Artículos SCI
2014
2014
Reactividad de Sólidos
Mechanochemical Processing of CaCu3Ti4O12 with Giant Dielectric Properties
Espinoza-Gonzalez, R; Vega, E; Tamayo, R; Criado, JM; Dianez, MJMaterials and Manufacturing Processes, 29 (2014) 1179-1183
Show abstract ▽
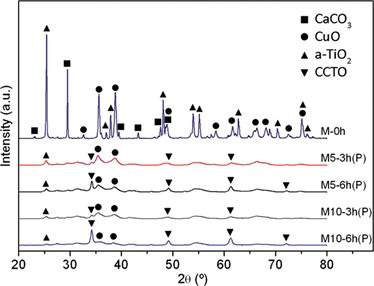
The dielectric properties of CaCu3Ti4O12 (CCTO) ceramic prepared by mechanochemical synthesis (MCS) were investigated. The effect on dielectric properties of ball-to-powder weight ratio and milling time was investigated and compared to the behavior of CCTO prepared by conventional solid state reaction (CSSR). CCTO ceramic was partially obtained after 6h of the milling process, while complete transformation was obtained during the sintering step of milled powders. It was shown that the dielectric properties of CCTO processed by MCS are dramatically improved compared with samples prepared by CSSR.
Octubre, 2014 | DOI: 10.1080/10426914.2014.921702
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Heterostructured Er3+ doped BiVO4 with exceptional photocatalytic performance by cooperative electronic and luminescence sensitization mechanism
Obregon, S; Colon, GApplied Catalysis B: Environmental, 158-159 (2014) 242-249
Show abstract ▽
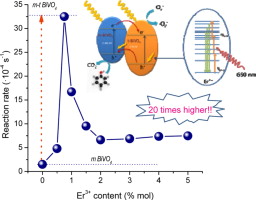
Er-BiVO4 has been synthesized by means of mw-assisted hydrothermal method having good photoactivity under sun-like excitation. It is stated that the precursor addition sequence plays a critical role which determine the further structural feature of BiVO4. From the structural and morphological characterization, it can be demonstrated that the presence of Er3+ would induce the stabilization of the tetragonal phase probably due to the formation of tetragonal-ErVO4 seeds previous to BiVO4 formation. The best photocatalytic performance is attained for the sample with 0.75 at% Er3+ content. At this dopant loading a mixture of tetragonal and monoclinic phase (70% tetragonal) is obtained. The dramatic increase in the photocatalytic activity for 0.75 at% Er-BiVO4 is related to the occurrence of such heterostructure. For this system, the MB degradation rate constant appears drastically higher as bare m-BiVO4. Furthermore, activities of photocatalysts for visible-light-driven O2 evolution have been evaluated, demonstrating that the photocatalytic activity of this Er-doped system (O2 evolution rate, 1014 μmol g−1 h−1) is 20 times as that of undoped m-BiVO4 (O2 evolution rate, 54 μmol g−1 h−1). From the obtained results, the cooperative conjunction of electronic and luminescence mechanism involved in the reaction is proposed to be the origin of the enhanced photocatalytic efficiencies of such systems.
Octubre, 2014 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.04.029
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
The Use of Fluorocarbons to Mitigate the Oxygen Dependence of Glucose Microbiosensors for Neuroscience Applications
Martin, M; O'Neill, RD; Gonzalez-Mora, JL; Salazar, PJournal of The Electrochemical Society, 161 (2014) H689-H695
Show abstract ▽
First-generation amperometric glucose biosensors are the most commonly used method for glucose monitoring in neuroscience. Nevertheless, biosensors of this genre suffer from the so-called "oxygen deficit". This problem is particularly acute when the oxygen concentration is low, as is the case in brain extracellular fluid. In the present work we use different fluorocarbons, such as Nafion and H700, to mitigate the oxygen deficit. These fluorocarbon-derived materials display a remarkable solubility for oxygen, and are able to act as oxygen reservoirs supporting the enzymatic reaction. Different biosensor configurations are presented, evaluating their sensitivity, linear range and oxygen dependence. Optimized Nafion- and H700-modified biosensors displayed a remarkable oxygen tolerance, with K-M(O-2) values as low as 11 and 4 mu mol L-1, respectively, and an appropriate sensitivity for in-vivo applications. Finally, in-vivo data are reported in order to illustrate the application of such devices in neuroscience applications.
Octubre, 2014 | DOI: 10.1149/2.1071410jes
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Active Site Considerations on the Photocatalytic H-2 Evolution Performance of Cu-Doped TiO2 Obtained by Different Doping Methods
Valero, JM; Obregon, S; Colon, GACS Catalysis, 4 (2014) 3320-3329
Show abstract ▽
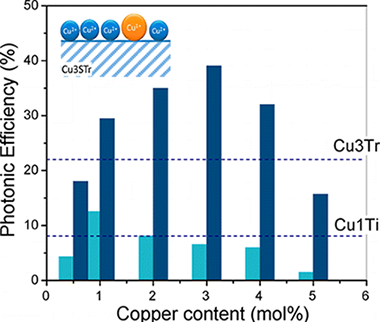
A photocatalytic H2 evolution reaction was performed over copper doped TiO2. The influence of sulfate pretreatment over fresh TiO2 support and the Cu doping method has been evaluated. Wide structural and surface characterization of catalysts was carried out in order to establish a correlation between the effect of sulfuric acid treatment and the further Cu-TiO2photocatalytic properties. Notably a different copper dispersion and oxidation state is obtained by different metal decoration methods. From the structural and surface analysis of the catalysts we have stated that the occurrence of highly disperse and reducible Cu2+ species is directly related to the photocatalytic activity for the H2 production reaction. Highly active materials have been obtained from a chemical reduction method leading to 18 mmol·h–1·g–1for 3 mol % copper loading.
Octubre, 2014 | DOI: 10.1021/cs500865y
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Study of the early stages of growth of Co oxides on oxide substrates
Diaz-Fernandez, D; Mendez, J; Yubero, F; Dominguez-Canizares, G; Gutierrez, A; Soriano, LSurface and Interface Analysis, 46 (2014) 975-979
Show abstract ▽
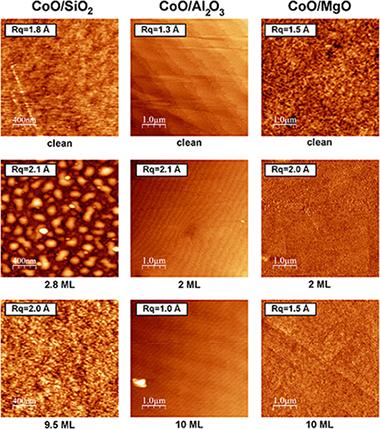
The growth of Cobalt oxides by reactive thermal evaporation of metallic Cobalt in an oxygen atmosphere on a series of oxide substrates, namely SiO2, Al2O3 and MgO, has been chemically and morphologically studied by means of XPS and atomic force microscopy (AFM). The XPS results reveal that cobalt oxide grows as CoO (Co2+) for coverages up to some tens of equivalent monolayers on all substrates. For larger coverages, the formation of the spinel oxide Co3O4 has been observed. AFM and XPS quantification allowed us to determine the way of growth of CoO on all substrates, being of Volmer-Weber (i.e. islands) mode for SiO2, whereas for Al2O3 and MgO, the growth follows the Frank-van der Merwe (i.e. layer-by-layer) mode. The results are discussed in terms of the mismatch of the lattice parameters of the CoO adsorbates with the substrates
Octubre, 2014 | DOI: 10.1002/sia.5366
- ‹ anterior
- 265 of 420
- siguiente ›














