Artículos SCI
2013
2013
Reactividad de Sólidos
Porous Aluminas: The biotemplate method for the synthesis of stable high surface area aluminas
Guerrero, MB; Maqueda, LP; Castro, PP; Cosp, JPBoletin de la Sociedad Española de Cerámica y Vidrio, 52 (2013) 251-267 DOI: 10.3989/cyv.322013
Abstract
Development of porous alumina has been the objective of numerous studies in recent decades, due to the intrinsic properties of aluminium oxide, such as high melting point, low thermal conductivity, chemical inertness and corrosion resistance which, in addition to a high surface area and permeability, make aluminas being used for many different industrial and technical applications. The crystallographic and textural stability of alumina acquires significant importance in those processes involving high temperatures; however, most of the synthesis methods yield metastable oxides of little interest in high-temperature processes due to the transformation to alpha phase, with the consequent reduction in surface area. The present article reviews diverse procedures for obtaining porous alumina with high specific surface area, including methods and strategies for preparing high surface alpha-alumina. Within this framework, the paper analyzes the results obtained through bioreplica of lignocellulosic materials. This technology allows preparing aluminas with the complex structural hierarchy of the lignocellulosic templates.
Noviembre, 2013 · DOI: 10.3989/cyv.322013
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Synthesis and tribological properties of WSex films prepared by magnetron sputtering
Dominguez-Meister, S; Justo, A; Sanchez-Lopez, JCMaterials Chemistry and Physics, 142 (2013) 186-194 DOI: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2013.07.004
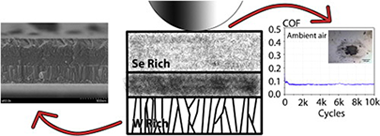
Abstract
WSex films with variable Se/W ratio were deposited by non-reactive r.f. magnetron sputtering from WSe2 target changing the applied d.c. pulsed bias conditions and substrate temperature. The structural and chemical properties were measured by cross-sectional scanning electron microscopy (X-SEM), energy dispersive analysis (EDX), X-ray diffraction (XRD), Raman and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The tribological properties were measured in ambient air (RH = 30–40%) and dry nitrogen by means of a reciprocating ball-on-disk tribometer. A clear correlation was found between the Se/W ratio and the measured friction coefficient displaying values below 0.1 (in ambient air) and 0.03 (in dry N2) for ratios Se/W ≥ 0.6 as determined by electron probe microanalysis (EPMA). The results demonstrated that notable tribological results could be obtained even in ambient air (friction ≤ 0.07 and wear rate ≈10−7 mm3 Nm−1) by controlling the film microstructure and chemical composition. By incorporating carbon, wear and chemical resistance can be gained by formation of non-stoichiometric carbides and/or alloying into the defective WSex hexagonal structure. The existence of a WSe2 rich interfacial layer (either on the ball scar or embedded in the film track) was evidenced by Raman in low friction conditions. The improvement in tribological performance is therefore obtained by means of layered WSex, the formation of gradient composition from metallic W (hard) to WSe2 (lubricant) and carbon incorporation.
Octubre, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2013.07.004
Materiales Coloidales
Perfectly Transparent Sr3Al2O6 Polycrystalline Ceramic Elaborated from Glass Crystallization
Alahrache, S; Al Saghir, K; Chenu, S; Veron, E; Meneses, DD; Becerro, AI; Ocana, M; Moretti, F; Patton, G; Dujardin, C; Cusso, F; Guin, JP; Nivard, M; Sangleboeuf, JC; Matzen, G; Allix, MChemistry of Materials, 25 (2013) 4017-4024 DOI: 10.1021/cm401953d
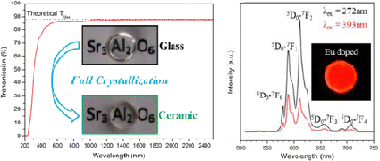
Abstract
The highly visible and infrared (up to 6 mu m) transparent Sr3Al2O6 polycrystalline ceramic was obtained by full crystallization of the corresponding glass composition. The glass synthesis and the direct congruent crystallization processes are described, and the material transparency is discussed in light of its microstructure. This new transparent ceramic exhibits a high density (i.e., complete absence of porosity) and micrometer-scale crystallites with very thin grain boundaries. These microstructural characteristics, inherent to the preparation method, minimize light scattering and demonstrate the advantages of this synthesis route compared to the high-pressure process used for the few reported transparent polycrystalline materials. This Sr3Al2O6 ceramic shows a H = 10.5 GPa hardness, a E-r = 150 GPa reduced elasticity modulus, and a 9.6 x 10(-6) K-1 thermal expansion coefficient. Such a transparent strontium aluminate ceramic opens the way to a wide range of applications, especially photonics when doped by various doping agents. As examples, the luminescence of Sr3Al2O6:Eu3+ and Sr3Al2O6:Er3+, which show strong emissions in the visible and infrared ranges, respectively, is presented. Moreover, the Sr3Al2O6:Ce3+ material was found to exhibit scintillation properties under X-ray excitation. Interestingly, the analogous Sr3Ga2O6 transparent polycrystalline ceramic material could equally be prepared using the same elaboration method, although its hygroscopicity prevents the preservation of its high transparency under normal conditions. The establishment of the key factors for the transparency of this economical and innovative synthesis method should enable the prediction of new classes of technologically relevant transparent ceramics.
Octubre, 2013 · DOI: 10.1021/cm401953d
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
In situ FT-IR study of the adsorption and photocatalytic oxidation of ethanol over sulfated and metallized TiO2
Murcia, JJ; Hidalgo, MC; Navio, JA; Arana, J; Dona-Rodriguez, JMApplied Catalysis B: Environmental, 142-143 (2013) 205-213 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.05.022
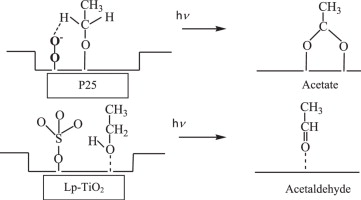
Abstract
TiO2 Degussa P25, TiO2 prepared by sol–gel submitted to sulfation pre-treatment and some metallized catalysts obtained by photodeposition of Au or Pt over the sulfated TiO2, were evaluated in the reaction of ethanol photo-oxidation. FT-IR spectroscopy was used to investigate the surface features of the photocatalysts, identifying adsorbed species and following the evolution of intermediate products in the ethanol photo-oxidation reaction. Nature of surface acidity in terms of Brönsted and Lewis centers was also studied.
Results showed that sulfation pre-treatment and metallization were important factors influencing the selectivity. Acetaldehyde was the main oxidation product on sulfated TiO2; in the case of P25 also acetates production was observed. The photodeposition of metals had a detrimental effect on the selectivity to acetaldehyde; on metallized catalysts the formation of stable secondary intermediates was detected.
Based on these findings, a reaction pathway for the ethanol photo-oxidation over the different photocatalysts, via acetaldehyde or via acetate formation is proposed.
Octubre, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.05.022
Materiales Coloidales - Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Monoclinic–Tetragonal Heterostructured BiVO4 by Yttrium Doping with Improved Photocatalytic Activity
Usai, S; Obregon, S; Becerro, AI; Colon, GJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 117 (2013) 24479-24484 DOI: 10.1021/jp409170y
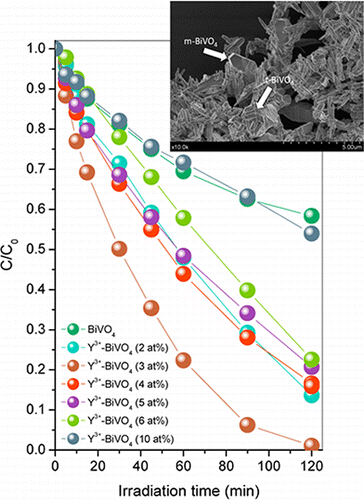
Abstract
Yttrium-doped BiVO4 has been synthesized by means of a surfactant free hydrothermal method having good photoactivities under sun-like excitation for the degradation of Methylene Blue (MB). From the structural and morphological characterization it has been stated that the presence of Y3+ induces the progressive stabilization of the tetragonal phase and the slight higher surface area values. By following the tetragonal cell parameters, the substitutional incorporation of Y3+ into the BiVO4 tetragonal lattice might be considered. Best photocatalytic performances were attained for the samples with Y3+ content of 3.0 at. % for which the MB degradation rate constant appears 2-fold higher. Furthermore, photoactivities for visible-light-driven O2 evolution demonstrate that the photocatalytic performance of the best Y-doped system (initial rate of O2 evolution, 285 μmol g–1 h–1) was more than 5 times that of undoped m-BiVO4 (initial rate of O2 evolution, 53 μmol g–1 h–1). The occurrence of Y3+ doping and a monoclinic–tetragonal heterostructured BiVO4 system induces the higher photocatalytic activities. PL analysis provides a clear evidence of the lower charge carriers recombination in heterostructured yttrium-doped systems.
Octubre, 2013 · DOI: 10.1021/jp409170y
Reactividad de Sólidos
Mechanosynthesis of nanocrystalline ZrB2-based powders by mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction method
Jalaly, M; Bafghi, MS; Tamizifar, M; Gotor, FJAdvances in Applied Ceramics, 112 (2013) 383-388 DOI: 10.1179/1743676113Y.0000000091
Abstract
Preparation of nanocrystalline ZrB2-based powder by aluminothermic and magnesiothermic reductions in M/ZrO2/B2O3 (M=Al or Mg) systems was investigated. In this research, high energy ball milling was employed to persuade necessary conditions for the occurrence of a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction (MSR). The course of MSR reactions were recorded by a noticeable pressure rise in the system during milling. Ignition times for ZrB2 formation by aluminothermic and magnesiothermic reductions were found to be 13 and 6 min, respectively. Zirconium diboride formation mechanism in both systems was explained through the analysis of the relevant sub-reactions.
Octubre, 2013 · DOI: 10.1179/1743676113Y.0000000091
Materiales Coloidales
Crystal Structure and Luminescent Properties of Eu3+-Doped A-La2Si2O7 Tetragonal Phase Stabilized by Spray Pyrolysis Synthesis
Fernandez-Carrion, Alberto J.; Ocana, Manuel; Florian, Pierre; Garcia-Sevillano, Jorge; Cantelar, Eugenio; Fitch, Andrew N.; Suchomel, Matthew R.; Becerro, Ana I.Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 117 (2013) 20876-20886 DOI: 10.1021/jp407172z
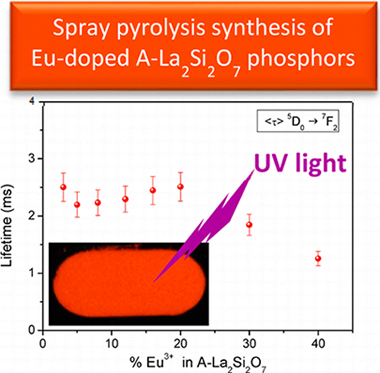
Abstract
Pure A-La2Si2O7 powder has been synthesized through a spray pyrolysis method followed by calcination at 1100 degrees C for 15 h. The crystallographic structure, refined from the synchrotron powder diffraction pattern of the sample, showed tetragonal symmetry with space group P4(1), a = 6.83565(1) angstrom, and c = 24.84133(1) angstrom. The Si-29 and La-139 NMR spectra have been described here for the first time in the literature and could be simulated with four Si and four La resonances, respectively, in good agreement with the presence of four Si and four La crystallographic sites in the unit cell. The same synthesis method was 2 successful for the synthesis of Eu3+-doped A-La2Si2O7 (%Eu = 3-40). The analysis of the unit cell volumes indicated that Eu3+ replaces La3+ in the unit cell for all Eu3+ substitution levels investigated. However, anomalous diffraction data indicated that the La/Eu substitution mechanism was not homogeneous, but Eu much prefers to occupy the RE3 sites. The Eu-doped A-La2Si2O7 phosphors thus synthesized exhibited a strong orange-red luminescence after excitation at 393 nm. Lifetime measurements indicated that the optimum phosphor was that with an Eu3+ content of 20%, which showed a lifetime of 2.3 ms. The quantum yield of the latter was found to be 12% at 393 nm excitation. These experimental observations together with the high purity of the phase obtained by the proposed spray pyrolysis method make this material an excellent phosphor for optoelectronic applications.
Octubre, 2013 · DOI: 10.1021/jp407172z
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
In situ imaging and strain determination during fracture in a SiC/SiC ceramic matrix composite
Ramirez-Rico, J; Stolzenburg, F; Almer, JD; Routbort, JL; Singh, D; Faber, KTScripta Materialia, 69 (2013) 497-500 DOI: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2013.05.032

Abstract
A combined imaging and microdiffraction technique using high-energy synchrotron X-rays is described and used to reveal microstructure, damage and strain evolution around notches in SiC/SiC composites. This technique allows for monitoring the material for cracks while loading and mapping the strain distribution in fibers and matrix with a resolution of tens of microns. We show that at current resolutions this technique is capable of measuring the strain distribution near crack tips in ceramic matrix composites and observe load transfer effects.
Octubre, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2013.05.032
Reactividad de Sólidos
Evidence of nanograin cluster coalescence in spark plasma sintered α-Al2O3
Morales-Rodriguez, A; Poyato, R; Gallardo-Lopez, A; Munoz, A; Dominguez-Rodriguez, AScripta Materialia, 69 (2013) 529-532 DOI: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2013.06.019
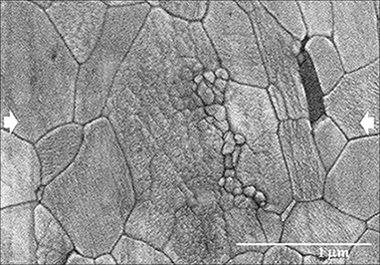
Abstract
The aim of this study is to elucidate the coarsening kinetics involved during densification of fine-grained pure α-alumina by spark plasma sintering. Low temperature and short dwell time sintering conditions were used to preserve the nanocrystalline structure of the starting commercial powder (about 50 nm). Notwithstanding the above, submicron grain coarsened microstructures have been developed. The microstructure evolution of alumina under different sintering conditions points to a nanograin rotation densification mechanism as being responsible for the fast grain growth observed.
Octubre, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2013.06.019
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Gold(III) stabilized over ionic liquids grafted on MCM-41 for highly efficient three-component coupling reactions
Bobadilla, LF; Blasco, T; Odriozola, JAPhysical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 39 (2013) 16927-16934 DOI: 10.1039/C3CP52924J
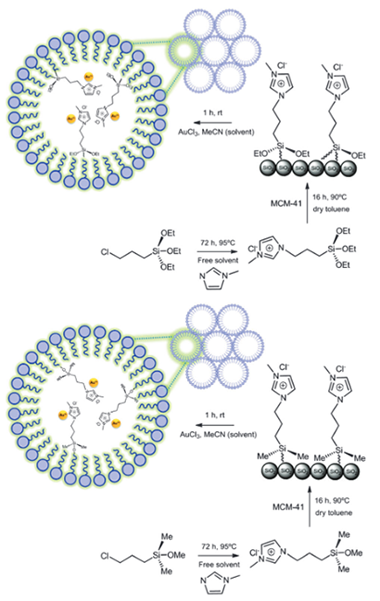
Abstract
Two alkoxysilyl-modified ionic liquids (ILs) have been synthesized and further grafted onto mesoporous silica, MCM-41; these ionic liquids were used for dispersing AuCl3 catalysts that activate C–H bonds as required for the synthesis of propargylamines by coupling alkyne, aldehyde and amine (A3 coupling) species. 29Si NMR experiments demonstrate the formation of covalent bonds between alkoxysilyl-modified Bmim IL and the MCM-41 surface through silanol groups. The catalytic activities of Au(III)-supported MCM-41 and Au(III) homogeneous catalysts are lower than those obtained for the IL functionalized Au–MCM-41 solids when the same gold loading is considered. An interaction between Au(III) species and the IL is proposed for explaining the stabilization of gold(III) species. However, successive reaction cycles result in a decrease in the catalytic activity that has been explained on the basis of gold leaching.
Octubre, 2013 · DOI: 10.1039/C3CP52924J
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Thermal conductivity of wood-derived graphite and copper–graphite composites produced via electrodeposition
Johnson, MT; Childers, AS; Ramirez-Rico, J; Wang, H; Faber, KTComposites Part A: Applied Science and Manufaturing, 63 (2013) 182-189 DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2013.06.009
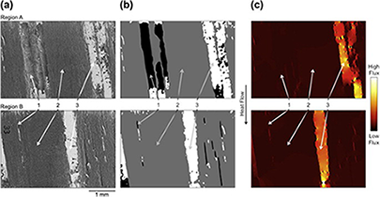
Abstract
The thermal conductivity of wood-derived graphite and graphite/copper composites was studied both experimentally and using finite element analysis. The unique, naturally-derived, anisotropic porosity inherent to wood-derived carbon makes standard porosity-based approximations for thermal conductivity poor estimators. For this reason, a finite element technique which uses sample microstructure as model input was utilized to determine the conductivity of the carbon phase independent of porosity. Similar modeling techniques were also applied to carbon/copper composite microstructures and predicted conductivities compared well to those determined via experiment.
Octubre, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2013.06.009
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Role of activated carbon on the increased photocatalytic activity of AC/Bi2WO6 coupled materials
Murcia-López, S; Navío, J.A.; Hidalgo, M.C.Applied Catalysis A: General, 466 (2013) 51-59 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2013.06.022
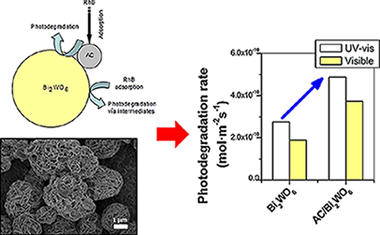
Abstract
The photocatalytic activities of several Bi2WO6 and TiO2/Bi2WO6 materials with different activated carbon (AC) contents were studied for Rhodamine B (RhB) (and Phenol) photodegradation under UV–vis and vis illumination. A wide characterization of the materials was carried out. The addition of AC strongly affected the Bi2WO6 morphology although not the crystalline phase. Even in the material with the lowest AC content (2 wt% nominal content) a structure with hierarchical porosity was formed. AC presence increased the initial reaction rates in the degradation of RhB. An important improvement in the photoactivity under both UV–vis and vis illumination conditions was obtained with the lowest AC content (2 wt%) when compared to the pristine material Bi2WO6 or to the systems with higher AC additions. AC/TiO2/Bi2WO6 materials were also improved in comparison to the TiO2/Bi2WO6 heterostructure without carbon. The improvement cannot be only ascribed to adsorption capability and surface area effects. A mechanism explaining the role of AC on the photocatalytic activity improvement is proposed.
Septiembre, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2013.06.022
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
On the different photocatalytic performance of BiVO4 catalysts for Methylene Blue and Rhodamine B degradation
Obregon, S; Colon, GJournal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical, 376 (2013) 40-47 DOI: 10.1016/j.molcata.2013.04.012
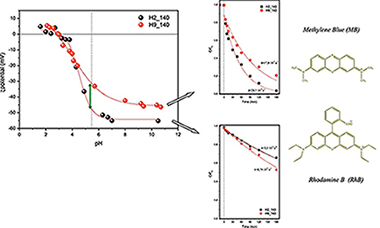
Abstract
BiVO4 hierarchical structures were synthesized by means of a surfactant free hydrothermal method having good photoactivities for the degradation of Methylene Blue and Rhodamine B under UV–vis irradiation. From the structural and morphological characterization it has been stated that BiVO4 present the monoclinic crystalline phase with different morphologies depending on the pH value. For Methylene Blue the photodegradation rate is strongly affected by the crystallite size and higher (0 0 4) facet exposition. On the contrary, for Rhodamine B, the ζ-potential of the surface clearly determines the photocatalytic performance of BiVO4 catalyst.
Septiembre, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.molcata.2013.04.012
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
A low-temperature single-source route to an efficient broad-band cerium(III) photocatalyst using a bimetallic polyoxotitanium cage
Lv, YK; Yao, MM; Holgado, JP; Roth, T; Steiner, A; Gan, LH; Lambert, RM; Wright, DSRSC Advances, 3 (2013) 13659-13662 DOI: 10.1039/C3RA41524D

Abstract
Aqueous hydrolysis of a series of cerium-containing polyoxotitanium cages gives Ce(III)-doped TiO2 [TiO2(Ce)] or TiO2-supported Ce(III)2Ti2O7, depending on the starting Ti : Ce ratio of the precursor. TiO2-supported Ce2Ti2O7 exhibits superior photocatalytic activity to the Ce-doped TiO2 materials and unusual broad-band absorption behaviour across the visible and near-infrared regions.
Septiembre, 2013 · DOI: 10.1039/C3RA41524D
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Effect of the alloy on micro-structured reactors for methanol steam reforming
Echave, FJ; Sanz, O; Velasco, I; Odriozola, JA; Montes, MCatalysis Today, 213 (2013) 145-154 DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2013.02.027

Abstract
Micro-monoliths and foams made of aluminium, Fecralloy® and brass were studied as substrates for structured systems for methanol steam reforming (MSR). All the alloys exhibited very adherent oxide layer produced by pre-treatment to improve the adhesion between substrate and catalyst. 2.5% Pd/ZnO catalyst was prepared and deposited on structured substrates. Both, good catalyst adhesion and stable catalytic performance were achieved in the case of brass micro-monoliths. The Fecralloy® and aluminium substrates reacted with the catalytic active components resulting in catalyst modification. The aluminium based substrates promoted dimethyl ether (DME) formation. Aluminium foam produced better performance than aluminium micro-monoliths that could be related to improved mass and heat transfer properties in foams.
Septiembre, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2013.02.027
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Low refractive index SiOF thin films prepared by reactive magnetron sputtering
Garcia-Garcia, FJ; Gil-Rostra, J; Terriza, A; Gonzalez, JC; Cotrino, J; Frutos, F; Ferrer, FJ; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Yubero, FThin Solid Films, 542 (2013) 332-337 DOI: 10.1016/j.tsf.2013.07.009
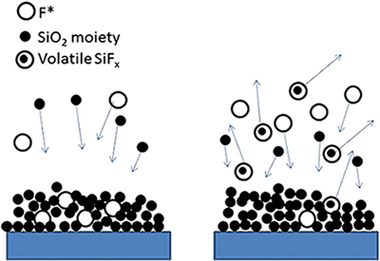
Abstract
We have studied low refractive index fluorine doped silica thin films prepared by reactive magnetron sputtering. Two experimental parameters were varied to increase the porosity of the films, the geometry of the deposition process (i.e., the use of glancing angle deposition) and the presence of chemical etching agents (fluorine species) at the plasma discharge during film growth. The microstructure, chemistry, optical properties, and porosity of the films have been characterized by scanning electron and atomic force microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, UV–vis, and spectroscopic ellipsometry. It is found that either the deposition at glancing angles or the incorporation of CFx species in the plasma discharge during film growth produces a decrease in the refractive index of the deposited films. The combined effect of the two experimental approaches further enhances the porosity of the films. Finally, the films prepared in a glancing geometry exhibit negative uniaxial birefringence.
Septiembre, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.tsf.2013.07.009
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Enhanced reactivity and related optical changes of Ag nanoparticles on amorphous Al2O3 supports
Pelaez, RJ; Castelo, A; Afonso, CN; Borras, A; Espinos, JP; Riedel, S; Leiderer, P; Boneberg, JNanotechnology, 24 (2013) 365702 DOI: 10.1088/0957-4484/24/36/365702
Abstract
Pairs of samples containing Ag nanoparticles (NPs) of different dimensions have been produced under the same conditions but on different substrates, namely standard glass slides and a thin layer of amorphous aluminum oxide (a-Al2O3) on-glass. Upon storage in ambient conditions (air and room temperature) the color of samples changed and a blue-shift and damping of the surface plasmon resonance was observed. The changes are weaker for the samples on-glass and tend to saturate after 12 months. In contrast, the changes for the samples on a-Al2O3 appear to be still progressing after 25 months. While x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy shows a slight sulfurization and negligible oxidation of the Ag for the on-glass samples upon 25 months aging, it shows that Ag is strongly oxidized for the on a-Al2O3 samples and sulfurization is negligible. Both optical and chemical results are consistent with the production of a shell at the expense of a reduction of the metal core dimensions, the latter being responsible for the blue-shift and related to the small (<10 nm initial diameter) of the NPs. The enhanced reactivity of the Ag NPs on the a-Al2O3 supports goes along with specific morphological changes of the Ag NPs and the observation of nitrogen.
Septiembre, 2013 · DOI: 10.1088/0957-4484/24/36/365702
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Promotional effect of the base metal on bimetallic Au-Ni/CeO2 catalysts prepared from core-shell nanoparticles
Holgado, JP; Ternero, F; Gonzalez-delaCruz, VM; Caballero, AACS Catalysis, 3 (2013) 2169-2180 DOI: 10.1021/cs400293b
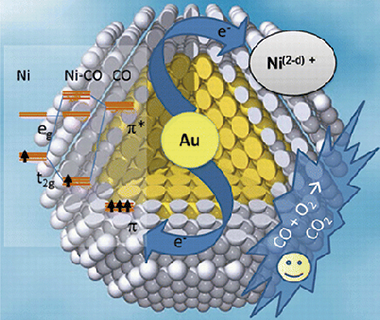
Abstract
A set of three catalysts (a Au–Ni bimetallic and their corresponding Au and Ni monometallics) has been prepared by impregnation of previously prepared suspensions of monodisperse metallic particles to ensure the precise control of their physicochemical characteristics (size and composition). The Au–Ni/CeO2 bimetallic catalysts present better reactivity toward CO oxidation than monometallic Au/CeO2 and Ni/CeO2 prepared under identical conditions. “operando-like” characterization of Ni and Au atoms into the bimetallic particles using, among other techniques, ambient-pressure photoelectron spectroscopy and diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier transform spectroscopy has allowed us to determine that under oxidative conditions the samples present a Au@NiO core–shell distribution, where Ni surface atoms are affected by an electronic effect from inner Au atoms.
Septiembre, 2013 · DOI: 10.1021/cs400293b
Reactividad de Sólidos
The Ozawa’s generalized time concept and YZ-master plots as a convenient tool for kinetic analysis of complex processes
Malek, J; Koga, N; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Criado, JMJournal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 113 (2013) 1437-1446 DOI: 10.1007/s10973-013-2939-0
Abstract
The concept of generalized time θ=∫exp(−Ea/RT)dt θ = ∫ exp ( − E a / RT ) d t in non-isothermal kinetics was introduced by Ozawa in 1965, together with the well-known isoconversional plot, i.e., Ozawa plot. The generalized time is the key concept to tie the kinetic data under varying temperature to the kinetic relationship at a constant temperature. It is well known that many processes studied by thermal analysis and calorimetry reveal a complex nature. Therefore, the generalized time concept seems to be very useful for the description of the change in the rate behavior depending on the fractional conversion. Using the concept of θ, three kinds of experimental master plots can be formalized in differential, integral, and multiplied forms. Among others, combination of the differential and multiplied master plots, y(α) = (dα/dθ) and z(α) = (dα/dθ)θ, show a high performance to discriminate the kinetic model based on the maxima condition of y(α y*) and z(α z*). The α y* − α y* kinetic plot is a useful tool to visualize the complexity of the kinetic process and to determine the most suitable kinetic model. The usefulness of α y* − α y* kinetic plot and the YZ-master plots is illustrated as exemplified by the kinetic analyses of complex crystallization processes of the as-prepared, thermally and mechanically treated amorphous zirconia.
Septiembre, 2013 · DOI: 10.1007/s10973-013-2939-0
Materiales Avanzados
Planning collection and solid waste flow (construction and demolition, concrete, ceramics and others) by utilizing a computerized tool for sustainable management
Garzon, E; Sanchez-Soto, PJBoletin de la Sociedad Española de Cerámica y Vidrio, 5 (2013) V-XIV (Notas Técnicas) DOI: 10.3989/cyv.2013.v52.i5
Abstract
Se presenta un procedimiento para la planificación de recogida y flujo de los residuos sólidos (de construcción y demolición, hormigón, cerámica, vidrio y otros) basado en la utilización de una herramienta informatizada, para conseguir una optimización de su gestión. Dicho procedimiento parte de normativa establecida según un Plan Director Territorial de la Gestión de Residuos Sólidos Urbanos (RSU) aprobado en una Comunidad Autónoma, en este caso se particulariza a la de Andalucía, tomando como ejemplo el volumen de residuos que se producen en una colectividad de tamaño medio (provincia de Almería), siendo extensible a otras mayores en población y territorio, disponiendo de datos actualizados.
El procedimiento utiliza una herramienta informática de gran difusión en el mundo, como es Google Earth y, de este modo, genera un número de “Centros deTransferencia” con objeto de minimizar el gasto de transporte, partiendo de una premisa previa en cuanto a distancia entre núcleos poblacionales y centros de tratamiento. Los Centros generados con la aplicación del procedimiento se pueden visualizar en un mapa topográfico, con áreas de influencia y vías de acceso a los mismos y se le pueden asociar una serie de datos tabulados con información adicional de utilidad. El procedimiento propuesto se va retroalimentando de manera constante con datos reales e información de campo, permitiendo a las empresas que producen residuos de distinta tipología como son los residuos de construcción y demolición principalmente, pero también hormigón, cerámica, vidrio, mezclas de todos ellos, residuos clasificados como peligrosos e incluso de otros materiales, a la propia administración y a la sociedad, en general, conocer las tasas de cada planta de tratamiento y qué se hace con los residuos entregados para contribuir a la reducción del impacto medioambiental de los mismos y a su gestión sostenible.
Septiembre, 2013 · DOI: 10.3989/cyv.2013.v52.i5
Materiales Coloidales
Small Particle-Size Talc Is Associated with Poor Outcome and Increased Inflammation in Thoracoscopic Pleurodesis
Arellano-Orden, E; Romero-Falcon, A; Juan, JM; Jurado, MO; Rodriguez-Panadero, F; Montes-Worboys, ARespiration, 86 (2013) 201-209 DOI: 10.1159/000342042
Abstract
Rationale: Talc is very effective for pleurodesis, but there is concern about complications, especially acute respiratory distress syndrome. Objectives: It was the aim of this study to investigate if talc with a high concentration of small particles induces greater production of cytokines, and if pleural tumor burden has any influence on the local production and spillover of cytokines to the systemic circulation and eventual complications. Methods: We investigated 227 consecutive patients with malignant effusion submitted to talc pleurodesis. One hundred and three patients received ‘small-particle talc' (ST; containing about 50% particles <10 µm) and 124 received ‘large-particle talc' (with <20% particles <10 µm). Serial samples of both pleural fluid and blood were taken before and 3, 24, 48 and 72 h after thoracoscopy. Also, mesothelial cells were stimulated with both types of talc in vitro. Measurements and Results: Interleukin-8, tumor necrosis factor-α, vascular endothelial growth factor, basic fibroblast growth factor and thrombin-antithrombin complex were measured in all samples. Early death (<7 days after talc) occurred in 8 of 103 patients in the ST and in 1 of 124 in the ‘large-particle talc' group (p = 0.007). Patients who received ST had significantly higher proinflammatory cytokines in pleural fluid and serum after talc application, and also in supernatants of the in vitro study. Pleural tumor burden correlated positively with proinflammatory cytokines in serum, suggesting that advanced tumor states induce stronger systemic reactions after talc application. Conclusions: ST provokes a strong inflammatory reaction in both pleural space and serum, which is associated with a higher rate of early deaths observed in patients receiving it.
Septiembre, 2013 · DOI: 10.1159/000342042
Reactividad de Sólidos
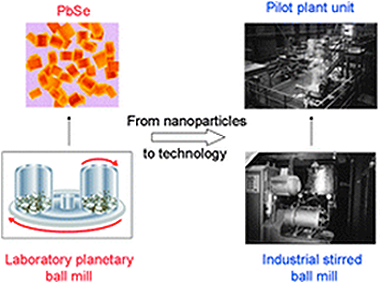
Hallmarks of mechanochemistry: from nanoparticles to technology
Balaz, P; Achimovicova, M; Balaz, M; Billik, P; Cherkezova-Zheleva, Z; Criado, JM; Delogu, F; Dutkova, E; Gaffet, E; Gotor, FJ; Kumar, R; Mitov, I; Rojac, T; Senna, M; Streletskii, A; Wieczorek-Ciurowa, KChemical Society Reviews, 42 (2013) 7571-7637 DOI: 10.1039/C3CS35468G
Abstract
The aim of this review article on recent developments of mechanochemistry (nowadays established as a part of chemistry) is to provide a comprehensive overview of advances achieved in the field of atomistic processes, phase transformations, simple and multicomponent nanosystems and peculiarities of mechanochemical reactions. Industrial aspects with successful penetration into fields like materials engineering, heterogeneous catalysis and extractive metallurgy are also reviewed. The hallmarks of mechanochemistry include influencing reactivity of solids by the presence of solid-state defects, interphases and relaxation phenomena, enabling processes to take place under non-equilibrium conditions, creating a well-crystallized core of nanoparticles with disordered near-surface shell regions and performing simple dry time-convenient one-step syntheses. Underlying these hallmarks are technological consequences like preparing new nanomaterials with the desired properties or producing these materials in a reproducible way with high yield and under simple and easy operating conditions. The last but not least hallmark is enabling work under environmentally friendly and essentially waste-free conditions (822 references).
Septiembre, 2013 · DOI: 10.1039/C3CS35468G
Reactividad de Sólidos
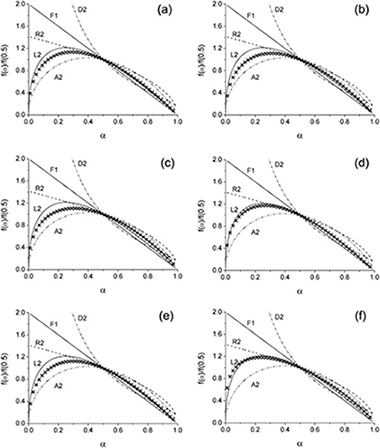
Pyrolysis kinetics of ethylene–propylene (EPM) and ethylene–propylene–diene (EPDM)
Perejon, A; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Gil-Gonzalez, E; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Criado, JMPolymer Degradation and Stability, 98 (2013) 1571-1577 DOI: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2013.06.029
Abstract
The thermal degradation kinetics of several ethylene–propylene copolymers (EPM) and ethylene–propylene–diene terpolymers (EPDM), with different chemical compositions, have been studied by means of the combined kinetic analysis. Until now, attempts to establish the kinetic model for the process have been unsuccessful and previous reports suggest that a model other than a conventional nth order might be responsible. Here, a random scission kinetic model, based on the breakage and evaporation of cleavaged fragments, is found to describe the degradation of all compositions studied. The suitability of the kinetic parameters resulting from the analysis has been asserted by successfully reconstructing the experimental curves. Additionally, it has been shown that the activation energy for the pyrolysis of the EPM copolymers decreases by increasing the propylene content. An explanation for this behavior is given. A low dependence of the EPDM chemical composition on the activation energy for the pyrolysis has been reported, although the thermal stability is influenced by the composition of the diene used.
Septiembre, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2013.06.029
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Atomistic model of ultra-smooth amorphous thin film growth by low-energy ion-assisted physical vapour deposition
Alvarez, R; Vazquez, L; Gago, R; Redondo-Cubero, A; Cotrino, J; Palmero, AJournal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 46 (2013) 395303 DOI: 10.1088/0022-3727/46/39/395303
Abstract
The growth of ultra-smooth amorphous thin films induced by low-energy (below 1 keV) ion-assistance processes is studied. The relative contribution of ion-induced smoothening effects is analysed by means of a Monte Carlo model and experimental data. In general, highly rough granular or ultra-smooth (with roughness below one monolayer) films are produced depending on the competition between surface shadowing and ion-induced adatom mobility and sputtering. The ultra-smooth growth regime is experimentally and theoretically consistent with the Edwards–Wilkinson growth mode, which is related to the ion-induced enhancement of surface mobility. Overall, the framework and the fundamentals to analyse this type of growth are developed and discussed.
Septiembre, 2013 · DOI: 10.1088/0022-3727/46/39/395303
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
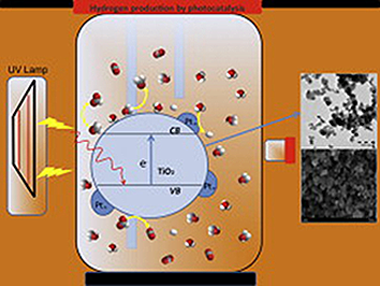
Hydrogen production using Pt-loaded TiO2 photocatalysts
Melian, EP; Lopez, CR; Mendez, AO; Diaz, OG; Suarez, MN; Rodriguez, JMD; Navio, JA; Hevia, DFInternational Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 38 (2013) 11737-11748 DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.07.006
Abstract
A series of synthesised TiO2-based and commercial photocatalysts were modified by Pt photodeposition and a study made of their photocatalytic activity in hydrogen production. The modified commercial photocatalysts were Evonik P25, Kronos vlp7000 and Hombikat UV-100, and the other modified photocatalysts were synthesised by our group using sol–gel and sol–gel hydrothermal processes (SG400, SG750 and HT). Pt weight percentages used in the study were 0.5, 1.0 and 2.1 wt.% (Pt/TiO2). The photocatalysts were extensively characterised by X-ray diffraction (XRD), UV–vis diffuse reflectance, Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) surface area measurement, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM–EDX), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and laser light dispersion. Methanol (25% vol.) was used as sacrificial agent over the 8 h of the hydrogen production tests and measurements were taken of the final concentrations of formaldehyde and formic acid as well as initial and final TOC. Photoactivity of all photocatalysts increased in the presence of Pt. The most efficient of the synthesised photocatalysts was SG750 and of the commercial photocatalysts P25. Maximum production of SG750 was 1846 μmol h−1 at 1.0 wt.% Pt and its production per surface unit was notably higher than that of P25.
Septiembre, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.07.006
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Structure-mediated transition in the behavior of elastic and inelastic properties of beach tree bio-carbon
Kardashev, BK; Orlova, TS; Smirnov, BI; Gutierrez, A; Ramirez-Rico, JPhysics of the Solid State, 55 (2013) 1884-1891 DOI: 10.1134/S1063783413090151
Abstract
Microstructural characteristics and amplitude dependences of the Young modulus E and of internal friction (logarithmic decrement δ) of bio-carbon matrices prepared from beech tree wood at different carbonization temperatures T carb ranging from 600 to 1600°C have been studied. The dependences E(T carb) and δ(T carb) thus obtained revealed two linear regions of increase of the Young modulus and of decrease of the decrement with increasing carbonization temperature, namely, ΔE ∼ AΔT carb and Δδ ∼ BΔT carb, with A ≈ 13.4 MPa/K and B ≈ −2.2 × 10−6 K−1 for T carb < 1000°C and A ≈ 2.5 MPa/K and B ≈ −3.0 × 10−7 K−1 for T carb > 1000°C. The transition observed in the behavior of E(T carb) and δ(T carb) at T carb = 900–1000°C can be assigned to a change of sample microstructure, more specifically, a change in the ratio of the fractions of the amorphous matrix and of the nanocrystalline phase. For T carb < 1000°C, the elastic properties are governed primarily by the amorphous matrix, whereas for T carb > 1000°C the nanocrystalline phase plays the dominant part. The structurally induced transition in the behavior of the elastic and microplastic characteristics at a temperature close to 1000°C correlates with the variation of the physical properties, such as electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and thermopower, reported in the literature.
Septiembre, 2013 · DOI: 10.1134/S1063783413090151
Reactividad de Sólidos
Kinetic studies in solid state reactions by sample-controlled methods and advanced analysis procedures
Perez-Maqueda, LA; Criado, JM; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perejon, AJournal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 113 (2013) 1447-1453 DOI: 10.1007/s10973-013-3114-3
Abstract
A comparative study of both conventional rising temperature and sample-controlled methods, like constant rate thermal analysis (CRTA), is carried out after analyzing a set of solid state reactions using both methods. It is shown that CRTA avoids the influence of heat and mass transfer phenomena for a wide range of sample sizes leading to reliable kinetic parameters. On the other hand, conventional rising temperature methods yield α–T plots dependent on experimental conditions, even when using samples sizes smaller than 2 mg. Moreover, it is shown that the discrimination of overlapping processes is dramatically improved using sample-controlled methods instead of conventional heating procedures. An advanced method for performing the kinetic analysis of complex processes from a single CRTA experiment is proposed.
Septiembre, 2013 · DOI: 10.1007/s10973-013-3114-3
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
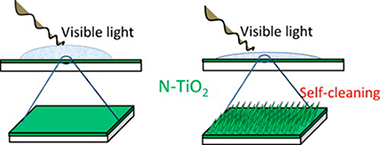
Enhancement of visible light-induced surface photo-activity of nanostructured N–TiO2 thin films modified by ion implantation
Romero-Gomez, P; Lopez-Santos, C; Borras, A; Espinos, JP; Palmero, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARChemical Physics Letters, 582 (2013) 95-99 DOI: 10.1016/j.cplett.2013.07.025
Abstract
This work reports the morphological and chemical modifications induced in TiO2 thin films by bombardment with high energy N+ ions at different temperatures and their different photo-activity responses after implantation under visible and UV light illumination. When implanted samples are illuminated with visible light, no dye photo-decolouration takes place despite that light transformed the surfaces from hydrophobic to hydrophilic. In agreement with the Wenzel model of wetting, correlation is found between visible light photo-activity and film morphology. We conclude that the photo-activity response can be separated into shallow and Schottky barrier photo-activity, this latter involving a thicker layer of material.
Septiembre, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cplett.2013.07.025
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Erbium doped TiO2–Bi2WO6 heterostructure with improved photocatalytic activity under sun-like irradiation
Obregon, S; Colon, GApplied Catalysis B: Environmental, 140-141 (2013) 299-305 DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.04.014
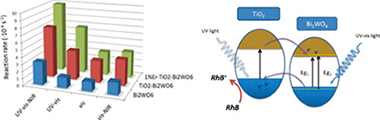
Abstract
Erbium doped TiO2–Bi2WO6 have been synthesized by means of a surfactant free hydrothermal method having good photoactivities under sun-like excitation for the degradation of Rhodamine B. From the structural and morphological characterization it has been stated that the presence of Er3+ induces a progressive russelite cell contraction due to its incorporation in the Bi2WO6 lattice in substitutional sites. The best photocatalytic performance was attained for the samples with 1 at% of Er. From the study of the photocatalytic activity under different irradiation conditions it can be inferred that Er3+ presence induces a significant improvement of the photoactivity in the UV range. The evolution of band-gap values seems to be similarly related with the reaction rate progression. Thus, the higher band-gap values in lower Er doped systems would be the cause of a better electron hole separation under UV irradiation.
Agosto, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.04.014
Materiales Coloidales
Surface modified Eu:GdVO4 nanocrystals for optical and MRI imaging
Nuñez, Nuria O.; Rivera, Sara; Alcantara, David; de la Fuente, Jesus M.; Garcia-Sevillano, Jorge; Ocaña, ManuelDalton Transactions, 42 (2013) 10725-10734 DOI: 10.1039/C3DT50676B
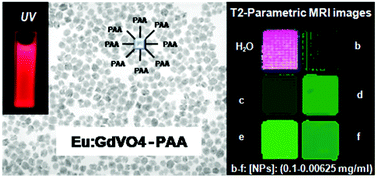
Abstract
A facile solvothermal route has been developed for the preparation of europium doped gadolinium orthovanadate nanoparticles ([similar]70 nm) with tetragonal structure, based on a homogenous precipitation reaction at 120 °C from rare earth precursors (yttrium nitrate and europium nitrate) and sodium orthovanadate solutions using an ethylene glycol–water mixture as the solvent. The effects of the doping level on the luminescence properties were evaluated in order to find the optimum nanophosphors. These nanocrystals were successfully functionalized with amino (two step process) and carboxylate (one-pot process) groups provided by amino-dextran polymers (AMD) and polyacrylic acid (PAA), respectively. It was found that while the luminescent properties of both kinds of functionalized systems were similar, the colloidal stability of the PAA-modified sample was higher, because of which, it was selected to study their cytotoxicity and magnetic properties (relaxivity and phantom analyses) to assess their potentiality as multifunctional probes for both “in vitro” optical biolabels and negative contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging.
Agosto, 2013 · DOI: 10.1039/C3DT50676B
Propiedades mecánicas, modelización y caracterización de cerámicos avanzados
High temperature plasticity in yttria stabilised tetragonal zirconia polycrystals (Y-TZP)
Dominguez-Rodriguez, A; Gomez-Garcia, D; Wakai, FInternational Materials Reviews, 58 (2013) 399-417 DOI: 10.1179/1743280413Y.0000000018
Abstract
The literature data on the superplastic deformation of high purity yttria stabilised tetragonal zirconia polycrystals is reviewed in detail. It is shown that, based on the existence of a threshold stress, the single mechanism of grain boundary sliding (GBS) accommodated by diffusional processes can explain the superplasticity of these materials over all the ranges of temperature, stress, grain size, and surrounding atmosphere that have been studied. The origin of the threshold stress and its quantitative dependence on temperature and grain size is explained in terms of the segregation of yttrium atoms at the grain boundaries. A new model for GBS accommodated by lattice or grain-boundary diffusion is presented which can explain the transition of the stress exponent from 2 to 1.
Agosto, 2013 · DOI: 10.1179/1743280413Y.0000000018
Materiales Avanzados
Historic preservation, GIS, & rural development: The case of Almería province, Spain
Cano, M; Garzon, E; Sanchez-Soto, PJApplied Geograhpy, 42 (2013) 34-47 DOI: 10.1016/j.apgeog.2013.04.014
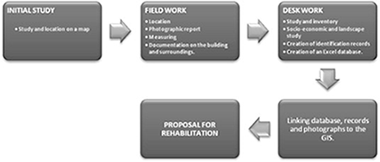
Abstract
A computerized database was created, based on a Geographic Information System (GIS), with hyperlinks to the website for a Rural Development Association (Almería province, Andalusia, Spain). Thus, a catalogue of traditional rural buildings in this particular area was compiled, identifying and characterizing each one, establishing criteria for a dynamic and rational selection. The purpose to select this example was to facilitate their management by public organizations or private individuals, for their reuse, restoration or both. The cataloguing and promotion of rural architecture will contribute to creating jobs by stimulating new economic activity, such as the promotion of cultural tourism, while preserving a valuable source of information on rural culture, recovering local construction techniques, encouraging a sense of community, and making villages and rural areas more attractive to visitors. The assessment of the rehabilitation potential of rural buildings in this region has helped to establish a priority order for their reuse, and so an intervention map has been devised in terms of a “Decision Index” corresponding to each considered building.
Agosto, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apgeog.2013.04.014
Materiales para Bioingeniería y Regeneración Tisular
Tuning of Cell–Biomaterial Anchorage for Tissue Regeneration
Leal-Egana, Aldo; Diaz-Cuenca, Aranzazu; Boccaccini, Aldo RAdvanced Materials, 25 (2013) 4049-4057 DOI: 10.1002/adma.201301227
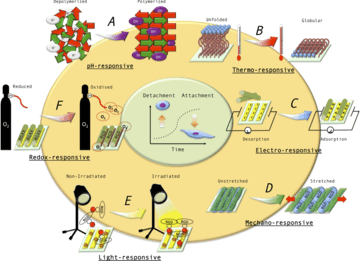
Abstract
Which mechanisms mediate cell attachment to biomaterials? What role does the surface charge or wettability play on cell–material anchorage? What are the currently investigated strategies to modify cell–matrix adherence spatiotemporally? Considering the development of scaffolds made of biocompatible materials to temporarily replace the structure and/or function of the extracellular matrix, focus is given to the analysis of the specific (i.e., cell adhesive peptide sequences) and unspecific (i.e., surface charge, wettability) mechanisms mediating cell-matrix interactions. Furthermore, because natural tissue regeneration is characterized by the dynamic attachment/detachment of different cell populations, the design of advanced scaffolds for tissue engineering, based in the spatiotemporal tuning of cell–matrix anchorage is discussed.
Agosto, 2013 · DOI: 10.1002/adma.201301227
Reactividad de Sólidos
Studies of isothermal crystallisation kinetics of sunflower hard stearin-based confectionery fats
Bootello, MA; Hartel, RW; Levin, M; Martinez-Blanes, JM; Real, C; Garces, R; Martinez-Force, E; Salas, JJFood Chemistry, 139 (2013) 184-195 DOI: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.11.141
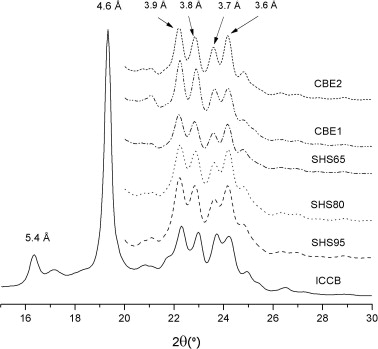
Abstract
The crystallisation and polymorphic properties of three sunflower hard stearins (SHSs) and cocoa butter equivalents (CBEs) formulated by blending SHSs and palm mid fraction (PMF) were studied and compared with those from cocoa butter (CB), to explore their possibilities as confectionery fats. The isothermal crystallisation kinetics of these fats were examined by pNMR and DSC at three different temperatures. All samples studied displayed a two-step crystallisation profile that could be fitted to an exponential-Gompertz equation. Stop-and-return DSC studies showed that SHSs and CBEs exhibited different crystallisation mechanisms according to their triacylglycerol composition, with a quick formation of metastable crystals, followed by a polymorphic transition to the more stable β or β′ forms. X-ray diffraction (XRD) was used to investigate the polymorphic forms of tempered SHSs and CBEs in the long term. In all cases the resulting fats displayed short spacing patterns associated with β polymorphism. These formulations based on SHSs and PMF met all the requirements to be considered as CBEs; therefore they could be used as an alternative to traditional confectionery fats.
Agosto, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.11.141
Reactividad de Sólidos
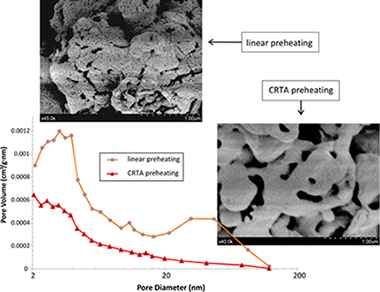
Constant rate thermal analysis for enhancing the long-term CO2 capture of CaO at Ca-looping conditions
Valverde, JM; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perejon, A; Perez-Maqueda, LAApplied Energy, 108 (2013) 108-120 DOI: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2013.03.013
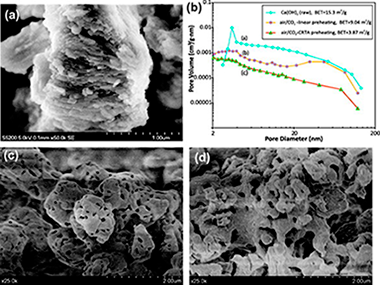
Abstract
Experimental results are reported on the (Ca-looping) multicyclic CO2 capture of CaO and nanosilica/CaO composites derived from Ca(OH)2 and nanosilica/Ca(OH)2 dry mixtures subjected in situ to linear and constant rate thermal analysis (CRTA) preheating programs in either air or air/CO2 atmospheres. By means of CRTA preheating the rates of the reactions taking place during pretreatment are kept at a constant and small value along the entire process. In agreement with a pore skeleton model, previously proposed in the literature for explaining the behavior of natural limestones thermally pretreated, our results suggest that air/CO2-CRTA pretreatment yields a thermally stable hard skeleton of poorly reactive CaO on which a soft skeleton of reactive CaO would be supported. The sorbent subjected to this preheating program exhibits a reactivation in the very first carbonation/calcination cycles, after which CaO conversion decays slowly with the cycle number. In contrast, linearly or air-CRTA preheated sorbents show a significant decrease of CaO conversion within the first cycles. In the latter case, CaO multicyclic conversion fits well to a model where it is assumed that the progressive reduction of surface area as the number of carbonation/calcination cycles is increased obeys to sintering of the preheated sorbent skeleton as it is subjected to repeated calcinations during cycling. In the former case, CaO conversion data conforms to the prediction by a model in which the loss of surface area is mainly due to sintering of a nascent CaO soft skeleton regenerated in the diffusive carbonation phase, which is enhanced by the air/CO2-CRTA pretreatment. As regards the effect of nanosilica, the results indicate that it slows down CaO sintering during pretreatment, which hinders the development of a stable CaO skeleton thus hampering reactivation and stabilization of conversion. On the other hand, as CaO sintering is also lessened during looping calcination, nanosilica is useful to increase the absolute values of CaO conversion.
Agosto, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2013.03.013
Reactividad de Sólidos
Spark plasma sintering of TixTa1−xC0.5N0.5-based cermets: Effects of processing conditions on chemistry, microstructure and mechanical properties
Cordoba, Jose M.; Chicardi, Ernesto; Poyato, Rosalia; Gotor, Francisco J.; Medri, Valentina; Guicciardi, Stefano; Melandri, CesareChemical Engineering Journal, 230 (2013) 558-566 DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2013.06.104
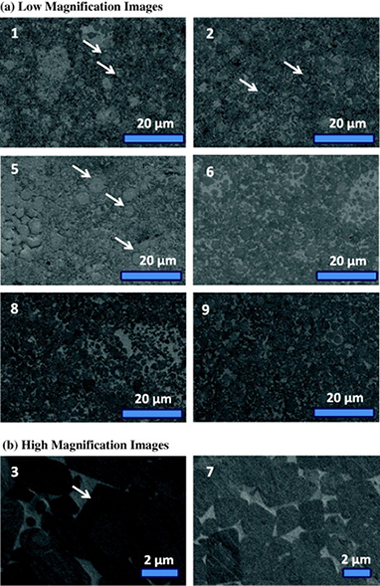
Abstract
Nanometric powdered TixTa1−xC0.5N0.5-based cermets were fabricated using a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction and consolidated by spark plasma sintering. Highly dense cermets were obtained, and their chemistry, microstructure and mechanical properties were characterised by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, image analysis, microindentation and nanoindentation. The microhardness was found to depend directly on the contiguity and size of the ceramic hard particles. The samples synthesised at the lowest temperature (1150 °C) exhibited more homogeneous microstructures and smaller ceramic particles and the best combination of microhardness and fracture toughness.
Agosto, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2013.06.104
Reactividad de Sólidos
Enhanced general analytical equation for the kinetics of the thermal degradation of poly(lactic acid) driven by random scission
Carrasco, F; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perejon, A; Santana, OO; Maspoch, MLPolymer Testing, 32 (2013) 937-945 DOI: 10.1016/j.polymertesting.2013.04.013
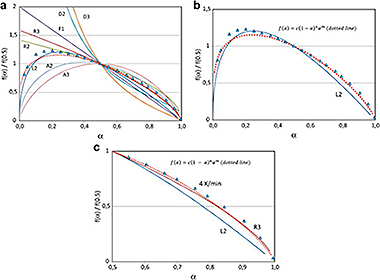
Abstract
An enhanced general analytical equation has been developed in order to evaluate the kinetic parameters of the thermal degradation of poly(lactic acid) (PLA) at various linear heating rates and at constant rate conditions. This improvement consisted of replacing the n-order conversion function by a modified form of the Sestak-Berggren equation f(α) = c(1−α)nαm, which led to better adjustment of experimental data, and also adequately represented the conventional mechanisms for solid-state processes. The kinetic parameters so obtained have been compared to those determined by conventional differential and isoconversional methods. Given that the thermal degradation of PLA has been argued to be caused by random chain scission reactions of ester groups, the conversion function (α) = 2(α1/2−α), corresponding to a random scission mechanism, has been tested.
Agosto, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.polymertesting.2013.04.013
Materiales Coloidales
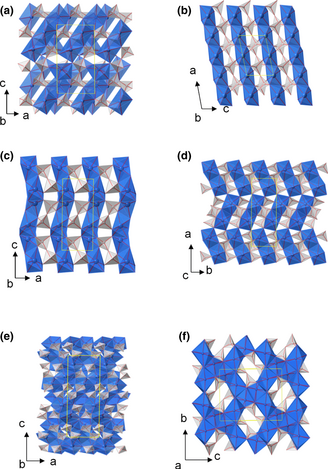
Thermal Expansion of Rare-Earth Pyrosilicates
Fernandez-Carrion, AJ; Allix, M; Becerro, AIJournal of the American Ceramic Society, 96 (2013) 2298-2305 DOI: 10.1111/jace.12388
Abstract
The use of RE2Si2O7 materials as environmental barrier coatings (EBCs) and in the sintering process of advanced ceramics demands a precise knowledge of the coefficient of thermal expansion of the RE2Si2O7. High-temperature X-ray diffraction (HTXRD) patterns were collected on different RE2Si2O7 polymorphs, namely A, G, α, β, γ, and δ, to determine the changes in unit cell dimensions. RE2Si2O7 compounds belonging to the same polymorph showed, qualitatively, very similar unit cell parameters behavior with temperature, whereas the different polymorphs of a given RE2Si2O7 compound exhibited markedly different thermal expansion evolution. The isotropy of thermal expansion was demonstrated for the A-RE2Si2O7 polymorph while the rest of polymorphs exhibited an anisotropic unit cell expansion with the biggest expansion directed along the REOx polyhedral chains. The apparent bulk thermal expansion coeficcients (ABCTE) were calculated from the unit cell volume expansion for each RE2Si2O7 compound. All compounds belonging to the same polymorph exhibited similar ABCTE values. However, the ABCTE values differ significantly from one polymorph to the other. The highest ABCTE values correspond to A-RE2Si2O7 compounds, with an average of 12.1 × 10−6 K−1, whereas the lowest values are those of β- and γ-RE2Si2O7, which showed average ABCTE values of ~4.0 × 10−6 K−1.
Julio, 2013 · DOI: 10.1111/jace.12388
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Characterisation of Co@Fe3O4 core@shell nanoparticles using advanced electron microscopy
Knappett, BR; Abdulkin, P; Ringe, E; Jefferson, DA; Lozano-Perez, S; Rojas, TC; Fernandez, A; Wheatley, AEHNanoscale, 5 (2013) 5765-5772 DOI: 10.1039/C3NR33789H
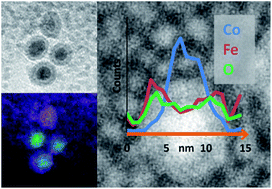
Abstract
Cobalt nanoparticles were synthesised via the thermal decomposition of Co2(CO)8 and were coated in iron oxide using Fe(CO)5. While previous work focused on the subsequent thermal alloying of these nanoparticles, this study fully elucidates their composition and core@shell structure. State-of-the-art electron microscopy and statistical data processing enabled chemical mapping of individual particles through the acquisition of energy-filtered transmission electron microscopy (EFTEM) images and detailed electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS) analysis. Multivariate statistical analysis (MSA) has been used to greatly improve the quality of elemental mapping data from core@shell nanoparticles. Results from a combination of spatially resolved microanalysis reveal the shell as Fe3O4 and show that the core is composed of oxidatively stable metallic Co. For the first time, a region of lower atom density between the particle core and shell has been observed and identified as a trapped carbon residue attributable to the organic capping agents present in the initial Co nanoparticle synthesis.
Julio, 2013 · DOI: 10.1039/C3NR33789H
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Liquids Analysis with Optofluidic Bragg Microcavities
Oliva-Ramirez, M; Gonzalez-Garcia, L; Parra-Barranco, J; Yubero, F; Barranco, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 5 (2013) 6743-650 DOI: 10.1021/am401685r
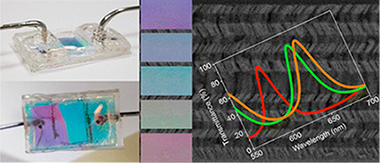
Abstract
Porous Bragg microcavities formed by stacking a series of porous nanocolumnar layers with alternate low (SiO2) and high (TiO2) refractive index materials have been prepared by physical vapor deposition at glancing angles (GLAD). By strictly controlling the porosity and refractive index of the individual films, as well as the relative orientation of the nanocolumns from one layer to the next, very porous and nondispersive high optical quality microcavities have been manufactured. These photonic structures have been implemented into responsive devices to characterize liquids, mixtures of liquids, or solutions flowing through them. The large displacements observed in the optical spectral features (Bragg reflector gap and resonant peak) of the photonic structures have been quantitatively correlated by optical modeling with the refractive index of the circulating liquids. Experiments carried out with different glucose and NaCl solutions and mixtures of water plus glycerol illustrate the potentialities of these materials to serve as optofluidic devices to determine the concentration of solutions or the proportion of two phases in a liquid mixture.
Julio, 2013 · DOI: 10.1021/am401685r
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Monolayer arrangement of fatty hydroxystearic acids on graphite: Influence of hydroxyl groups
Medina, S; Benitez, JJ; Castro, MA; Cerrillos, C; Millan, C; Alba, MDThin Solid Films, 539 (2013) 194-200 DOI: 10.1016/j.tsf.2013.05.053
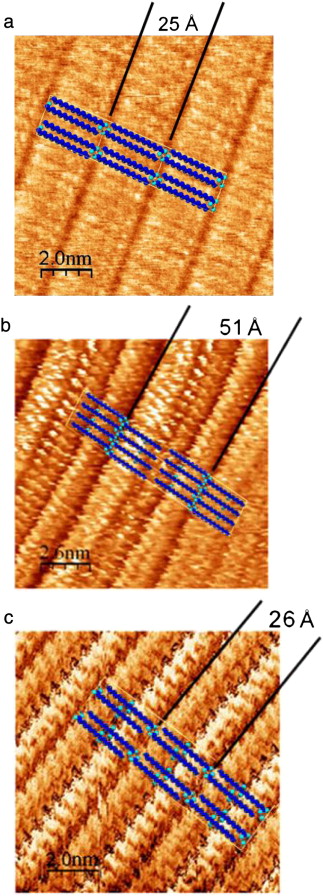
Abstract
Previous studies have indicated that long-chain linear carboxylic acids form commensurate packed crystalline monolayers on graphite even at temperatures above their melting point. This study examines the effect on the monolayer formation and structure of adding one or more secondary hydroxyl, functional groups to the stearic acid skeleton (namely, 12-hydroxystearic and 9,10-dihydroxystearic acid). Moreover, a comparative study of the monolayer formation on recompressed and monocrystalline graphite has been performed through X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Scanning Tunneling Microscopy (STM), respectively. The Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) and XRD data were used to confirm the formation of solid monolayers and XRD data have provided a detailed structural analysis of the monolayers in good correspondence with obtained STM images. DSC and XRD have demonstrated that, in stearic acid and 12-hydroxystearic acid adsorbed onto graphite, the monolayer melted at a higher temperature than the bulk form of the carboxylic acid. However, no difference was observed between the melting point of the monolayer and the bulk form for 9,10-dihydroxystearic acid adsorbed onto graphite. STM results indicated that all acids on the surface have a rectangular p2 monolayer structure, whose lattice parameters were uniaxially commensurate on the a-axis. This structure does not correlate with the initial structure of the pure compounds after dissolving, but it is conditioned to favor a) hydrogen bond formation between the carboxylic groups and b) formation of hydrogen bonds between secondary hydroxyl groups, if spatially permissible. Therefore, the presence of hydroxyl functional groups affects the secondary structure and behavior of stearic acid in the monolayer.
Julio, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.tsf.2013.05.053
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Preparation and characterization of CrO2 films by Low Pressure Chemical Vapor Deposition from CrO3
Aguilera, C; Gonzalez, JC; Borras, A; Margineda, D; Gonzalez, JM; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Espinos, JPThin Solid Films, 539 (2013) 1-11 DOI: 10.1016/j.tsf.2013.04.118
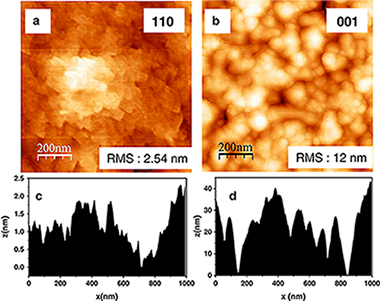
Abstract
Highly oriented CrO2 thin films have been heteroepitaxially grown on TiO2 rutile (110), (100) and (001) single crystalline substrates, by Low Pressure Chemical Vapor Deposition from CrO3 as precursor and flowing oxygen as carrier gas, under a pressure of 67 Pa. The experimental conditions were fine tuned by depositing on polycrystalline Ti foils, to improve the purity of the films and the deposition rate. A maximum deposition rate of 175 nm h− 1 was obtained.
The composition and texture of films, up to 2 μm thick, have been determined by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Micro Raman, while their microstructure has been examined by Scanning Electron Microcopy and Atomic Force Microscopy, and their magnetic behavior has been tested by superconducting quantum interference device magnetometry. These techniques reveal that the phase purity, texture, microstructure and thickness of these films are dependent on the crystalline face of the rutile substrate and the deposition temperature. Thus, microscopy techniques, XRD and Raman spectroscopy confirm that highly textured CrO2 films were always obtained on the three rutile substrate faces when deposition temperature ranges between 616 K and 636 K. But these techniques also show that CrO2 films are unpurified with inclusions or patches of Cr2O3, for the most of the substrates and especially at high deposition temperatures. Magnetic measurements conclusively demonstrate that pure CrO2 films are only obtained when TiO2 (110) is used as a substrate.
Julio, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.tsf.2013.04.118
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Degradation of Rhodamine B/Phenol Mixtures in Water by Sun-Like Excitation of a Bi2WO6–TiO2 Photocatalyst
Murcia-López, S; Navío, J.A.; Hidalgo, M.C.Photochemistry and Photobiology, 89 (2013) 832-840 DOI: 10.1111/php.12054
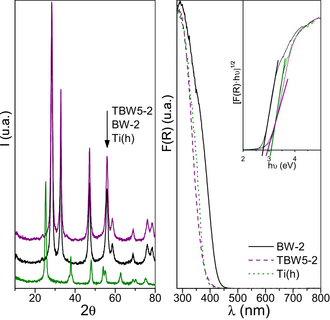
Abstract
Bi2WO6 and Bi2WO6–TiO2 (5% molar Ti) nano-heterostructures were synthesized by a hydrothermal method. The properties of the synthesized catalysts were characterized, having high photoactivity for Rhodamine B degradation under sun-like illumination, explained by a synergetic mechanism previously proposed through UV and visible induced processes, in which the photosensitization effect of Rhodamine B is considered. We now report that using Phenol, a molecule which does not lead the photosensitization process, the photoactivity decreased considerably, thus emphasizing how important is the model molecule selected as degradation substrate for evaluating the photoactivity. The photocatalytic properties of the synthesized catalysts have been evaluated by exposing a mixture of Rhodamine B and Phenol in water, to different illumination conditions. It can be confirmed that the photoinduced mechanism via the photosensitization of Rhodamine B is a key factor responsible for the increase on the photocatalytic activity showed by the Bi2WO6–TiO2 compound and that the degradation mechanism of Rhodamine B is not changed by the simultaneous presence of other transparent substrate as Phenol.
Julio, 2013 · DOI: 10.1111/php.12054
Reactividad de Sólidos
CO2 multicyclic capture of pretreated/doped CaO in the Ca-looping process. Theory and experiments
Valverde, JM; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perejon, A; Perez-Maqueda, LAPhysical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 15 (2013) 11775-11793 DOI: 10.1039/C3CP50480H
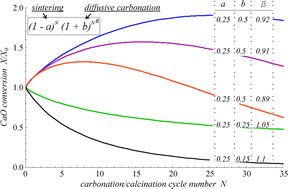
Abstract
We study in this paper the conversion of CaO-based CO2 sorbents when subjected to repeated carbonation–calcination cycles with a focus on thermally pretreated/doped sorbents. Analytical equations are derived to describe the evolution of conversion with the cycle number from a unifying model based on the balance between surface area loss due to sintering in the looping-calcination stage and surface area regeneration as a consequence of solid-state diffusion during the looping-carbonation stage. Multicyclic CaO conversion is governed by the evolution of surface area loss/regeneration that strongly depends on the initial state of the pore skeleton. In the case of thermally pretreated sorbents, the initial pore skeleton is highly sintered and regeneration is relevant, whereas for nonpretreated sorbents the initial pore skeleton is soft and regeneration is negligible. Experimental results are obtained for sorbents subjected to a preheating controlled rate thermal analysis (CRTA) program. By applying this preheating program in a CO2 enriched atmosphere, CaO can be subjected to a rapid carbonation followed by a slow rate controlled decarbonation, which yields a highly sintered skeleton displaying a small conversion in the first cycle and self-reactivation in the next ones. Conversely, carbonation of the sorbent at a slow controlled rate enhances CO2 solid-state diffusion, which gives rise, after a quick decarbonation, to a highly porous skeleton. In this case, CaO conversion in the first cycle is very large but it decays abruptly in subsequent cycles. Data for CaO conversion retrieved from the literature and from further experimental measurements performed in our work are analyzed as influenced by a variety of experimental variables such as preheating temperature program, preheating exposition time, atmosphere composition, presence of additives, and carbonation–calcination conditions. Conversion data are well fitted by the proposed model equations, which are of help for a quantitative interpretation of the effect of experimental conditions on the multicyclic sorbent performance as a function of sintering/regeneration parameters inferred from the fittings and allow foreseeing the critical conditions to promote reactivation. The peculiar behavior of some pretreated sorbents, showing a maximum conversion in a small number of cycles, is explained in light of the model.
Julio, 2013 · DOI: 10.1039/C3CP50480H
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura - Tribología y Protección de Superficies
A new bottom-up methodology to produce silicon layers with a closed porosity nanostructure and reduced refractive index
Godinho, V; Caballero-Hernandez, J; Jamon, D; Rojas, TC; Schierholz, R; Garcia-Lopez, J; Ferrer, FJ; Fernandez, ANanotechnology, 24 (2013) 275604 DOI: 10.1088/0957-4484/24/27/275604
Abstract
A new approach is presented to produce amorphous porous silicon coatings (a-pSi) with closed porosity by magnetron sputtering of a silicon target. It is shown how the use of He as the process gas at moderated power (50–150 W RF) promotes the formation of closed nanometric pores during the growth of the silicon films. The use of oblique-angle deposition demonstrates the possibility of aligning and orientating the pores in one direction. The control of the deposition power allows the control of the pore size distribution. The films have been characterized by a variety of techniques, including scanning and transmission electron microscopy, electron energy loss spectroscopy, Rutherford back scattering and x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, showing the incorporation of He into the films (most probably inside the closed pores) and limited surface oxidation of the silicon coating. The ellipsometry measurements show a significant decrease in the refractive index of porous coatings (n500 nm = 3.75) in comparison to dense coatings (n500 nm = 4.75). The capability of the method to prepare coatings with a tailored refractive index is therefore demonstrated. The versatility of the methodology is shown in this paper by preparing intrinsic or doped silicon and also depositing (under DC or RF discharge) a-pSi films on a variety of substrates, including flexible materials, with good chemical and mechanical stability. The fabrication of multilayers of silicon films of controlled refractive index in a simple (one-target chamber) deposition methodology is also presented.
Julio, 2013 · DOI: 10.1088/0957-4484/24/27/275604
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Cyclohexane photocatalytic oxidation on Pt/TiO2 catalysts
Murcia, JJ; Hidalgo, MC; Navio, JA; Vaiano, V; Sannino, D; Ciambelli, PCatalysis Today, 209 (2013) 164-169 DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2012.11.018
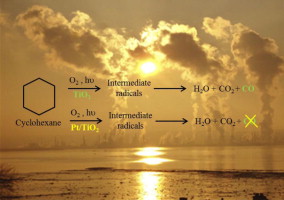
Abstract
Gas-solid heterogeneous photocatalytic oxidation (PCO) of cyclohexane in humidified air over TiO2 and Pt/TiO2 catalyst was studied.
Pt/TiO2 photocatalysts were synthesized by photodeposition method at different Pt loadings (0.5–2 wt.%). The addition of 0.5 wt.% Pt does not significantly modify the TiO2 properties. The increase in Pt loading induces to an aggregation of metallic particles on TiO2 surface.
The cyclohexane PCO was performed in a fluidized bed photoreactor at 60 and 100 °C. Pure TiO2 was more active than 1 and 2 wt.% Pt/TiO2 samples at 60 °C. Nevertheless, the conversion level increases with temperature on Pt/TiO2 photocatalysts. The cyclohexane was mineralized into CO2, water and low amount of CO. A beneficial effect of Pt addition was found, since total CO2 selectivity was obtained. The Pt/TiO2 photocatalysts prepared by photodeposition provide the total cyclohexane PCO without CO production. Photocatalysts deactivation was not observed in any performed test. Evidence of an opportune tuning of temperature is highlighted.
Junio, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2012.11.018
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Exploring the benefits of depositing hard TiN thin films by non-reactive magnetron sputtering
Martinez-Martinez, D; Lopez-Cartes, C; Fernandez, A; Sanchez-Lopez, JCApplied Surface Science, 275 (2013) 121-126 DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.01.098
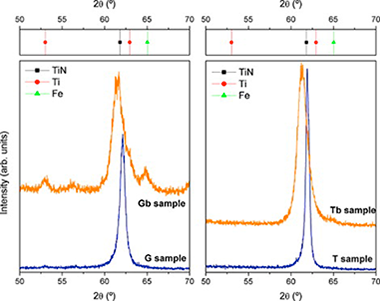
Abstract
The aim of this paper is to compare the mechanical and tribological properties of TiN coatings prepared in a conventional magnetron sputtering chamber according to two different routes: the usual reactive sputtering of a Ti target in an Ar/N2 atmosphere vs. the comparatively more simple sputtering of a TiN target in a pure Ar atmosphere. Improved properties in term of hardness and wear rates were obtained for films prepared by non-reactive sputtering route, due to the lower presence of oxynitride species and larger crystalline domain size. Additionally, a significant hardness enhancement (up to 45 GPa) is obtained when a −100 V d.c. bias is applied during growth. This behaviour is explained by non-columnar growth and small grain size induced by effective ion bombarding. These results demonstrate that non-reactive sputtering of TiN target appears a simple and efficient method to prepare hard wear-resistant TiN films.
Junio, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.01.098
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Evaluation of rare earth on layered silicates under subcritical conditions: Effect of the framework and interlayer space composition
Chain, P; Cota, A; El Mrabet, S; Pavon, E; Pazos, MC; Alba, MDChemical Geology, 347 (2013) 208-216 DOI: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2013.03.006
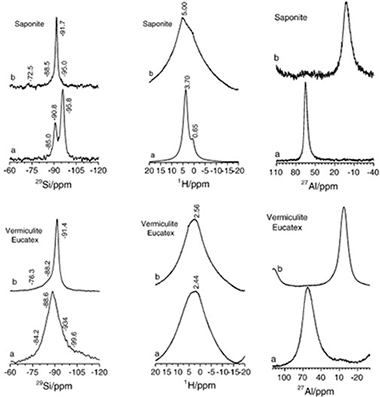
Abstract
Clay-based minerals are considered to be an important component in backfill barriers due to both their ability to seal and adsorb radioactive waste and to interact chemically with it under subcritical conditions. Herein, we describe a systematic study of the properties of layered silicates that could affect their hydrothermal reactivity, namely type of layers, octahedral occupancy, origin and total amount of the layer charge, and nature of the interlayer cation. The silicates studied were selected on the basis of their different characteristics associated with these properties and were treated hydrothermally at 300 °C for 48 h in a 7.3 · 10− 2 M Lu(NO3)3 · 3.6H2O solution. The final products were analyzed by X-ray diffraction and solid-state NMR spectroscopy. All the layered silicates studied were found to be able to generate a Lu2Si2O7 phase after hydrothermal treatment under subcritical conditions, thereby confirming the participation of a chemical mechanism of the clay barrier generating phases being stables with temperature and pH conditions. However, the extent of this reaction depends to a large extent on the physicochemical properties of the framework and the interlayer space composition, such as the presence or absence of an octahedral sheet, the degree of occupancy of this sheet, and the origin and total layer charge. Therefore, this study allows tuning the clay mineral framework characteristic that favors the rare earth cations (as trivalent actinide simulator) immobilization.
Junio, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2013.03.006
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Selective UV Reflecting Mirrors Based on Nanoparticle Multilayers
Smirnov, JRC; Calvo, ME; Miguez, HAdvanced Functional Materials, 23 (2013) 2805-2811 DOI: 10.1002/adfm.201202587
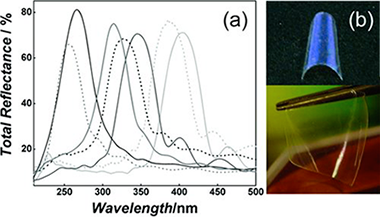
Abstract
A new type of nanostructured selective ultraviolet (UV) reflecting mirror is presented. Periodic porous multilayers with photonic crystal properties are built by spin-coating-assisted layer-by-layer deposition of colloidal suspensions of nanoparticles of ZrO2 and SiO2 (electronic band gap at λ < 220 nm). These optical filters are designed to block well-defined wavelength ranges of the UVA, UVB, and UVC regions of the electromagnetic spectrum while preserving transparency in the visible. The shielding against those spectral regions arises exclusively from optical interference phenomena and depends only on the number of stacked layers and the refractive index contrast between them. In addition, it is shown that the accessible pore network of the as-deposited multilayer allows preparing thin, flexible, self-standing, transferable, and adaptable selective UV filters by polymer infiltration, without significantly losing reflectance intensity, i.e., preserving the dielectric contrast. These films offer a degree of protection comparable to that of traditional ones, without any foreseeable unwanted secondary effects, such as photodegradation, increase of local temperature or, as is the case for organic absorbers, generation of free radicals, all of which are caused by light absorption.
Junio, 2013 · DOI: 10.1002/adfm.201202587
Role of Looping-Calcination Conditions on Self-Reactivation of Thermally Pretreated CO2 Sorbents Based on CaO
Valverde, JM; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perejon, A; Perez-Maqueda, LAEnergy & Fuels, 27 (2013) 3373-3384 DOI: 10.1021/ef400480j
Abstract
The conversion of thermally pretreated CaO along successive carbonation/calcination cycles has been investigated, as affected by looping-calcination conditions, by means of Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA). Sorbent samples have been subjected in situ to a thermal preheating program based on Constant Rate Thermal Analysis (CRTA) by virtue of which decarbonation is carried out at a low controlled rate, which is able to promote self-reactivation in the first carbonation/calcination cycles. Our observations support a pore-skeleton model according to which solid-state diffusion in the first carbonation stages, which is enhanced by thermal pretreatment, gives rise to a soft skeleton with increased surface area. Yet, the results show that self-reactivation is hindered as looping-calcination conditions are harshened. Increasing the looping-calcination temperature and/or the looping calcination time period favors sintering of the soft skeleton and eventually self-reactivation is precluded. A model is developed that retrieves the main features of multicyclic conversion of thermally pretreated sorbents in the first cycles based on the balance between surface area gain due to promoted solid-state diffusion carbonation and surface area loss due to sintering of the soft skeleton in the looping-calcination stage, which can be useful to investigate the critical looping-calcination conditions that nullify self-reactivation. The proposed model allows envisaging the behavior of the sorbent performance as a function of the pretreatment conditions.
Junio, 2013 · DOI: 10.1021/ef400480j
Reactividad de Sólidos
Direct mechanosynthesis of pure BiFeO3 perovskite nanoparticles: reaction mechanism
Perejon, A; Murafa, N; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Criado, JM; Subrt, J; Dianez, MJ; Perez-Maqueda, LAJournal of Materials Chemistry C, 1 (2013) 3551-3562 DOI: 10.1039/C3TC30446A
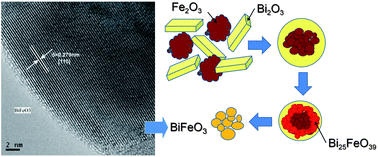
Abstract
In this work, a mechanochemical procedure is proposed as a simple and fast method to synthesize the pure BiFeO3 perovskite phase as a nanostructured material without the need for purification treatments, while the mechanochemical reaction mechanism has been investigated and correlated with that of the conventional solid-state reaction. Thus, different milling conditions have been used as a tool for tailoring the crystallite size of the resulting BiFeO3 nanoparticles. The materials prepared by the mechanochemical reaction could be annealed or sintered without the formation of undesirable phases. Both the ferroelectric and ferromagnetic transitions were observed by DSC. Finally, the dielectric constants of the prepared material at different frequencies as a function of the temperature have been measured, showing that the material is clearly an isolator below 200 °C, characteristic of a high quality BiFeO3 material.
Junio, 2013 · DOI: 10.1039/C3TC30446A
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Synthesis and characterization of kanemite from fluoride-containing media: Influence of the alkali cation
Corredor, JI; Cota, A; Pavon, E; Alba, MDAmerican Mineralogist, 98 (2013) 1000-1007 DOI: 10.2138/am.2013.4372
Abstract
Kanemite belongs to the group of naturally occurring sodium silicate minerals that was first found in Kanem, at the edge of the Lake Chad, and has been synthesized in different ways from NaOH-SiO2 mixtures and used as precursor for the design of microporous and mesoporous materials. The fluoride route to the synthesis of microporous materials is based on the substitution of OH− anions by fluoride anions, which may subsequently also play a mineralizing role, and gives rise to materials with higher hydrophobicity and thermal and hydrothermal stability. Moreover, F− plays an important role in the incorporation of framework heteroatoms, thereby affecting the activity of the final material. The aim of this study was to synthesize fluorokanemite using different synthetic routes and different F− source. The final product was characterized by a combination of methods that provided information regarding the incorporation of fluorine into the framework and the short- and long-range structural order of the fluorosilicate. Kanemite with water content close to ideal was obtained in all cases. The washing process was found to have no effect in the long- or short-range structural order of the layer framework, although it did affect the structure of the cation in the interlayer space of kanemite. The mineralizing agent therefore appears to be the key to the synthesis. Furthermore, it governs the resulting kanemite structure by controlling the formation of hydrogen bonds in the framework, and therefore the degree of lamellar structure condensation.
Mayo, 2013 · DOI: 10.2138/am.2013.4372
Materiales Avanzados
Estudio in-situ de la transformación térmica de limonita utilizada como pigmento procedente de Perú
Romero-Gomez, P; Gonzalez, JC; Bustamante, A; Ruiz-Conde, A; Sanchez-Soto, PJBoletin de la Sociedad Española de Cerámica y Vidrio, 52 (2013) 127-131 DOI: 10.3989/cyv.162013
Abstract
Se ha realizado un estudio cinético de la transformación térmica de limonita [FeO(OH).nH2O] mediante análisis térmico gravimétrico (TGA), termodifracción de rayos X (DRX) y espectroscopía μ-Raman. La muestra estudiada fue extraída de un yacimiento en el distrito de Taraco, provincia de Huancané, Región de Puno (Perú). La técnica DRX en polvo identificó la fase goetita como el principal componente mineralógico, además de cuarzo. La muestra se sometió a un tratamiento térmico
in-situ en un intervalo de temperaturas de 100 a 500 °C en atmósfera de aire e inerte (nitrógeno) y se estudió por DRX. Los resultados han mostrado que la fase goetita permanece estable desde la temperatura ambiente hasta 200 °C. A partir de los 250 °C se produce una transformación de fase α-FeO(OH)→α-Fe2O3
con un cambio cromático, es decir, el paso de la fase
hidroxilada goetita (amarillo) a la fase oxidada hematites (rojo) con una pérdida de peso de un 8 %, teniendo como evidencia la evolución de los perfiles de difracción y los resultados de ATG. Los espectros μ-Raman del tratamiento térmico in-situ corroboran que se produce también una transición de fase a la temperatura de 290 °C a través de la transformación de las bandas Raman características de la fase goetita hacia la fase hematites en el rango de frecuencias de 200 a 1800cm-1.
Mayo, 2013 · DOI: 10.3989/cyv.162013
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Solution Properties of the System ZrSiO4–HfSiO4: A Computational and Experimental Study
Cota, Agustin; Burton, Benjamin P.; Chain, Pablo; Pavon, Esperanza; Alba, Maria D.Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 117 (2013) 10013-10019 DOI: 10.1021/jp401539g

Abstract
ZrSiO4 and HfSiO4 are of considerable interest because of their low thermal expansions, thermal conductivities, and the optical properties of HfSiO4. In addition, silicate phases of both are studied as model radioactive waste disposal materials. Previous first principles calculations reported near ideal mixing in the Zr1–xHfxSiO4 system, with a very weak propensity for phase separation. Density functional theory (DFT)/cluster-expansion first principles calculations presented in this work indicate near ideal mixing with a very weak propensity for ordering. Zr1–xHfxSiO4 samples (x = 0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, and 1.0) were synthesized from intimate stoichiometric mixtures of constituent-oxides and annealing at 1823 K for 20 days in a platinum crucible. Samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD; Rietveld analysis) and 29Si MAS NMR. The XRD data exhibited a pronounced negative deviation from Vegard’s law in the excess volume of mixing, and the 29Si MAS NMR spectra also suggest nonideal mixing. Given the very weak energetics that favor cation ordering, it is clear that there must be some other cause(s) for the observed deviations from ideal mixing behavior.
Mayo, 2013 · DOI: 10.1021/jp401539g
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Resonant Photocurrent Generation in Dye-Sensitized Periodically Nanostructured Photoconductors by Optical Field Confinement Effects
Anaya, M; Calvo, ME; Luque-Raigon, JM; Miguez, HJournal of the American Chemical Society, 135 (2013) 7803-7806 DOI: 10.1021/ja401096k
Abstract
Herein we show experimental evidence of resonant photocurrent generation in dye-sensitized periodically nanostructured photoconductors, which is achieved by spectral matching of the sensitizer absorption band to different types of localized photon modes present in either periodic or broken symmetry structures. Results are explained in terms of the calculated spatial distribution of the electric field intensity within the configurations under analysis.
Mayo, 2013 · DOI: 10.1021/ja401096k
Materiales Coloidales
Energy transfer efficiency in YF3 nanocrystals: Quantifying the Yb3+ to Tm3+ infrared dynamics
Quintanilla, M; Nuñez, NO; Cantelar, E; Ocaña, M; Cussó, FJournal of Applied Physics, 113 (2013) 174308 (6 pages) DOI: 10.1063/1.4803540
Abstract
In this work, we report on the determination of the infrared Yb3+ → Tm3+ energy transfer efficiency in YF3:Yb3+/Tm3+ nanocrystals through the study of Yb3+ dynamics. The obtained results are compared to those previously reported in macrocrystals to analyze possible changes related to size reduction. Luminescence lifetimes are much shorter in the nanoparticles than in bulk samples, a behavior that can be related to Yb3+ → Yb3+ migration and the enhanced surface/volume ratio of the nanoparticles. On the other hand, Yb3+ → Tm3+ energy transfer macroparameter remains unaltered, demonstrating that spectroscopic intrinsic parameters such as radiative and non-radiative probabilities are not affected by size reduction. Finally, a formula that describes Yb3+ lifetime dependence with Yb3+ and Tm3+ concentration is proposed, considering both the effects produced by migration between Yb3+ ions and energy transfer from Yb3+ to Tm3+ ions.
Mayo, 2013 · DOI: 10.1063/1.4803540
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Combined reactive magnetron sputtering and plasma decomposition of non-volatile precursors to grow luminescent thin films
Gil-Rostra, J; Yubero, F; Ferrer, FJ; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARSurface and Coatings Technology, 222 (2013) 144-150 DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2013.02.016
Abstract
This paper reports a new procedure of the preparation of mixed oxide thin films that combines the traditional reactive magnetron sputtering deposition with the plasma activated decomposition of non-volatile precursors sublimated by means of an effusion cell. The possibilities of this new experimental procedure are illustrated with the preparation of luminescent thin films consisting of rare earth (RE) cations (Tb3 +, Eu3 +) incorporated in an oxide matrix (TiO2 and SiO2). The oxide matrix component was supplied by reactive magnetron sputtering from metallic Ti or Si targets, while the RE cation was dosed by sublimation of acetylacetonate compounds of the selected elements. The obtained mixed oxide thin films have been fully characterized by different methods and their luminescent properties studied as a function of the matrix type and concentration of the RE element present in the film. The advantages of the synthesis procedure are highlighted with regard to its versatility and the possibility of tailoring the properties of complex luminescent materials.
Mayo, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2013.02.016
Reactividad de Sólidos
Effect of sintering time on the microstructure and mechanical properties of (Ti,Ta)(C,N)-based cermets
Chicardi, E; Torres, Y; Cordoba, JM; Sayagues, MJ; Rodriguez, JA; Gotor, FJInternational Journal of Refractory Metals & Hard Materials, 38 (2013) 73-80 DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2013.01.001
Abstract
Complete solid-solution cermets based on titanium–tantalum carbonitride using a starting nominal composition with 80 wt.% of (Ti0.8Ta0.2)(C0.5N0.5) and 20 wt.% of Co were performed by pressure-less sintering at 1550 °C for different times (from 0 to 180 min) in an inert atmosphere. Chemical and phase analyses were conducted using X-ray diffraction (XRD), elemental analysis and energy dispersive X-ray spectrometry (EDX). The binder mean free path and the contiguity of the carbonitride particles were used to rationalise the microstructural effects of the mechanical behaviour. Mechanical characterisation included determining the Vickers hardness, the fracture toughness (conventional indentation microfractures, IM), the dynamic Young's modulus (ultrasonic technique), the biaxial strength (ball on three ball) and a detailed fractographic examination. Finally, the experimental findings were combined with a theoretical fracture mechanics analysis to estimate the critical processing flaw sizes. Binder-less carbonitride clusters, pores and coarse carbonitride grains were the main defects observed and were responsible for the fractures.
Mayo, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2013.01.001
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Steam reforming of methanol over supported Ni and Ni–Sn nanoparticles
Bobadilla, LF; Palma, S; Ivanova, S; Dominguez, MI; Romero-Sarria, F; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAInternational Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 38 (2013) 6646-6656 DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.03.143

Abstract
The influence of the synthesis method and Sn addition on Ni/CeO2–MgO–Al2O3 catalyst is correlated to its catalytic behavior in the reaction of methanol steam reforming. The catalysts prepared by impregnation method are compared to samples obtained by deposition of previously obtained nanoparticles by the polyol method. X-ray diffraction (XRD), specific surface area measurements and H2-temperature programmed reduction (TPR) were used to characterize the catalysts. The differences of the structure, phase transformation and reduction behavior are discussed and related to the catalytic performance of the samples as well as the nature of the carbonaceous deposits formed during the reaction.
Mayo, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.03.143
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma - Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura - Tribología y Protección de Superficies
Structure and tribological properties of MoCN-Ag coatings in the temperature range of 25–700 °C
Shtansky, DV; Bondarev, AV; Kiryukhantsev-Korneev, PV; Rojas, TC; Godinho, V; Fernandez, AApplied Surface Science, 273 (2013) 408-414 DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.02.055
Abstract
The preparation of hard coatings with low friction coefficient over a wide temperature range is still a challenge for the tribological community. The development of new nanocomposite materials consisting of different metal-ceramic phases, each of which exhibiting self-lubricating characteristics at different temperatures, may help to solve this problem. We report on the structure and tribological properties of MoCN-Ag coatings deposited by magnetron co-sputtering of Mo and C (graphite) targets and simultaneous sputtering of an Ag target either in pure nitrogen or in a gaseous mixture of Ar + N2. The structure and elemental composition of the coatings were studied by means of X-ray diffraction, scanning and transmission electron microscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, energy dispersive spectroscopy, Raman spectroscopy, and glow discharge optical emission spectroscopy. The tribological properties of the coatings against an Al2O3 ball were investigated first at discrete temperatures of 25, 500, and 700 °C, and then during continuous heating in the temperature range of 25–700 °C. The coating structure and their respective wear tracks were also examined to elucidate their phase transformations during heat treatments. The lowest friction coefficients (<0.4) were observed in the temperature ranges of 25–100 °C and 400–700 °C and can be explained by the presence of a free amorphous carbon phase, which served as a lubricant at low temperatures, and by a positive role of silver and two phases forming at elevated temperatures, molybdenum oxide and silver molybdate, which provided lubrication above 400 °C. In the temperature range between 100 and 400 °C, the friction coefficient was relatively high. This problem is to be addressed in future works.
Mayo, 2013 · DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.02.055
- ‹ anterior
- 27 of 37
- siguiente ›














