Artículos SCI
2014
2014
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
The growth of cobalt oxides on HOPG and SiO2 surfaces: A comparative study
Diaz-Fernandez, D; Mendez, J; Bomati-Miguel, O; Yubero, F; Mossanek, RJO; Abbate, M; Dominguez-Canizares, G; Gutierrez, A; Tougaard, S; Soriano, LSurface Science, 624 (2014) 145-153
Show abstract ▽
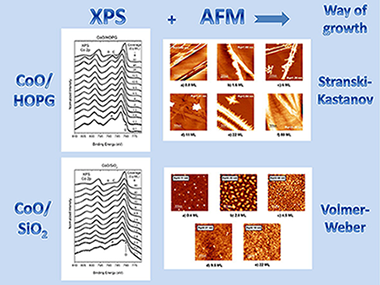
The growth of cobalt oxides by reactive thermal evaporation of metallic cobalt on highly oriented pyrolytic graphite (HOPG) and SiO2 (X cut quartz surface), in an oxygen atmosphere at room temperature, has been chemically and morphologically studied by means of X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and atomic force microscopy. The chemical analysis, which also includes cluster calculations, reveals that for the early deposition stages on both substrates, Co2 + species are stabilized at the surface up to a coverage which depends on the substrate. Further coverages lead to the formation of the spinel oxide Co3O4. The results are discussed in terms of the dependence of the surface energy on the size of the CoO deposited moieties. On the other hand, it has been found that the initial way of growth of cobalt oxides on HOPG is of Stranski–Krastanov mode whereas on SiO2 the growth is of Volmer–Weber mode. The differences in the growth morphology have been discussed in terms of the surface diffusivity of the CoO deposits on the substrates.
Junio, 2014 | DOI: 10.1016/j.susc.2014.02.007
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
A General Perspective of the Characterization and Quantification of Nanoparticles: Imaging, Spectroscopic, and Separation Techniques
Lapresta-Fernandez, A; Salinas-Castillo, A; de la Llana, SA; Costa-Fernandez, JM; Dominguez-Meister, S; Cecchini, R; Capitan-Vallvey, LF; Moreno-Bondi, MC; Marco, MP; Sanchez-Lopez, JC; Anderson, ISCritical Reviews in Solid State and Materials Sciences, 39 (2014) 423-458
Show abstract ▽
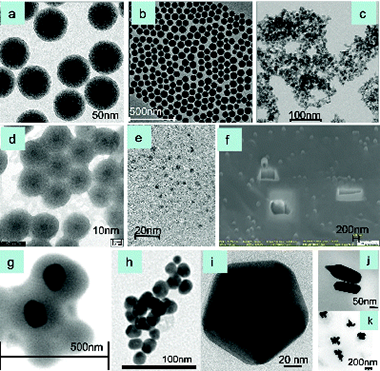
This article gives an overview of the different techniques used to identify, characterize, and quantify engineered nanoparticles (ENPs). The state-of-the-art of the field is summarized, and the different characterization techniques have been grouped according to the information they can provide. In addition, some selected applications are highlighted for each technique. The classification of the techniques has been carried out according to the main physical and chemical properties of the nanoparticles such as morphology, size, polydispersity characteristics, structural information, and elemental composition. Microscopy techniques including optical, electron and X-ray microscopy, and separation techniques with and without hyphenated detection systems are discussed. For each of these groups, a brief description of the techniques, specific features, and concepts, as well as several examples, are described.
Junio, 2014 | DOI: 10.1080/10408436.2014.899890
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Tomographic Heating Holder for In Situ TEM: Study of Pt/C and PtPd/Al2O3 Catalysts as a Function of Temperature
Gontard, LC; Dunin-Borkowski, RE; Fernandez, A; Ozkaya, D; Kasama, TMicroscoy and Microanalysis, 20 (2014) 982-990
Show abstract ▽
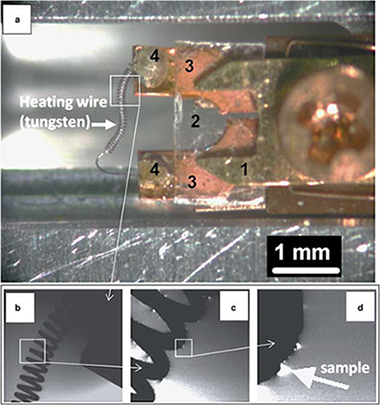
A tomographic heating holder for transmission electron microscopy that can be used to study supported catalysts at temperatures of up to similar to 1,500 degrees C is described. The specimen is placed in direct thermal contact with a tungsten filament that is oriented perpendicular to the axis of the holder without using a support film, allowing tomographic image acquisition at high specimen tilt angles with minimum optical shadowing. We use the holder to illustrate the evolution of the active phases of Pt nanoparticles on carbon black and PtPd nanoparticles on gamma-alumina with temperature. Particle size distributions and changes in active surface area are quantified from tilt series of images acquired after subjecting the specimens to increasing temperatures. The porosity of the alumina support and the sintering mechanisms of the catalysts are shown to depend on distance from the heating filament.
Junio, 2014 | DOI: 10.1017/S1431927614000373
Materials characteristics of Roman and Arabic mortars and stuccoes from The Patio de Banderas in the Real Alcazar of Seville (SPAIN)
Garofano, I; Robador, MD; Duran, AArchaeometry, 56 (2014) 541-561
Show abstract ▽
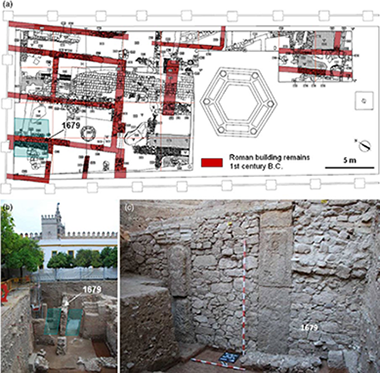
This study discusses the materials and traditional knowledge used in the manufacture and application of lime mortars and stuccoes by Romans and Arabs in Seville (southern Iberian Peninsula). All of the samples studied contain calcite as a binder, combined with aggregates based on river sand from the filling materials of the Guadalquivir River's depression, located in the vicinity of the Real Alcazar Palace in Seville, Spain, where the artefacts were discovered. The Romans used high-quality production technology, as evidenced by the careful selection of raw materials as well as by the adequate binder-to-aggregate ratio and the elevated homogeneity of the mortars and stuccoes. The suitable distribution of aggregates resulted in higher density values for Roman fragments than for Arabic ones. Results derived from Arabic samples suggest a decline in technology manufacture over time. This work provides useful information, particularly regarding the Roman and Arabic periods in the Iberian Peninsula. The analytical techniques employed in this study were X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray fluorescence (XRF)—using conventional and portable systems, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), petrographic microscopy, differential thermal analysis/thermogravimetry (DTA/TG), particle-size analysis and mercury intrusion porosimetry.
Junio, 2014 | DOI: 10.1111/arcm.12041
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Excellent photocatalytic activity of Yb3+, Er3+ co-doped BiVO4 photocatalyst
Obregon, S.; Colon, G.Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 152-153 (2014) 328-334
Show abstract ▽
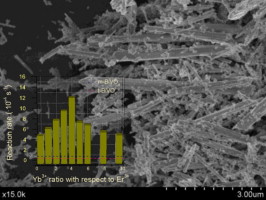
Ytterbium-Erbium co-doped BiVO4 have been synthesized by means of a surfactant free hydrothermal method having good photoactivities under sun-like excitation for the degradation of Methylene Blue and O2 evolution reactions. From the structural and morphological characterization it has been stated that the presence of Yb3+ and Er3+ induces the stabilization of the tetragonal phase probably due to its substitutional incorporation in the BiVO4 lattice. The occurrence of the Yb3+,Er3+ co-doped monoclinic-tetragonal BiVO4 heterostructure induces the higher photocatalytic activities. The best photocatalytic performance was attained for the sample with 1:4 Er3+:Yb3+ ratio. The observed NIR photoactivity clearly denotes the occurrence of an up-conversion mechanism involved in the overall photocatalytic process.
Junio, 2014 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2014.01.054
- ‹ anterior
- 273 of 420
- siguiente ›














