Artículos SCI
2015
2015
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Ionic liquid immobilization on carbon nanofibers and zeolites: Catalyst design for the liquid-phase toluene chlorination
Losch, Pit; Martinez Pascual, Antonio; Boltz, Marilyne; Ivanova, Svetlana; Louis, Benoit; Montilla, Francisco; Antonio Odriozola, JoseComptes Rendus Chimie, 18 (2015) 324-329
Show abstract ▽
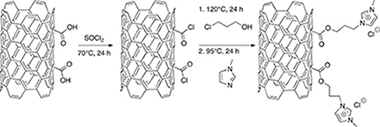
The environmental-friendly chlorination reaction of toluene by trichloroisocyanuric acid (TCCA, C3N3O3Cl3) was investigated applying immobilized ionic liquids (ILs) on different supports. Ionic liquids were grafted either on carbon nanofibers (CNF) or encapsulated in zeolites. Their influence on the chlorination activity as well as on the selectivity in different chlorinated products was studied. An unusually high selectivity toward meta-chlorotoluene was achieved, up to 36%. Hence, the selectivity could be tuned to produce either expected ortho-/para-chlorotoluene or meta-chlorotoluene with a proper support choice.
Marzo, 2015 | DOI: 10.1016/j.crci.2014.06.006
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Nanocolumnar coatings with selective behavior towards osteoblast and Staphylococcus aureus proliferation
Izquierdo-Barba, Isabel; Miguel Garcia-Martin, Jose; Alvarez, Rafael; Palmero, Alberto; Esteban, Jaime; Perez-Jorge, Concepcion; Arcos, Daniel; Vallet-Regi, MariaActa Biomaterialia, 15 (2015) 20-28
Show abstract ▽
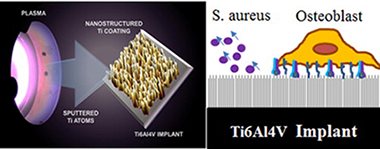
Bacterial colonization and biofilm formation on orthopedic implants is one of the worst scenarios in orthopedic surgery, in terms of both patient prognosis and healthcare costs. Tailoring the surfaces of implants at the nanoscale to actively promote bone bonding while avoiding bacterial colonization represents an interesting challenge to achieving better clinical outcomes. Herein, a Ti6Al4V alloy of medical grade has been coated with Ti nanostructures employing the glancing angle deposition technique by magnetron sputtering. The resulting surfaces have a high density of nanocolumnar structures, which exhibit strongly impaired bacterial adhesion that inhibits biofilm formation, while osteoblasts exhibit good cell response with similar behavior to the initial substrates. These results are discussed on the basis of a "lotus leaf effect" induced by the surface nanostructures and the different sizes and biological characteristics of osteoblasts and Staphylococcus aureus.
Marzo, 2015 | DOI: 10.1016/j.actbio.2014.12.023
Materiales Avanzados
Valorization and inertization of galvanic sludge waste in clay bricks
Perez-Villarejo, L; Martinez-Martinez, S; Carrasco-Hurtado, B; Eliche-Quesada, D; Urena-Nieto, C; Sanchez-Soto, PJApplied Clay Science, 105-106 (2015) 89-99
Show abstract ▽
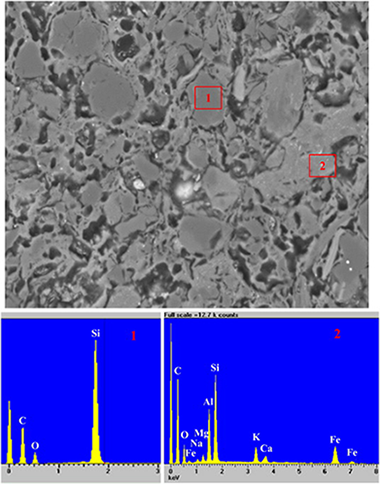
Galvanic sludge wastes (GSW) are produced by the physico-chemical treatments of wastewater generated by electroplating plants. These materials have a significant potential for the production of clay ceramic bricks. This paper focuses on the viability of the inertization of heavy metals from GSW mixed with clays. The original materials were obtained by mixing three types of raw clay (red, yellow and black) in equal parts with GSW. These mixtures were characterized by XRD, XRF, and chemical elemental analysis CHNS. The dosage of GSW in the clay–GSW bricks was up to 5 wt.%. The bricks were then manufactured using conventional processes. The influence of the amount of GSW was evaluated after firing the clay–GSW composites at 950 °C for 1 h. The engineering properties of the fired samples, such as density, water absorption, open porosity, water suction and compressive strength, with and without the GSW, were determined. The incorporation of GSW into the clay mix clearly decreased the linear shrinkage and bulk density of the bricks in comparison with the fired clay used as a control. These GSW–clay composites also showed lower open porosity. According to the results obtained for the bulk density of the bricks, samples with GSW addition showed slightly lower values of open porosity than clay bodies, indicating that the GSW–clay samples had slightly higher closed porosity values. This was also shown by SEM. The open porosity, SEM and pore size distribution tests indicated that the porosity generated by the addition of GSW was mainly closed and, therefore, GSW bricks had excellent mechanical properties. The environmental risks of the incorporation of GSW, rich in heavy metals (Cr, Zn, Ni and others), to a clay matrix were evaluated by leaching tests of the fired products. The results indicated a successful inertization of the pollutants.
Marzo, 2015 | DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2014.12.022
Reactividad de Sólidos
Nanoindentation of (Ti,Ta)(C,N)-Co cermets prepared by methods of mechanochemistry
Hvizdos, Pavol; Balko, Jan; Manuel Cordoba, Jose; Chicardi, ErnestoInternational Journal of Refractory Metals & Hard Materials, 49 (2015) 219-224
Show abstract ▽
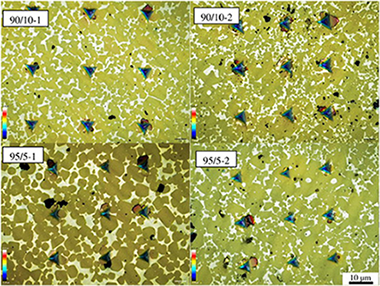
Four materials TixTa(1 - x)C(0.5)N(0.5)-20%Co of two chemical compositions (x = 0.9 and 0.95) and two high energy milling methods (one stage and two stage milling) have been prepared. Nano-hardness and elastic modulus for microstructure as a whole and for individual constituent phases (matrix and carbide grains) were obtained by instrumented indentation. Individual targeted indentations as well as grid nanoindentation technique were used to discern the individual constituents' properties. Maximum loads of 20 mN for individual phases and 300 mN for composite microstructure were applied. Materials with higher amount of Ti had larger grains but the milling procedure had stronger influence on the grain size. The two step milling resulted in finer microstructures but with a much wider grain size distribution. Final composite mechanical properties, however, were very similar. Hardness and indentation elasticity modulus of all materials were comparable within the errors of measurement.
Marzo, 2015 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2014.07.038
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Sunlight Absorption Engineering for Thermophotovoltaics: Contributions from the Optical Design
Miguez, HChemSusChem, 8 (2015) 786-788
Show abstract ▽
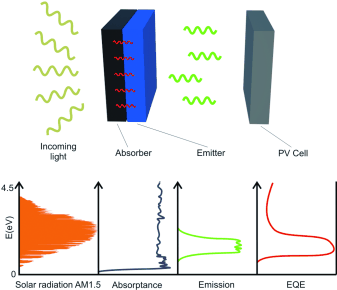
Nowadays, solar thermophotovoltaic systems constitute a platform in which sophisticated optical material designs are put into practice with the aim of achieving the long sought after dream of developing an efficient energy conversion device based on this concept. Recent advances demonstrate that higher efficiencies are at reach using photonic nanostructures amenable to mass production and scale-up.
Marzo, 2015 | DOI: 10.1002/cssc.201403361
- ‹ anterior
- 254 of 420
- siguiente ›














