.1039/C3DT51923F
Reactividad de Sólidos
CdSe@ZnS nanocomposites prepared by a mechanochemical route: No release of Cd2+ ions and negligible in vitro cytotoxicity
Balaz, P; Sayagues, MJ; Balaz, M; Zorkovska, A; Hronec, P; Kovac, J; Kovac, J; Dutkova, E; Mojzisova, G; Mojzis, JMaterials Research Bulletin, 49 (2014) 302-309 DOI: 10.1016/j.materresbull.2013.08.070
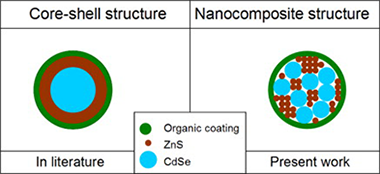
Abstract
CdSe@ZnS nanocomposites have been prepared by a two-step solid state mechanochemical synthesis. CdSe prepared from Cd and Se elements in the first step was mixed with zinc acetate and sodium sulphide in the second step of milling to prepare a CdSe@ZnS nanocomposite. In the third step, the obtained nanocomposite was coated with l-cysteine to prepare a biocompatible system. The crystallite size of the new type of nanocomposite was 20–35 nm for cubic CdSe and 3–8 nm for hexagonal ZnS as calculated from XRD, TEM and SEM data. The synthesised samples show good crystallinity and have been tested for dissolution and cytotoxicity. The dissolution of cadmium from CdSe@ZnS was less than 0.05 μg mL−1, whereas a value of 0.8 μg mL−1 was measured for CdSe alone. The binding of ZnS with CdSe in the nanocomposite practically eliminated the release of cadmium into solution. As a consequence, a very low cytotoxic activity has been evidenced for CdSe@ZnS. The nanocomposites coated with l-cysteine have a great potential as fluorescent labels in biomedical engineering.
Enero, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.materresbull.2013.08.070
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
On the kinetic and thermodynamic electron temperatures in non-thermal plasmas
Alvarez, R; Cotrino, J; Palmero, AEPL (Europhysic Letters), 105 (2014) DOI: 10.1209/0295-5075/105/15001
Abstract
The framework to describe the out-of-equilibrium free electrons in cold plasmas is developed assuming the electron entropy is defined through the Boltzmann H-theorem. Our theory explains why the Saha-Boltzmann relation among higher-lying excited states by means of the electron kinetic temperature is fulfilled, even when free electrons are far from equilibrium. The thermodynamic electron temperature, pressure and chemical potential have been introduced through the derivatives of the electron entropy. It is demonstrated that under usual conditions in cold plasmas, e.g. when the electron distribution function possesses the Maxwellian, Druyvestein or Kappa functional forms, kinetic and thermodynamic electron temperatures yield the same value.
Enero, 2014 · DOI: 10.1209/0295-5075/105/15001
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Effect of gold on a NiLaO3 perovskite catalyst for methane steam reforming
Palma, S; Bobadilla, LF; Corrales, A; Ivanova, S; Romero-Sarria, F; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis B: Environmental, 144 (2014) 846-854 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.07.055
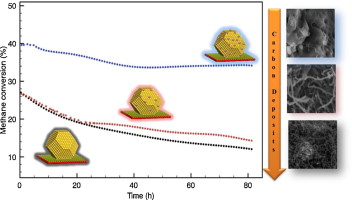
Abstract
The effect of gold addition to a supported Ni SRM catalyst has been studied in this work in order to determine the influence of gold on both the amount and type of carbon species formed during the reaction. The structure of the support, a mixed La–Al perovskite, determines the catalyst reducibility and Ni particle size. Gold addition affects the metal particle size increasing metal dispersion on increasing the gold content. Therefore, although gold blocks step Ni sites, the more active sites for Csingle bondH activation, and increases electron density on nickel, the higher dispersion results in an apparently higher activity upon gold addition. Moreover, gold addition increases the catalyst stability by decreasing the rate of growth of carbon nanotubes.
Enero, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.07.055
Reactividad de Sólidos
Effect of tantalum content on the microstructure and mechanical behavior of cermets based on (TixTa1−x)(C0.5N0.5) solid solutions
Chicardi, E; Torres, Y; Cordoba, JM; Hvizdos, P; Gotor, FJMaterials & Design, 53 (2014) 435-444 DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2013.07.039
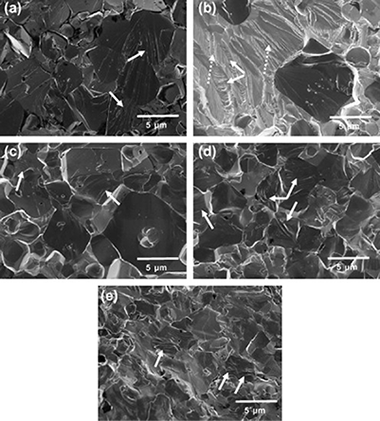
Abstract
Titanium–tantalum carbonitride, (Ti, Ta)(C, N), based cermets with different Ti and Ta contents were prepared using a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction and then densified using a pressureless sintering process. Complete microstructural and mechanical characterizations were performed on the materials, which revealed that the size of the carbonitride ceramic particle was significantly reduced when the Ta content was increased. The flexural strength and fracture toughness were measured using the ball on three balls test and the indentation microfracture test, respectively. The strength profile was analyzed under the framework of Weibull theory. The change in the mechanical properties as a function of the Ta content was correlated with the normalized microstructural parameters, such as the binder mean free path. The decrease in toughness and flexural strength was attributed to the presence of intermetallic compounds in the binder phase, which was also corroborated by the nanoindentation tests.
Enero, 2014 · DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2013.07.039
2013
2013
Reactividad de Sólidos
Bio-inspired mechanochemical synthesis of semiconductor nanomaterial using eggshell membrane
Balaz, M; Balaz, P; Sayagues, MJ; Zorkovska, AMaterials Science in Semiconductor Processing, 16 (2013) 1899-1903 DOI: 10.1016/j.mssp.2013.06.024
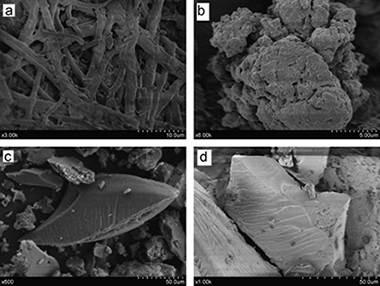
Abstract
Eggshell membrane and lead acetate were successfully used as precursors for the mechanochemical synthesis of lead sulphide nanocrystals with crystallite sizes ∼8 nm. XRD, specific surface area measurements, SEM and EDX were used to characterise the synthesised material. The mechanochemical synthesis follows three-step mechanism. The “fish-like” grains with sizes around 30 μm were obtained.
Diciembre, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.mssp.2013.06.024
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Symmetry analysis of the numerical instabilities in the transfer matrix method
Luque-Raigon, JM; Halme, J; Miguez, H; Lozano, GJournal of Optics, 15 (2013) 125719 DOI: 10.1088/2040-8978/15/12/125719
Abstract
This paper discusses the numerical exponential instability of the transfer matrix method (TMM) in the framework of the symmetry formalism. This numerical weakness is attributed to a series of increasingly extreme exponentials that appear in the TMM when it is applied to geometries involving total internal reflection (TIR) or very high absorption. We design a TMM formalism that identifies the internal symmetries of the multilayer geometry. These symmetries suggest particular transformations of a reference system in the TMM that improve its ill-conditioned exponentials. To illustrate the numerical improvements, we present examples with calculations of electric fields.
Diciembre, 2013 · DOI: 10.1088/2040-8978/15/12/125719
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Preparation of Titanium Oxide/Silicon Oxide (TiO2/SiO2) systems through the solvothermal method for applications in photocatalysis
Galeano, L.; Navío, J.A.; Restrepo, G.M.; Marín, J.M.Información Tecnológica, 24 (2013) 81-92 DOI: 10.4067/S0718-07642013000500010
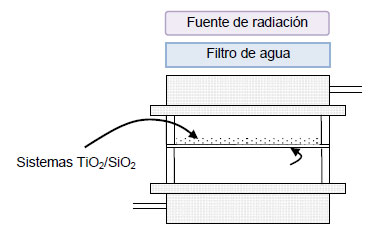
Abstract
Sistemas Óxido de Titanio/Óxido de Silicio (TiO2/SiO2) fueron obtenidos por anclaje de TiO2 en SiO2. El fotocatalizador TiO2 se obtuvo por alcohólisis del TiCl4 con 2-propanol y posterior cristalización a presión autógena a 200 °C, excluyendo etapas de calcinación a altas temperaturas. Se emplearon diferentes relaciones SiO2/TiCl4 para determinar su influencia en la estabilidad, propiedades y fotoactividad de los sistemas TiO2/SiO2. La actividad fotocatalítica fue evaluada por la fotodegradación de metanol en fase gaseosa. El TiO2 cristalizó como fase anatasa o como una mezcla rutilo/anatasa, dependiendo por la relación SiO2/TiCl4 inicial. Los resultados muestran que se producen materiales compuestos con alta cristalinidad del TiO2. Se encontró también que hay una fuerte relación entre la actividad fotocatalítica con las propiedades fisicoquímicas y de estas con las composiciones iniciales de síntesis.
Diciembre, 2013 · DOI: 10.4067/S0718-07642013000500010
Reactividad de Sólidos
Mechanochemical synthesis of ZrB2–SiC–ZrC nanocomposite powder by metallothermic reduction of zircon
Jalaly, M; Tamizifar, M; Bafghi, MS; Gotor, FJJournal of Alloys and Compounds, 581 (2013) 782-787 DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.07.142
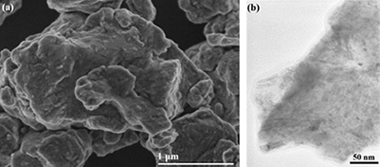
Abstract
Aluminium and magnesium were used in the M/ZrSiO4/B2O3/C (M = Al, Mg) system to induce a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction (MSR). Aluminium was not able to reduce the system to the desired products, and the system became amorphous after 10 h milling. However, nanocomposite powder of ZrB2–SiC–ZrC was in situ synthesized by the magnesiothermic reduction with an ignition time of approximately 6 min. The mechanism for the formation of the product in this system was determined by studying the relevant sub-reactions.
Diciembre, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.07.142
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Vertically Aligned Hybrid Core/Shell Semiconductor Nanowires for Photonics Applications
Macias-Montero, M; Filippin, AN; Saghi, Z; Aparicio, FJ; Barranco, A; Espinos, JP; Frutos, F; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Borras, AAdvanced Functional Materiales, 23 (2013) 5981-5989 DOI: 10.1002/adfm.201301120
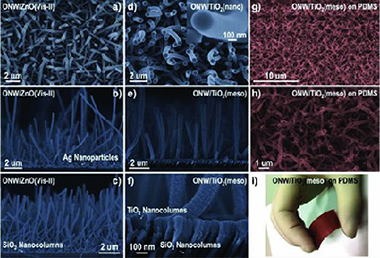
Abstract
A family of 1D organic/inorganic core/shell materials formed by an inner organic nanowire (ONW) conformally covered with an inorganic wide band gap semiconductor (ZnO or TiO2) layer is presented. The developed procedure is a two-steps vacuum methodology involving the formation of supported single crystal small-molecule nanowires by physical vapor deposition and plasma enhance chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) of the inorganic shell. Critical characteristics of the last technique are the possibilities of low temperature and remote configuration deposition. Additionally, an initial step has to be included in order to create nucleation centers for the growth of the ONWs. The procedure and its general character in terms of the variability in organic core and inorganic shells composition and the applicability of the technique to different substrates are presented. The formation of the inorganic shell with no damage of the organic core single-crystalline structure is demonstrated by high resolution transmission electron microscopy. The vertical alignment of the hybrid nanostructure is achieved thanks to the interaction of the 1D organic nanostructured surfaces and the glow discharge during the deposition of the inorganic shell by PECVD. The optical properties of these core/shell NWs are studied by fluorescence spectroscopy and microscopy, and their application as nanoscale waveguides in the 550–750 nm range addressed.
Diciembre, 2013 · DOI: 10.1002/adfm.201301120
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Modeling Macro-Sized, High Aspect Ratio Through-Hole Filling by Multi-Component Additive-Assisted Copper Electrodeposition
Childers, AS; Johnson, MT; Ramirez-Rico, J; Faber, KTJournal of the Electrochemical Society, 160 (2013) D3093-D3102 DOI: 10.1149/2.018312jes
Abstract
A multi-element, time-dependent model is used to examine additive-assisted copper electroplating in macro-channels. This model is an adaptation of the work of Akolkar and Landau [J. Electrochem. Soc., 156, D351 (2009)], used to describe plating in micro-vias for integrated circuits. Using their method for describing species movement in the channel, the model has been expanded to include transport and adsorption limitations of the inhibitor and accelerator, as well as the copper ions in solution. The model is used to investigate copper plating as an infiltration method across many size scales and aspect ratios. Biomorphic graphite scaffolds produced from wood are used as a representative system and the results of a two-additive bath are used to characterize the behavior of the additives and determine the effectiveness of the plating. The results indicate that at macro-scales, channel dimensions play an increasingly important role in dictating the behavior of additive-assisted plating. Because additive systems are designed to establish differential surface coverage within the channel, the success of which is determined by the additive's rates of diffusion and adsorption, certain size scale/aspect ratio combinations preclude such coverage. A guide for sample geometries that may be successfully infiltrated with a two-additive bath is provided.
Diciembre, 2013 · DOI: 10.1149/2.018312jes
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Au/CeO2 metallic monolith catalysts: influence of the metallic substrate
Tejada, LMM; Dominguez, MI; Sanz, O; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAGold Bulletin, 46 (2013) 221-231 DOI: 10.1007/s13404-013-0102-0
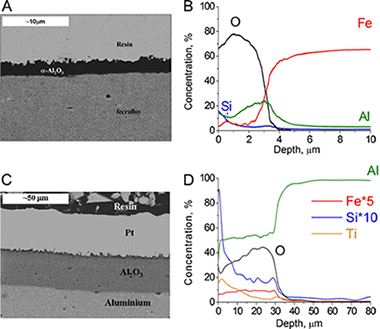
Abstract
Ceria-based gold catalysts were successfully deposited on ferritic stainless steel (Fecralloy) and aluminium monoliths. The prepared monolithic and reference powder catalysts were characterized by means of S-BET, X-ray diffraction, glow discharge optical emission spectroscopy and scanning electron microscopy-energy dispersive X-ray analysis techniques and tested in the CO oxidation reaction. Characterization results put in evidence the diffusion of cations from the catalytic layer on the surface of the monoliths to the metallic oxide scale and inversely, from the oxide scale to the catalysts, thus altering the catalytic formulation and affecting the CO oxidation properties of the catalytic device. The extension and nature of the modifications produced depend on the nature of the catalysts and the metallic substrate, as well as the reaction conditions applied. These facts must be considered when gold catalysts are supported on metallic-structured devices.
Diciembre, 2013 · DOI: 10.1007/s13404-013-0102-0
Reactividad de Sólidos
Reversible reactions of Ni and Pd hydroxo pincer complexes [( iPrPCP)M-OH] with CO2: Solid-state study of the decarboxylation of the monomeric bicarbonate complexes [(i PrPCP)M-OCOOH] (M = Ni, Pd)
Martinez-Prieto, LM; Real, C; Avila, E; Alvarez, E; Palma, P; Campora, JEuropean Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 32 (2013) 5555-5566 DOI: 10.1002/ejic.201300995
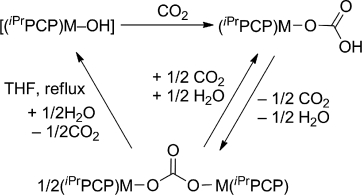
Abstract
Monomeric Ni and Pd hydroxides stabilized by the iPrPCP pincer ligand react with CO2 to give labile terminal bicarbonate complexes that readily lose CO2 and water to give binuclear carbonate complexes. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) has been used to monitor the decomposition of both bicarcabonates in the solid state. When the carbonate complexes are heated under reflux in thf in the presence of water, full decarboxylation takes place, restoring the starting hydroxides and demonstrating that CO2 insertion is a fully reversible process. The decarboxylation of the nickel carbonate complex is completed more readily, suggesting that the reaction of the Pd hydroxide with CO2 is more favourable than that of its nickel counterpart. This is supported by DFT calculations, which also shows that CO2 insertion takes place through a concerted Lipscomb-type mechanism. Monomeric Ni and Pd hydroxides stabilized by the iPrPCP pincer ligand react with CO2 to give labile terminal hydrogen carbonate complexes that readily lose CO2 and water to give binuclear carbonate complexes.
Noviembre, 2013 · DOI: 10.1002/ejic.201300995
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Preferential oxidation of CO over Au/CuOx–CeO2 catalyst in microstructured reactors studied through CFD simulations
Uriz, I; Arzamendi, G; Dieguez, PM; Laguna, OH; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JA; Gandia, LMCatalysis Today, 216 (2013) 283-291 DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2013.04.023
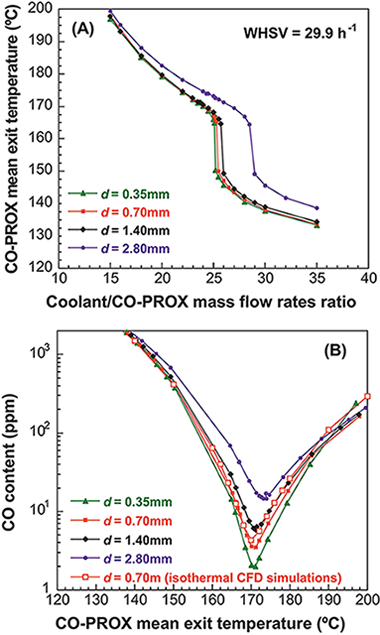
Abstract
A computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulation study of the preferential oxidation of CO (CO-PROX) in microstructured reactors consisting in square and semicircular microchannels coated with an Au/CuOx–CeO2 catalyst is presented. The CO content of the feed stream was set at 1 vol.%. A parametric sensitivity analysis has been performed under isothermal conditions revealing that an optimal reaction temperature exists that leads to a minimum CO content at the microreactor exit. The influence of the space velocity, CO2 concentration and oxygen-to-CO molar ratio in the feed stream (λ), catalyst loading, and microchannel characteristic dimension (d) on the microreactor performance has been investigated. Under suitable conditions, the CO concentration can be reduced below 10 ppm at relatively low temperatures within the 155–175 °C range. A negative effect of the increase of d from 0.35 mm to 2.8 mm on the CO removal efficiency has been found and attributed to a more detrimental effect of the mass transport limitations on the oxidation of CO than that of H2. Non-isothermal CFD simulations have been performed to investigate the cooling of the CO-PROX reactor with air or a fuel cell anode off gas surrogate in parallel microchannels. Due to the very rapid heat transfer allowed by the microreactor and the strong influence of the reaction temperature on the exit CO concentration, a careful control of the coolant flow rate and inlet temperature is required for proper reactor operation. The microreactor behavior is virtually isothermal.
Noviembre, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2013.04.023
Materiales Coloidales
Crystal Structures and Photoluminescence across the La2Si2O7–Ho2Si2O7 System
Fernandez-Carrion, AJ; Allix, M; Ocana, M; Garcia-Sevillano, J; Cusso, F; Fitch, AN; Suard, E; Becerro, AIInorganic Chemistry, 52 (2013) 13469-13479 DOI: 10.1021/ic401867c
Abstract
The La2Si2O7−Ho2Si2O7 system displays a solid solubility region of G-(La,Ho)2Si2O7 which extends to the La0.6Ho1.4Si2O7 composition. Compositions richer in Ho3+ show a two-phase domain (G+δ), while δ-(La,Ho)2Si2O7 is the stable phase for Ho3+ contents higher than La0.2Ho1.8Si2O7. A preferential occupation of Ho for the RE2 site of the G-unit cell is observed. Luminescence measurements have shown that the lifetimes remain unchanged in the range 0.5% < [Ho3+] < 10%, and only above this value does concentration quenching become operative.
Noviembre, 2013 · DOI: 10.1021/ic401867c
Reactividad de Sólidos
Porous Aluminas: The biotemplate method for the synthesis of stable high surface area aluminas
Guerrero, MB; Maqueda, LP; Castro, PP; Cosp, JPBoletin de la Sociedad Española de Cerámica y Vidrio, 52 (2013) 251-267 DOI: 10.3989/cyv.322013
Abstract
Development of porous alumina has been the objective of numerous studies in recent decades, due to the intrinsic properties of aluminium oxide, such as high melting point, low thermal conductivity, chemical inertness and corrosion resistance which, in addition to a high surface area and permeability, make aluminas being used for many different industrial and technical applications. The crystallographic and textural stability of alumina acquires significant importance in those processes involving high temperatures; however, most of the synthesis methods yield metastable oxides of little interest in high-temperature processes due to the transformation to alpha phase, with the consequent reduction in surface area. The present article reviews diverse procedures for obtaining porous alumina with high specific surface area, including methods and strategies for preparing high surface alpha-alumina. Within this framework, the paper analyzes the results obtained through bioreplica of lignocellulosic materials. This technology allows preparing aluminas with the complex structural hierarchy of the lignocellulosic templates.
Noviembre, 2013 · DOI: 10.3989/cyv.322013
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
A single-source route to bulk samples of C3N and the co-evolution of graphitic carbon microspheres
King, TC; Matthews, PD; Holgado, JP; Jefferson, DA; Lambert, RM; Alavi, A; Wright, DSCarbon, 64 (2013) 6-10 DOI: 10.1016/j.carbon.2013.04.043
Abstract
The thermolysis of commercially available m-phenylenediamine (1,3-(NH2)2C6H4) at 800 °C under a static vacuum in a sealed quartz tube provides the first bulk synthesis of C3N, whose properties have only been predicted theoretically previously. Hollow carbon microspheres (CMSs) which do not contain significant nitrogen doping (1–3 μm diameter) are co-produced in the reaction and readily separated from the C3N flakes. The separate C3N flakes and CMSs have been characterized by electron microscopy, X-ray spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction. These studies show that the samples of C3N and CMSs both possess multi-layered turbostratic graphitic structures. A new mechanism for the template-free assembly of CMSs is proposed on the basis of electron microscopy that involves bubble evolution from a static carbonized layer.
Noviembre, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.carbon.2013.04.043
Reactividad de Sólidos
Arsenic sorption by nanocrystalline magnetite: An example of environmentally promising interface with geosphere
Bujnakova, Z; Balaz, P; Zorkovska, A; Sayagues, MJ; Kovac, J; Timko, MJournal of Hazardous Materials, 262 (2013) 1204-1212 DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.03.007
Abstract
In this paper, the sorption of arsenic onto nanocrystalline magnetite mineral Fe3O4 was studied in a model system. Nanocrystalline magnetite was produced by mechanical activation in a planetary ball mill from natural microcrystalline magnetite. As a consequence of milling, the specific surface area increased from 0.1 m2/g to 11.9 m2/g and the surface site concentration enhanced from 2.2 sites/nm2 to 8.4 sites/nm2. These changes in surface properties of magnetite lead to the enhancement of arsenic removal from model system. The best sorption ability was achieved with magnetite sample activated for 90 min. In this case the sample was able to absorb around 4 mg/g. The structural changes of magnetite were also observed and the new hematite phase was detected after 120 min of milling. A good correlation between the decreasing particle size, increasing specific surface area and reduction of saturation magnetization was found. In desorption study, KOH and NaOH were found as the best eluents where more than 70% of arsenic was released back into the solution. The principal novelty of the paper is that mineral magnetite, truly one nature's gift can be used after “smart” milling (mechanical activation) as an effective arsenic sorbent.
Noviembre, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.03.007
Materiales Coloidales
Synthesis of metallic silver nanoparticles and silver organometallic nanodisks mediated by extracts of Capsicum annuum var. aviculare (piquin) fruits
Mendoza-Resendez, R; Nunez, NO; Barriga-Castro, ED; Luna, CRSC Advances, 43 (2013) 20765-20771 DOI: 10.1039/C3RA43524E
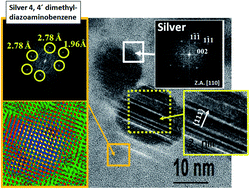
Abstract
Silver-based nanostructures were prepared through reduction/oxidation reactions of aqueous silver nitrate solutions mediated by extracts of red fruits of the piquin pepper (Capsicum annuum var. aviculare) at room temperature. Detailed morphological and microstructural studies using X-ray diffraction, conventional and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy and selected area electron diffraction revealed that the product was constituted by three kinds of nanoparticles. One of them was composed of twinned metallic silver nanoparticles with a size of few nanometers. Other kind of particles was ultrafine disk-like single crystals of silver 4,4′-dimethyldiazoaminobenzene, being in our best knowledge the first time that this compound is reported in the form of nanoparticles. Both kinds of nanoparticles experienced processes of self-assembly and subsequent grain growth to form the third kind of nanoparticles. Such resulting nanostructures are monocrystalline and flattened metallic silver nanoparticles that have diameters around tens of nanometers, the [112] direction perpendicular to the particle plane, and are coated by a surface organometallic layer and residues of biomolecules. The ultraviolet-visible spectrum of the biosynthesized product showed a surface plasmon resonance (SPR) extinction band with an absorbance maximum at around 400 nm, thereby confirming the presence of fine Ag particles. Studies carried out by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy indicated that the principal active compounds responsible of the reduction of the Ag ions are proteins and capsaicin (through the amino groups) and phenolic compounds (through hydroxyl groups).
Noviembre, 2013 · DOI: 10.1039/C3RA43524E
- ‹ anterior
- 26 of 37
- siguiente ›














