Artículos SCI
2015
2015
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Long-Chain Polyhydroxyesters from Natural Occurring Aleuritic Acid as Potential Material for Food Packaging
Benitez, JJ; Heredia-Guerrero, JA; Guzman-Puyol, S; Dominguez, E; Heredia, ASoft Materials, 13 (2015) 5-11
Show abstract ▽
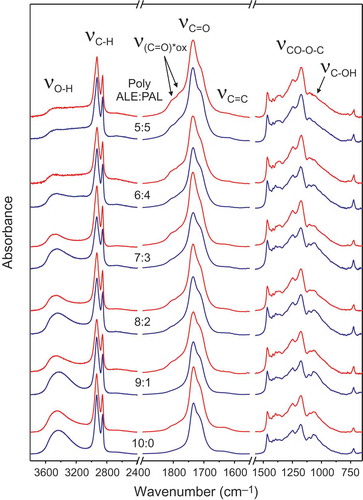
Fatty polyhydroxyesters (C≥16) are present in nature as barrier polymers like cutin in some protective tissues of higher plants. The mimicry of these biopolymers is regarded as a strategy to design nontoxic and fully biodegradable food packaging films and coatings. To obtain cutin inspired materials we have used a natural occurring polyhydroxylated monomer like aleuritic (9,10,16-trihydroxypalmitic) acid and a direct and scalable synthesis route consisting in the noncatalyzed melt-condensation polymerization in air. To reduce the number of hydroxyl groups and to increase hydrophobicity, palmitic acid has been used as a capping agent. Aleuritic-palmitic polyhydroxyesteres films have been obtained and characterized.
Enero, 2015 | DOI: 10.1080/1539445X.2014.993476
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Biotribological behavior of Ag–ZrCxN1−x coatings against UHMWPE for joint prostheses devices
Calderon, SV; Sanchez-Lopez, JC; Cavaleiro, A; Carvalho, SJournal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 41 (2015) 83-91
Show abstract ▽
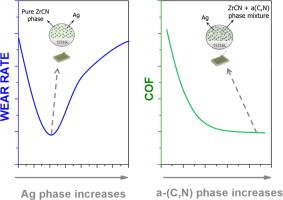
This study aims to evaluate the structural, mechanical and tribological properties of zirconium carbonitrides (ZrCxN1−x) coatings with embedded silver nanoparticles, produced with the intention of achieving a material with enhanced multi-functional properties, including mechanical strength, corrosion resistance, tribological performance and antibacterial behavior suitable for their use in joint prostheses. The coatings were deposited by direct current (DC) reactive magnetron sputtering onto 316 L stainless steel, changing the silver content from 0 to 20 at% by modifying the current density applied to the targets. Different nitrogen and acetylene gas fluxes were used as reactive gases. The coatings revealed different mixtures of crystalline ZrCxN1−x, silver nanoparticles and amorphous carbon phases. The hardness of the films was found to be mainly controlled by the ratio between the hard (ZrCxN1−x) and soft (Ag and amorphous carbon) phases in the films, fluctuating between 7.4 and 20.4 GPa. The coefficient of friction, measured against ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) in Hank’s balanced salt solution with 10 g L−1albumin, is governed by the surface roughness and hardness. The UHMWPE wear rates were in the same order of magnitude (between 1.4 and 2.0×10−6 mm3 N−1 m−1), justified by the effect of the protective layer of albumin formed during the tests. The small differences were due to the hydrophobic/hydrophilic character of the surface, as well as to the silver content.
Enero, 2015 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2014.09.028
Reactividad de Sólidos
Uniform, luminescent Eu: LuF3 nanoparticles
Becerro, AI; Gonzalez-Mancebo, D; Ocana, MJournal of Nanoparticle Research, 17 (2015) 58
Show abstract ▽
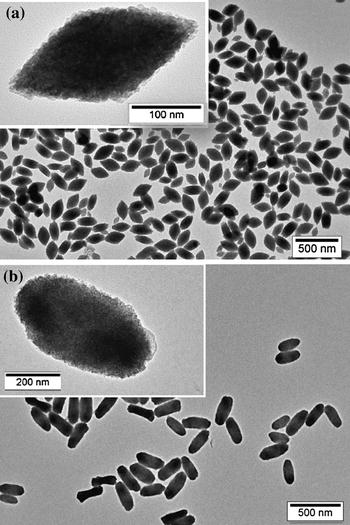
A simple procedure for the synthesis of orthorhombic, uniform, LuF3 particles with two different morphologies (rhombus- and cocoon-like) and nanometer and sub-micrometer size, respectively, is reported. The method consists in the aging, at 120 °C for 2 h, a solution containing [BMIM]BF4 ionic liquid (0.5 mL) and lutetium acetate (in the case of the rhombi) or lutetium nitrate (in the case of the cocoons) (0.02 M) in ethylene glycol (total volume 10 mL). This synthesis method was also adequate for the synthesis of Eu3+-doped LuF3 particles of both morphologies, whose luminescence properties were investigated in detail. The experimental observations reported herein suggest that these materials are suitable phosphors for optoelectronic as well as in vitro biotechnological applications.
Enero, 2015 | DOI: 10.1007/s11051-015-2874-z
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Effect of magnesium and titanium on the cathodic behaviour of aluminium in nitric acid
Garcia-Garcia, FJ, Chiu, TY, Skeldon, P, Thompson, GESurface and Interface Analysis, 47 (2015) 30-36
Show abstract ▽
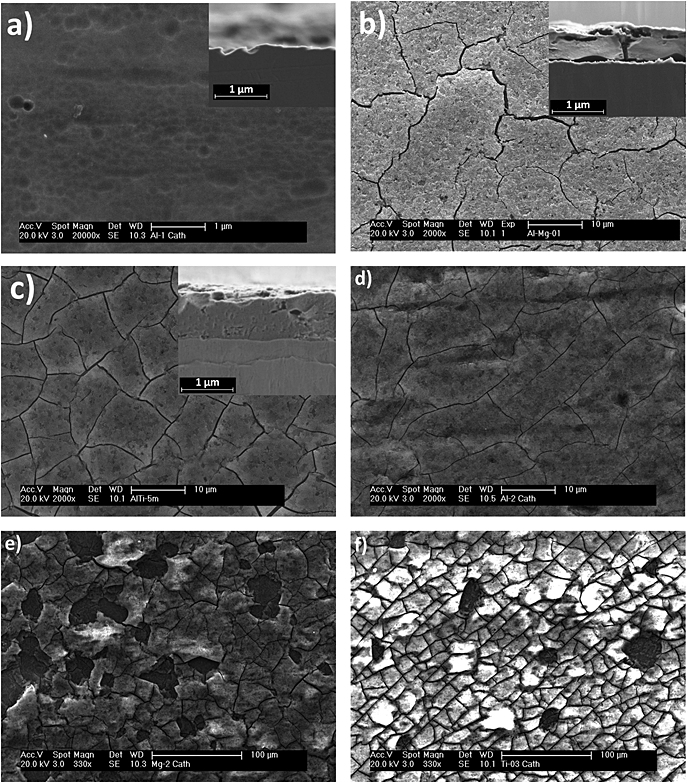

Cathodic polarization of aluminium and Al-0.18wt.%Mg and Al-0.08wt.% Ti alloys in 0.24moldm(-3) nitric acid solution at 38 degrees C has been employed to assist understanding of the roles of alloying elements in electrograining. The findings indicate that additions of magnesium and titanium to aluminium accelerate the corrosion of the substrate under the alkalization caused by the cathodic reactions. The accelerated dissolution and the consequent formation of hydrated alumina result in a decreased net cathodic current density in potentiostatic and potentiodynamic polarization conditions relative to the behaviour of aluminium.
Enero, 2015 | DOI: 10.1002/sia.5640
Reactividad de Sólidos
New Insights on the Kinetic Analysis of Isothermal Data: The Independence of the Activation Energy from the Assumed Kinetic Model
Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perejon, A; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Criado, JMEnergy & Fuels, 29 (2015) 392-397
Show abstract ▽
Isothermal experiments are widely employed to study the kinetics of solid-state reactions or processes to extract essential kinetic information needed for modeling the processes at an industrial scale. The kinetic analysis of isothermal data requires finding or assuming a kinetic function that can properly fit the evolution of the reaction rate with time, so that the resulting parameters, i.e., the activation energy and pre-exponential factor, can be considered reliable. In the present work, we demonstrate using both simulated and experimental data that the kinetic analysis of a set of isothermal plots obtained at different temperatures, considering a single-step solid-state reaction, necessarily leads to the real activation energy, regardless the mathematical function selected for performing the kinetic analysis. This makes irrelevant the election of the kinetic function used to fit the experimental data and greatly facilitates the estimation of the activation energy for any single process.
Enero, 2015 | DOI: 10.1021/ef502269r
- ‹ anterior
- 260 of 420
- siguiente ›














