Artículos SCI
2014
2014
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Supported Co catalysts prepared as thin films by magnetron sputtering for sodium borohydride and ammonia borane hydrolysis
Paladini, M; Arzac, GM; Godinho, V; De Haro, MCJ; Fernandez, AApplied Catalysis B: Environmental, 158-159 (2014) 400-409
Show abstract ▽
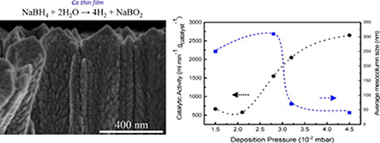
Supported Co catalysts were prepared for sodium borohydride and ammonia borane hydrolysis by magnetron sputtering for the first time under different conditions. Ni foam was selected as support. Deposition conditions (time, pressure, and power) were varied to improve catalytic activity. A decrease in deposition power from 200 to 50 W, leads to a decrease in crystallite and column size and a higher activity of catalysts. The increase in deposition pressure from 1.5 × 10−2 to 4.5 × 10−2 mbar produces same effect but in this case the enhancement in activity is higher because amorphous materials were obtained. The highest activity for SB hydrolysis was 2650 ml min−1 gcat−1 for the 50 W Co 4.5 (4 h) sample (Ea = 60 ± 2 kJ mol−1). For AB hydrolysis activity for the 50 W Co 3.2 (4 h) sample was similar. Durability of the thin films was tested for both reactions upon cycling (14 cycles). Diluted acid washing was effective to recover the activity for sodium borohydride reaction but not for ammonia borane hydrolysis. The strong Co–NH3 interactions explain the non-efficiency of the acid washing.
Octubre, 2014 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.04.047
Reactividad de Sólidos
Mechanochemically synthesized nanocrystalline Sb2S3 particles
Dutkova, E; Sayagues, MJ; Real, C; Zorkovska, A; Balaz, P; Satka, A; Kovac, J; Ficeriova, JActa Physica Polonica A, 126 (2014) 943-946
Show abstract ▽
Nanocrystalline Sb2S3 particles have been synthesized from Sb and S powders by high-energy milling in a planetary mill using argon protective atmosphere. X-ray diffraction, particle size analysis, scanning electron microscopy, energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy, electron diffraction, high resolution transmission electron microscopy, UV-VIS, and differential scanning calorimetry methods for characterization of the prepared particles were applied. The powder X-ray diffraction pattern shows that Sb2S3 nanocrystals belong to the orthorhombic phase with calculated crystallite size of about 36 nm. The nanocrystalline Sb2S3 particles are constituted by randomly distributed crystalline nanodomains (20 nm) and then these particles are forming aggregates. The monomodal distribution of Sb2S3 particles with the average hydrodynamic parameter 210 nm was obtained. The quantification of energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy analysis peaks give an atomic ratio of 2:3 for Sb:S. The optical band gap determined from the absorption spectrum is 4.9 eV, indicating a considerable blue shift relative to the bulk Sb2S3. Differential scanning calorimetry curves exhibit a broad exothermic peak between 200 and 300°C, suggesting recovery processes. This interpretation is supported by X-ray diffraction measurements that indicate a 23-fold increase of the crystallite size to about 827 nm as a consequence of application of high temperature process. The controlled mechanochemical synthesis of Sb2S3nanoparticles at ambient temperature and atmospheric pressure remains a great challenge.
Octubre, 2014 | DOI: 10.12693/APhysPolA.126.943
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Modeling of X-ray photoelectron spectra: surface and core hole effects
Pauly, N; Tougaard, S; Yubero, FSurface and Interface Analysis, 46 (2014) 920-923
Show abstract ▽
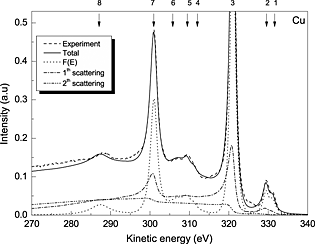
The shape and intensity of photoelectron peaks are strongly affected by extrinsic excitations due to electron transport out of the surface and by intrinsic excitations induced by the sudden creation of the static core hole. Besides, elastic electron scattering may also be important. These effects should be included in the theoretical description of the emitted photoelectron peaks. To investigate the importance of surface and core hole effects relative to elastic scattering effect, we have calculated full XPS spectra for the Cu 2p emissions of Cu and CuO with the simulation of electron spectra for surface analysis (SESSA) software and with a convolution procedure using the differential inelastic electron scattering cross-section obtained with the quantitative analysis of electron energy loss in XPS (QUEELS-XPS) software. Surface and core hole effects are included in QUEELS-XPS but absent in SESSA while elastic electron scattering effects are included in SESSA but absent in QUEELS-XPS. Our results show that the shape of the XPS spectra are strongly modified because of surface and core hole effects, especially for energy losses smaller than about 20eV.
Octubre, 2014 | DOI: 10.1002/sia.5372
Reactividad de Sólidos
Hardness and flexural strength of single-walled carbon nanotube/alumina composites
Gallardo-Lopez, A; Poyato, R; Morales-Rodriguez, A; Fernandez-Serrano, A; Munoz, A; Dominguez-Rodriguez, AJournal of Materials Science, 20 (2014) 7116-7123
Show abstract ▽
This work adds new experimental facts on room temperature hardness and flexural strength of alumina and composites with 1, 2, 5 and 10 vol% single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWNT) with similar grain size. Monolithic Al2O3 and composites were spark plasma sintered (SPS) in identical conditions at 1300 A degrees C, achieving high density, submicrometric grain size and a reasonably homogeneous distribution of SWNT along grain boundaries for all compositions with residual agglomerates. Vickers hardness values comparable to monolithic alumina were obtained for composites with low (1 vol%) SWNT content, though they decreased for higher concentrations, attributed to the fact that SWNT constitute a softer phase. Three-point bending flexural strength also decreased with increasing SWNT content. Correlation between experimental results and microstructural analysis by electron microscopy indicates that although SWNT agglomerates have often been blamed for detrimental effects on the mechanical properties of these composites, they are not the main cause for the reported decay in flexural strength.
Octubre, 2014 | DOI: 10.1007/s10853-014-8419-5
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Interpretation of electron Rutherford backscattering spectrometry for hydrogen quantification
Alvarez, R; Yubero, FSurface and Interface Analysis, 46 (2014) 812-816
Show abstract ▽
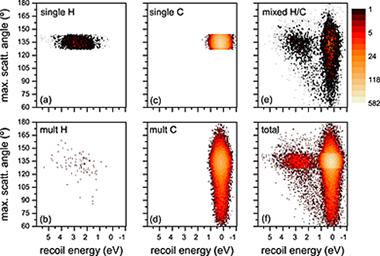
In the last few years, several papers have appeared showing the capabilities of electron Rutherford backscattering spectrometry (eRBS) to quantify the H content at surfaces. The basis of the H detection in this technique relies on the difference in recoil energy of the incident electrons depending on the mass of the atoms located at the surface that act as scatter centers. In this paper, we address the interpretation of eRBS spectra of hydrogen containing surfaces. The aim is to compare the naive single elastic scattering approximation with a more realistic description of eRBS spectra including multiple elastic scattering using the HQ-eRBS (hydrogen quantification eRBS) software based on a Monte Carlo algorithm. It is concluded that multiple elastic scattering is a significant contribution to experimentally measured eRBS spectra of a polyethylene surface. It induces significant broadening of the distribution of the maximum elastic scattering angle along the electron trajectories contributing to the measured spectra. However, it has weak effect in the energy distribution of the collected electrons (about 10% overestimation of the H content in the particular case of a polyethylene surface with respect to the corresponding ratio of elastic scattering cross sections).
Octubre, 2014 | DOI: 10.1002/sia.5486
- ‹ anterior
- 266 of 420
- siguiente ›














