Artículos SCI
2014
2014
Reactividad de Sólidos
Improvement of Vickers hardness measurement on SWNT/Al2O3 composites consolidated by spark plasma sintering
Rodriguez, AM; Lopez, AG; Fernandez-Serrano, A; Poyato, R; Munoz, A; Dominguez-Rodriguez, AJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 34 (2014) 3801-3809
Show abstract ▽
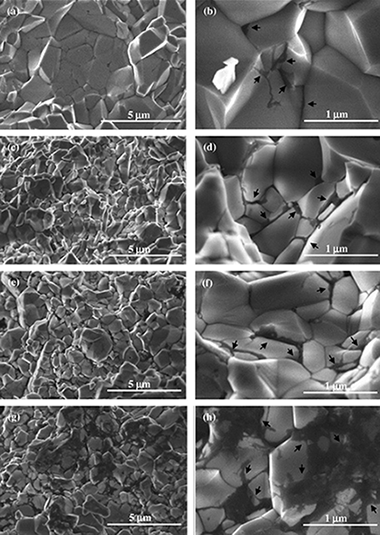
Dense alumina composites with different carbon nanotube content were prepared by colloidal processing and consolidated by Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS). Single-wall carbon nanotubes (SWNTs) were distributed at grain boundaries and also into agglomerates homogeneously dispersed. Carrying out Vickers hardness tests on the cross-section surfaces instead of top (or bottom) surfaces has shown a noticeable increase in the reliability of the hardness measurements. This improvement has been mainly attributed to the different morphology of carbon nanotube agglomerates, which however does not seem to affect the Vickers hardness value. Composites with lower SWNT content maintain the Vickers hardness of monolithic alumina, whereas it significantly decreases for the rest of compositions. The decreasing trend with increasing SWNT content has been explained by the presence of higher SWNT quantities at grain boundaries. Based on the results obtained, a method for optimizing Vickers hardness tests performance on SWNT/Al2O3 composites sintered by SPS is proposed.
Diciembre, 2014 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2014.05.048
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Chemistry, nanostructure and magnetic properties of Co-Ru-B-O nanoalloys
Arzac, GM; Rojas, TC; Gontard, LC; Chinchilla, LE; Otal, E; Crespo, P; Fernandez, ARSC Advances, 4 (2014) 46576-46586
Show abstract ▽
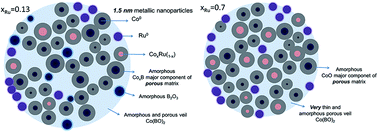
In our previous works, Co–B–O and Co–Ru–B–O ultrafine powders with variable Ru content (xRu) were studied as catalysts for hydrogen generation through sodium borohydride hydrolysis. These materials have shown a complex nanostructure in which small Co–Ru metallic nanoparticles are embedded in an amorphous matrix formed by Co–Ru–B–O based phases and B2O3. Catalytic activity was correlated to nanostructure, surface and bulk composition. However, some questions related to these materials remain unanswered and are studied in this work. Aspects such as: 3D morphology, metal nanoparticle size, chemical and electronic information on the nanoscale (composition and oxidation states), and the study of the formation or not of a CoxRu1−x alloy or solid solution are investigated and discussed using XAS (X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy) and Scanning Transmission Electron Microscopy (STEM) techniques. Also magnetic behavior of the series is studied for the first time and the structure–performance relationships discussed. All Co-containing samples exhibited ferromagnetic behavior up to room temperature while the Ru–B–O sample is diamagnetic. For the xRu = 0.13 sample, an enhancement in the Hc (coercitive field) and Ms (saturation magnetization) is produced with respect to the monometallic Co–B–O material. However this effect is not observed for samples with higher Ru content. The presence of the CoxB-rich (cobalt boride) amorphous ferromagnetic matrix, very small metal nanoparticles (Co and CoxRu(1−x)) embedded in the matrix, and the antiferromagnetic CoO phase (for the higher Ru content sample, xRu = 0.7), explain the magnetic behavior of the series.
Noviembre, 2014 | DOI:
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Ceramic Barrier Layers for Flexible Thin Film Solar Cells on Metallic Substrates: A Laboratory Scale Study for Process Optimization and Barrier Layer Properties
Delgado-Sanchez, JM; Guilera, N; Francesch, L; Alba, MD; Lopez, L; Sanchez, EACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 6 (2014) 18543-18549
Show abstract ▽
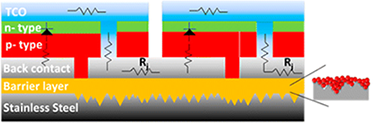
Flexible thin film solar cells are an alternative to both utility-scale and building integrated photovoltaic installations. The fabrication of these devices over electrically conducting low-cost foils requires the deposition of dielectric barrier layers to flatten the substrate surface, provide electrical isolation between the substrate and the device, and avoid the diffusion of metal impurities during the relatively high temperatures required to deposit the rest of the solar cell device layers. The typical roughness of low-cost stainless-steel foils is in the hundred-nanometer range, which is comparable or larger than the thin film layers comprising the device and this may result in electrical shunts that decrease solar cell performance. This manuscript assesses the properties of different single-layer and bilayer structures containing ceramics inks formulations based on Al2O3, AlN, or Si3N4 nanoparticles and deposited over stainless-steel foils using a rotogravure printing process. The best control of the substrate roughness was achieved for bilayers of Al2O3 or AlN with mixed particle size, which reduced the roughness and prevented the diffusion of metals impurities but AlN bilayers exhibited as well the best electrical insulation properties.
Noviembre, 2014 | DOI: 10.1021/am504923z
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Enhanced activity of clays and its crucial role for the activity in ethylene polymerization
Camejo-Abreu, C; Tabernero, V; Alba, MD; Cuenca, T; Terreros, PJournal of Molecular Catalysis A-Chemical, 393 (2014) 96-104
Show abstract ▽
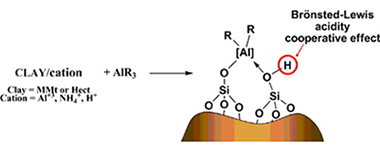
This paper presents a study of the effects of different treatments on the polymerization activity of modified clays as cocatalysts. To achieve this goal, an intercalating cation was introduced into two smectites and these clays were then modified with trimethyl aluminium. The results for ethylene polymerization, when a zirconocene complex was used as catalyst, and the structure analysis, allow us to obtain interesting deductions about the generation mode of the active species. All active materials employed as support activators presented aluminium in a pentahedral environment together with acidic hydrogen atoms. These two features were detected only after TMA treatment and they seem to be crucial elements in active cocatalyst generation. Moreover, a material without structural aluminium displayed the best activity pointing to the new aluminium species generated in the solid matrix as the determining factor for the activity. We proposed a synergic effect between Lewis acid aluminium centres and acidic Bronsted protons that generate the SiOHAl groups that activate the zirconium compound.
Noviembre, 2014 | DOI: 10.1016/j.molcata.2014.05.030
Reactividad de Sólidos
Properties of mechanochemically synthesized nanocrystalline Bi2S3 particles
Dutkova, E; Sayagues, MJ; Zorkovska, A; Real, C; Balaz, P; Satka, A; Kovac, JMaterials Science in Semiconductor Processing, 27 (2014) 267-272
Show abstract ▽
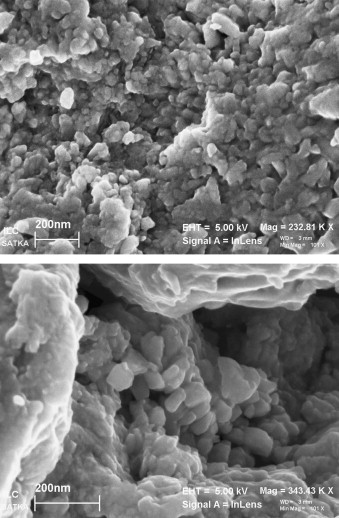
Nanocrystalline Bi2S3 particles have been synthesized from Bi and S powders by high-energy milling in a planetary mill. Structural and microstructural characterization of the prepared particles, including phase identification, specific surface area measurement and particle size analysis has been carried out. The optical properties were measured by spectroscopic methods and the structural stability up to 500 °C was studied by thermal analysis. The production of orthorhombic Bi2S3 with crystallite size of about 26 nm was confirmed by X-ray diffraction. The nanocrystals tend to agglomerate due to their large specific surface area. Accordingly, the average hydrodynamic diameter of the mechanochemically synthesized particles is 198 nm. EDS analysis shows that the synthesized material is pure Bi2S3. The band gap of the Bi2S3 nanoparticles is 4.5 eV which is wider than that in bulk materials. The nanoparticles exhibit good luminescent properties with a peak centered at 490 and 390 nm. Differential scanning calorimetry curves exhibit a broad exothermic peak between 200 and 300 °C, suggesting recovery processes. This interpretation is supported by X-ray diffraction measurements that indicate a 10-fold increase of the crystallite size to about 230 nm. The controlled mechanochemical synthesis of Bi2S3 nanoparticles at ambient temperature and atmospheric pressure remains a great challenge.
Noviembre, 2014 | DOI: 10.1016/j.mssp.2014.05.057
- ‹ anterior
- 263 of 420
- siguiente ›














