Artículos SCI
2014
2014
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Enhanced activity of clays and its crucial role for the activity in ethylene polymerization
Camejo-Abreu, C; Tabernero, V; Alba, MD; Cuenca, T; Terreros, PJournal of Molecular Catalysis A-Chemical, 393 (2014) 96-104
Show abstract ▽
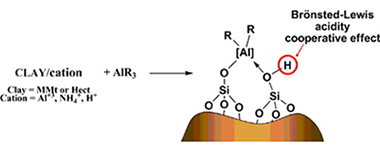
This paper presents a study of the effects of different treatments on the polymerization activity of modified clays as cocatalysts. To achieve this goal, an intercalating cation was introduced into two smectites and these clays were then modified with trimethyl aluminium. The results for ethylene polymerization, when a zirconocene complex was used as catalyst, and the structure analysis, allow us to obtain interesting deductions about the generation mode of the active species. All active materials employed as support activators presented aluminium in a pentahedral environment together with acidic hydrogen atoms. These two features were detected only after TMA treatment and they seem to be crucial elements in active cocatalyst generation. Moreover, a material without structural aluminium displayed the best activity pointing to the new aluminium species generated in the solid matrix as the determining factor for the activity. We proposed a synergic effect between Lewis acid aluminium centres and acidic Bronsted protons that generate the SiOHAl groups that activate the zirconium compound.
Noviembre, 2014 | DOI: 10.1016/j.molcata.2014.05.030
Reactividad de Sólidos
Thermal Stability of Multiferroic BiFeO3: Kinetic Nature of the beta-gamma Transition and Peritectic Decomposition
Perejon, A; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Criado, JM; Perez-Maqueda, LAJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 118 (2014) 26387-26395
Show abstract ▽
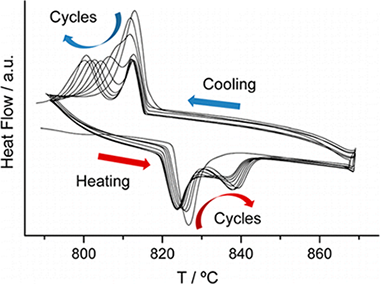
The thermal stability of BiFeO3 prepared by mechanosynthesis and sintered at 850 °C has been studied by DSC as a function of the atmosphere and temperature. It has been found that neither the phase transitions nor the thermal stability of BiFeO3 is affected by the atmosphere in which the heating process is performed. The material is unstable above the α–β transition (TC) and slowly decomposes to produce Bi2O3 and Bi2Fe4O9. The kinetics of this slow process has been studied by performing heating–cooling DSC cycles, concluding it follows an Avrami–Erofeev nucleation and growth kinetic model. The β–γ transition and the peritectic decomposition of BiFeO3 overlap and are kinetically controlled. The kinetics of this complex process has been studied for the first time employing a new kinetic analysis procedure implying the deconvolution and subsequent analysis of the individual contributing stages. Thus, it has been demonstrated that the decomposition of BiFeO3 is accelerated when the sample is heated above the β–γ transition and both processes also follow Avrami–Erofeev kinetic models.
Noviembre, 2014 | DOI: 10.1021/jp507831j
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Characterization of porous graphitic monoliths from pyrolyzed wood
Gutierrez-Pardo, A; Ramirez-Rico, J; de Arellano-Lopez, AR; Martinez-Fernandez, JJournal of Materials Science, 49 (2014) 7688-7696
Show abstract ▽
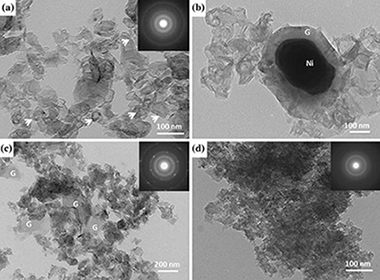
Porous graphitic carbons were obtained from wood precursors using Ni as a graphitization catalyst during pyrolysis. The structure of the resulting material retains that of the original wood precursors with highly aligned, hierarchical porosity. Thermal characterization was performed by means of thermogravimetry and differential scanning calorimetry, and the onset temperature for graphitization was determined to be similar to 900 A degrees C. Structural and microstructural characterization was performed by means of electron microscopy, electron and x-ray diffraction, and Raman spectroscopy. The effect of maximum pyrolysis temperature on the degree of graphitization was assessed. No significant temperature effect was detected by means of Raman scattering in the range of 1000-1400 A degrees C, but at temperatures over the melting point of the catalyst, the formation of graphite grains with long-range order was detected.
Noviembre, 2014 | DOI: 0.1007/s10853-014-8477-8
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Modeling of X-ray photoelectron spectra: surface and core hole effects
Pauly, N; Tougaard, S; Yubero, FSurface and Interface Analysis, 46 (2014) 920-923
Show abstract ▽
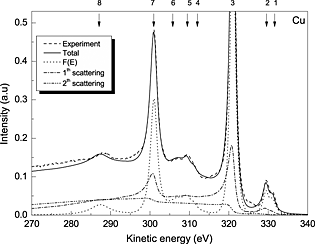
The shape and intensity of photoelectron peaks are strongly affected by extrinsic excitations due to electron transport out of the surface and by intrinsic excitations induced by the sudden creation of the static core hole. Besides, elastic electron scattering may also be important. These effects should be included in the theoretical description of the emitted photoelectron peaks. To investigate the importance of surface and core hole effects relative to elastic scattering effect, we have calculated full XPS spectra for the Cu 2p emissions of Cu and CuO with the simulation of electron spectra for surface analysis (SESSA) software and with a convolution procedure using the differential inelastic electron scattering cross-section obtained with the quantitative analysis of electron energy loss in XPS (QUEELS-XPS) software. Surface and core hole effects are included in QUEELS-XPS but absent in SESSA while elastic electron scattering effects are included in SESSA but absent in QUEELS-XPS. Our results show that the shape of the XPS spectra are strongly modified because of surface and core hole effects, especially for energy losses smaller than about 20eV.
Octubre, 2014 | DOI: 10.1002/sia.5372
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Shape-defined nanodimers by tailored heterometallic epitaxy
Garcia-Negrete, Carlos A; Rojas, Teresa C; Knappett, Benjamin R; Jefferson, David A; Wheatley, Andrew E H; Fernandez, AsuncionNanoscale, 6 (2014) 11090-11097
Show abstract ▽
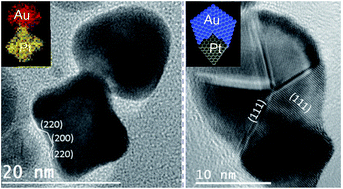
The systematic construction of heterogeneous nanoparticles composed of two distinct metal domains (Au and Pt) and exhibiting a broad range of morphologically defined shapes is reported. It is demonstrated that careful Au overgrowth on Pt nanocrystal seeds with shapes mainly corresponding to cubeoctahedra, octahedra and octapods can lead to heterometallic systems whose intrinsic structures result from specific epitaxial relationships such as {111} + {111}, {200} + {200} and {220} + {220}. Comprehensive analysis shows also that nanoparticles grown from octahedral seeds can be seen as comprising of four Au tetrahedral subunits and one Pt octahedral unit in a cyclic arrangement that is similar to the corresponding one in decahedral gold nanoparticles. However, in the present case, the multi-component system is characterized by a broken five-fold rotational symmetry about the [011] axis. This set of bimetallic dimers could provide new platforms for fuel cell catalysts and plasmonic devices.
Octubre, 2014 | DOI: 10.1039/C4NR01815J
- ‹ anterior
- 264 of 420
- siguiente ›














