Artículos SCI
2014
2014
Reactividad de Sólidos
The Mitigation Effect of Synthetic Polymers on Initiation Reactivity of CL-20: Physical Models and Chemical Pathways of Thermolysis
Yan, QL; Zeman, S; Jimenez, PES; Zhang, TL; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Elbeih, AJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 118 (2014) 22881-22895
Show abstract ▽
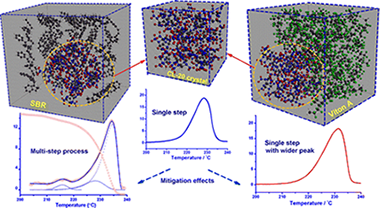
In this paper, the thermal decomposition physical models of different CL-20 polymorph crystals and their polymer bonded explosives (PBXs) bonded by polymeric matrices using polyisobutylene (PIB), acrylonitrile butadiene rubber (NBR), styrene butadiene rubber (SBR), Viton A, and Fluorel binders are obtained and used to predict the temperature profiles of constant rate decomposition. The physical models are further supported by the detailed decomposition pathways simulated by a reactive molecular dynamics (ReaxFF-lg) code. It has been shown that both ε-CL-20 and α-CL-20 decompose in the form of γ-CL-20, resulting in close activation energy (169 kJ mol–1) and physical model (first-order autoaccelerated model, AC1). Fluoropolymers could change the decomposition mechanism of ε-CL-20 from the “first-order autocatalytic” model to a “three-dimensional nucleation and growth” model (A3), while the polymer matrices of Formex P1, Semtex, and C4 could change ε-CL-20 decomposition from a single-step process to a multistep one with different activation energies and physical models. Compared to fluoropolymers, PIB, SBR and NBR may make ε-CL-20 undergo more complete N–NO2 scission before collapse of the cage structure. This is likely the main reason why those polymer bases could greatly mitigate the decomposition process of ε-CL-20 from a single step to a multistep, resulting in lower impact sensitivity, whereas fluoropolymers have only a little effect on that. For ε-CL-20 and its PBXs, the impact sensitivity depends not only on the heat built-up period of their decomposition, but also on the probability of hotspot generation (defects in solid crystals and interfaces) especially when it decomposes in a solid state.
Octubre, 2014 | DOI: 10.1021/jp505955n
Reactividad de Sólidos
Single phase, electrically insulating, multiferroic La-substituted BiFeO3 prepared by mechanosynthesis
Perejon, A; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Criado, JM; de Paz, JR; Saez-Puche, R; Maso, N; West, ARJournal of Materials Chemistry C, 2 (2014) 8398-8411
Show abstract ▽
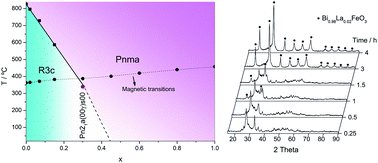
Single phase, electrically insulating samples of Bi1−xLaxFeO3 solid solutions have been prepared by mechanosynthesis over the whole compositional range for the first time. Lanthanum substitution influenced the kinetics of the mechanochemical reaction and crystallite size of the products. For 0 ≤ x ≤ 0.15, an increase in the La content produced a significant decrease in the weight-normalized cumulative kinetic energy required to obtain the final product and an increase in the resulting crystallite size. Larger La contents did not affect either the reactivity or the crystallite size. The effect of x on the structure has been identified. Samples in the ranges x ≤ 0.15 and x ≥ 0.45 gave single phase solid solutions with R3c and Pnma space groups, respectively, while for the intermediate range, a non-centrosymetric Pn21a(00γ)s00 super structure was obtained. For 0 ≤ x ≤ 0.30, differential scanning calorimetry showed two endothermic effects corresponding to the Néel temperature (TN, antiferromagnetic–paramagnetic transition) and the Curie temperature (TC, ferroelectric–paraelectric transition), demonstrating their multiferroic character. Compositions with a larger La content only showedTN. Dilatometric and permittivity measurements confirmed the results obtained by DSC for the ferroelectric–paraelectric transition. The composition dependence of TN and TC showed that, at low x, TN < TC, but a cross-over, or isoferroic transition occurred at x [[similar]] 0.28, when TN = TC = 386 °C. Ceramics with 0 ≤ x ≤ 0.15 were highly insulating at room temperature with a resistivity, extrapolated from the Arrhenius plots, of [[similar]] 7 × 1016 to 8 × 1014 Ω cm and an activation energy [[similar]] 1.14–1.20 eV. Magnetization of the samples improved with La substitution.
Octubre, 2014 | DOI: 10.1039/C4TC01426J
Reactividad de Sólidos
Hardness and flexural strength of single-walled carbon nanotube/alumina composites
Gallardo-Lopez, A; Poyato, R; Morales-Rodriguez, A; Fernandez-Serrano, A; Munoz, A; Dominguez-Rodriguez, AJournal of Materials Science, 20 (2014) 7116-7123
Show abstract ▽
This work adds new experimental facts on room temperature hardness and flexural strength of alumina and composites with 1, 2, 5 and 10 vol% single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWNT) with similar grain size. Monolithic Al2O3 and composites were spark plasma sintered (SPS) in identical conditions at 1300 A degrees C, achieving high density, submicrometric grain size and a reasonably homogeneous distribution of SWNT along grain boundaries for all compositions with residual agglomerates. Vickers hardness values comparable to monolithic alumina were obtained for composites with low (1 vol%) SWNT content, though they decreased for higher concentrations, attributed to the fact that SWNT constitute a softer phase. Three-point bending flexural strength also decreased with increasing SWNT content. Correlation between experimental results and microstructural analysis by electron microscopy indicates that although SWNT agglomerates have often been blamed for detrimental effects on the mechanical properties of these composites, they are not the main cause for the reported decay in flexural strength.
Octubre, 2014 | DOI: 10.1007/s10853-014-8419-5
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Multidirectional Light-Harvesting Enhancement in Dye Solar Cells by Surface Patterning
Lopez-Lopez, C; Colodrero, S; Jimenez-Solano, A; Lozano, G; Ortiz, R; Calvo, ME; Miguez, HAdvanced Optical Materials, 2 (2014) 879-884
Show abstract ▽
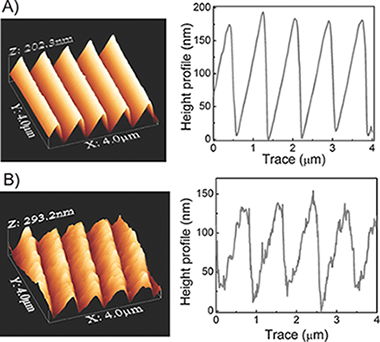
One dimensional gratings patterned on the surface of nanocrystalline titania electrodes are used as a light harvesting strategy to improve the overall performance of dye solar cells under both frontal and rear illumination conditions. A soft-lithography-based micromoulding approach is employed to replicate a periodic surface relief pattern onto the surface of the electrode, which is later sensitized with a dye. As the patterned surface acts as an optical grating both in reflection and transmission modes, its effect is to increase the light path of diffracted beams within the absorbing layer when it is irradiated either from the electrode or the counter electrode for a broad range of angles of incidence on each surface. Full optical and photovoltaic characterization demonstrates not only the optical quality of the patterned surfaces but also the multidirectional character of the enhancement of light harvesting and conversion efficiency. The approach herein presented thus permits to preserve the operation of the cell when irradiated from its two faces while increasing its overall power conversion efficiency. This feature is a key advantage over other light harvesting efficiency enhancing methods, such as the deposition of a back diffuse scattering layer, in which the performance of the cell under illumination from one of its sides is enlarged at the expense of reducing the output under reverse irradiation conditions.
Septiembre, 2014 | DOI: 10.1002/adom.201400160
Materiales para Bioingeniería y Regeneración Tisular
Reticulated bioactive scaffolds with improved textural properties for bone tissue engineering: Nanostructured surfaces and porosity
Ramiro-Gutierrez, ML; Will, J; Boccaccini, AR; Diaz-Cuenca, AJournal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A, 102 (2014) 2982-2992
Show abstract ▽
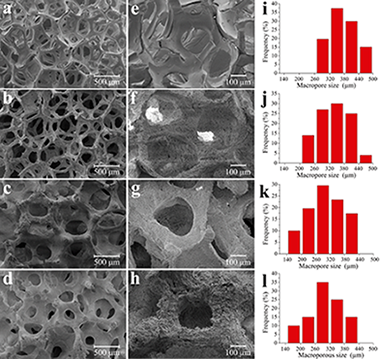
Organised nanoporous SBA-15 type silica precursor (SP) particulate material has been processed into three-dimensional macroporous, reticulated structures using a novel strategy consisting of blending increasing percentages of SP with a SiO2-CaO-P2O5 (80Si15Ca5P) mesoporous bioactive glass (MBG) sol. The procedure successfully produced consolidated and functionally competent open-cell scaffolds while preserving the nanoporous order of the SP. Scaffolds were prepared using four different (MBG)/(SP) ratios. These structures were then characterized using field emission gun scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD), nitrogen adsorption-desorption measurements, and compressive strength testing. Open-cell interconnected structures with dual macro (150-500 mu m) and nano (4-6 nm)-organised porosity were produced. Both the textural and mechanical properties were found to improve with increasing SBA-15 content. The in vitro bioactive response using simulated body fluid confirmed high reactivity for all prepared scaffolds. In addition, the SBA-15 containing scaffolds exhibited a superior ability to delay the pH-triggered lysozyme release with antibiotic activity. (C) 2013 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Septiembre, 2014 | DOI: 10.1002/jbm.a.34968
- ‹ anterior
- 267 of 420
- siguiente ›














