Artículos SCI
2014
2014
Materiales Coloidales
One-Step Synthesis and Polyacrylic Acid Functionalization of Multifunctional Europium-Doped NaGdF4 Nanoparticles with Selected Size for Optical and MRI Imaging
Nunez, NO; Garcia, M; Garcia-Sevillano, J; Rivera-Fernandez, S; de la Fuente, JM; Ocana, MEuropean Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 35 (2014) 6075-6084
Show abstract ▽
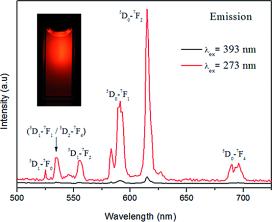
Multifunctional Eu:NaGdF4 nanospheres functionalized with polyacrylic acid (PAA) polymer have been prepared for the first time by a simple one-pot method that consists of a homogeneous precipitation reaction at 120 °C. The size of the nanospheres, which were polycrystalline and crystallized into a hexagonal structure, could be altered in the 60–95 nm range by adjusting the amount of polyacrylic acid added. The effects of Eu content and particle size of these nanomaterials on their optical properties (emission intensity and lifetime) as well as on their relaxivity (r1 and r2) values were also analyzed to find the optimum system for optical bioimaging and as a positive contrast agent for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) applications. Finally, such optimum nanoparticles showed negligible cytotoxicity for Vero cells for concentrations up to 0.5 mg mL–1 and a high colloidal stability in 2-morpholinoethanesulfonic acid solutions, thereby satisfying the most important requirements for their use in biotechnological applications.
Diciembre, 2014 | DOI: 10.1002/ejic.201402690
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
LMM Auger primary excitation spectra of copper
Pauly, N; Tougaard, S; Yubero, FSurface Science, 630 (2014) 294-299
Show abstract ▽
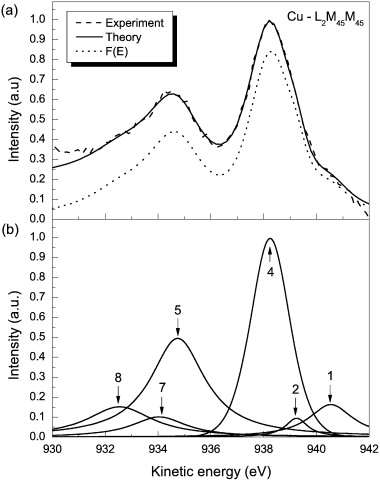
The shape and intensity of measured Auger peaks are strongly affected by extrinsic excitations due to electron transport out of the surface and to intrinsic excitations induced by the sudden creation of the two static core holes. Following a method developed for XPS in a previous work [N. Pauly, S. Tougaard, F. Yubero, Surf. Sci. 620 (2014) 17], we have calculated the effective energy-differential inelastic electron scattering cross-sections, including the effects of the surface and of the two core holes, within the dielectric response theory by means of the QUEELS-XPS software (QUantitative analysis of Electron Energy Losses at Surfaces for XPS). The Auger spectra are then modeled by convoluting this energy loss cross section with the primary excitation spectrum that accounts for all effects which are part of the initial Auger process, i.e. L–S coupling and vacancy satellite effects. The shape of this primary excitation spectrum is fitted to get close agreement between the theoretical and the experimental spectra obtained from X-ray excited Auger electron spectroscopy (XAES). We have performed these calculations of XAES spectra for various LMM Auger transitions of pure Cu (L3M45M45, L3M23M45, L3M23M23 and L2M45M45 transitions). We compare the resulting primary excitation spectra with theoretical results published in the literature and obtain reasonable quantitative agreement. In particular, we extract from experimental spectra quantitative intensities due to Coster–Kronig, shake-off and shake-up processes relative to the intensity from the “normal” Auger process.
Diciembre, 2014 | DOI: 10.1016/j.susc.2014.08.029
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Quinone-Rich Poly(dopamine) Magnetic Nanoparticles for Biosensor Applications
Martin, M; Orive, AG; Lorenzo-Luis, P; Creus, AH; Gonzalez-Mora, JL; Salazar, PChemPhysChem, 15 (2014) 3742-3752
Show abstract ▽
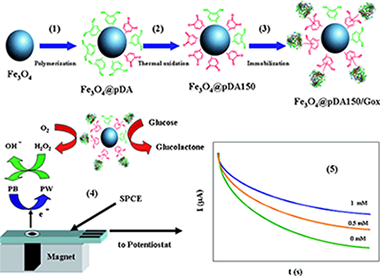
Novel core-shell quinone-rich poly(dopamine)–magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) were prepared by using an in situ polymerization method. Catechol groups were oxidized to quinone by using a thermal treatment. MNPs were characterized by using X-ray diffraction, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, atomic force microscopy, magnetic force microscopy, UV/Vis, Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, and electrochemical techniques. The hybrid nanomaterial showed an average core diameter of 17 nm and a polymer-film thickness of 2 nm. The core-shell nanoparticles showed high reactivity and were used as solid supports for the covalent immobilization of glucose oxidase (Gox) through Schiff base formation and Michael addition. The amount of Gox immobilized onto the nanoparticle surface was almost twice that of the nonoxidized film. The resulting biofunctionalized MNPs were used to construct an amperometric biosensor for glucose. The enzyme biosensor has a sensitivity of 8.7 mA m−1 cm−2, a low limit of detection (0.02 mm), and high stability for 45 days. Finally, the biosensor was used to determine glucose in blood samples and was checked against a commercial glucometer.
Diciembre, 2014 | DOI: 10.1002/cphc.201402417
Reactividad de Sólidos
Role of precalcination and regeneration conditions on postcombustion CO2 capture in the Ca-looping technology
Valverde, JM; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maqueda, LAApplied Energy, 136 (2014) 347-356
Show abstract ▽

The Ca-looping (CaL) technology is already recognized as a potentially viable method to capture CO2 from postcombustion gas in coal fired power plants. In this process, CO2 is chemisorbed by CaO solid particles derived from precalcination of cheap and widely available natural limestone. The partially carbonated solids are regenerated by calcination under high CO2 concentration. Novel CaL concepts are proposed to further improve the efficiency of the technology such as the introduction of a recarbonation reactor in between the carbonation and calcination stages to mitigate the progressive deactivation of the regenerated CaO. Process simulations aimed at retrieving optimum design parameters and operating conditions to scale-up the technology yield results critically dependent on the multicyclic sorbent performance. Nevertheless, technical limitations usually preclude lab-scale tests from mimicking realistic CaL conditions necessarily involving high CO2 concentration for sorbent regeneration and quick transitions between carbonation and calcination. In this work, a lab-scale experimental analysis is reported on the CaO multicyclic conversion at CaL conditions closely resembling those to be expected in practice. The results presented evidence a relevant role of precalcination conditions. Precalcination in air leads to a strongly adverse effect on the activity of the sorbent regenerated under high CO2 concentration, which is further hindered if a recarbonation stage is introduced. On the other hand, sorbent deactivation is mitigated if precalcination is carried out at conditions similar to those used for sorbent regeneration. In this case, recarbonation helps lessening the loss of multicyclic conversion, which is further enhanced by the synergistic combination with heat pretreatment. Moreover, the present study shows that the kinetics of carbonation is strongly dependent on precalcination and regeneration conditions. The diffusion controlled carbonation phase and recarbonation are intensified if the sorbent is precalcined and regenerated under high CO2 concentration whereas the reaction controlled carbonation phase is notably hampered.
Diciembre, 2014 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.09.052
Reactividad de Sólidos
Improvement of Vickers hardness measurement on SWNT/Al2O3 composites consolidated by spark plasma sintering
Rodriguez, AM; Lopez, AG; Fernandez-Serrano, A; Poyato, R; Munoz, A; Dominguez-Rodriguez, AJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 34 (2014) 3801-3809
Show abstract ▽
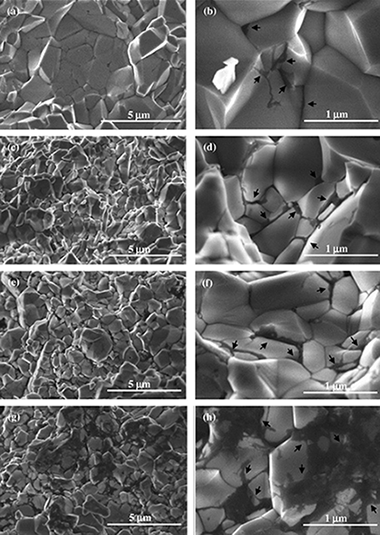
Dense alumina composites with different carbon nanotube content were prepared by colloidal processing and consolidated by Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS). Single-wall carbon nanotubes (SWNTs) were distributed at grain boundaries and also into agglomerates homogeneously dispersed. Carrying out Vickers hardness tests on the cross-section surfaces instead of top (or bottom) surfaces has shown a noticeable increase in the reliability of the hardness measurements. This improvement has been mainly attributed to the different morphology of carbon nanotube agglomerates, which however does not seem to affect the Vickers hardness value. Composites with lower SWNT content maintain the Vickers hardness of monolithic alumina, whereas it significantly decreases for the rest of compositions. The decreasing trend with increasing SWNT content has been explained by the presence of higher SWNT quantities at grain boundaries. Based on the results obtained, a method for optimizing Vickers hardness tests performance on SWNT/Al2O3 composites sintered by SPS is proposed.
Diciembre, 2014 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2014.05.048
- ‹ anterior
- 262 of 420
- siguiente ›














