Artículos SCI
2014
2014
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Influence of the synthesis parameter on the interlayer and framework structure of lamellar octadecyltrimethylammonium kanemite
Corredor, JI; Cota, A; Pavon, E; Osuna, FJ; Alba, MDApplied Clay Science, 95 (2014) 9-17
Show abstract ▽
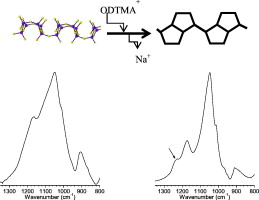
Inorganic–organic nanostructures, used as host materials for selective adsorption of functional molecules and as mesostructured material precursors, can be constructed by the interlayer modification of inorganic layered materials with surfactants. The formation mechanism is mainly determined by the surfactant assemblies in the 2D limited space. In this paper, a detailed structural analysis of the lamellar mesophases prepared from kanemite, a lamellar silicate, and octadecyltrimethylammonium (ODTMA) under various conditions was reported. The adsorbed amount of ODTMA and the long and short range structural orders were explored by TGA, XRD, IR/FT and MAS NMR spectroscopies. The results revealed that ODTMA molecules were efficiently intercalated in the interlayer space of kanemite and, in all synthesis conditions, an ordered lamellar structure was obtained. The ODTMA adsorption in kanemite caused changes not only in the interlayer space but also in the silicate framework, where five-member rings were formed. The characteristics of the final products were influenced by the synthesis conditions, although the separation mode, filtration or centrifugation, was not relevant. Therefore, the adsorption conditions of ODTMA in kanemite will contribute to the design of novel layered materials with potential environmental and technological use.
Junio, 2014 | DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2014.02.030
Reactividad de Sólidos
Improvement of the thermal stability of branched poly(lactic acid) obtained by reactive extrusion
Carrasco, F; Cailloux, J; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Maspoch, MLPolymer Degradation and Stability, 104 (2014) 40-49
Show abstract ▽
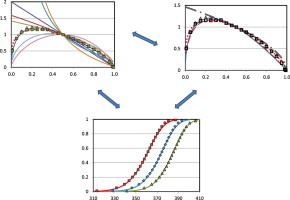
One-step reactive extrusion-calendering process (REX-calendering) has been used in order to obtain sheets of 1 mm from poly(lactic acid) modified with a styrene-acrylic multifunctional oligomeric agent. In a preliminary internal mixer study, torque versus time has been monitored in order to ascertain chain extender ratios and reaction time. Once all the parameters were optimized, reactive extrusion experiments have been performed. An enhanced general analytical equation has been developed in order to evaluate the kinetic parameters of the thermal degradation of PLA sheets manufactured by reactive extrusion. This improvement has consisted of replacing the n-order conversion function by a modified form of the Sestak–Berggren equation f(α) = c (1 − α)nαm that led to a better adjustment of experimental data and also adequately represented the conventional mechanisms for solid-state processes. The kinetic parameters so obtained have been compared to those determined by conventional differential methods and n-order reaction kinetics. Given that the thermal degradation of PLA has been argued to be caused by random chain scission reactions of ester groups, the conversion function f(α) = 2 (α1/2 − α), corresponding to a random scission mechanism for L = 2 (as well as other functions for L values up to 8), has been tested. Once optimized the kinetic model, the thermal degradation kinetics of sheets obtained by REX-calendering process was compared to that of conventional sheets and polymer matrix.
Junio, 2014 | DOI: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2014.03.026
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
On the Deposition Rates of Magnetron Sputtered Thin Films at Oblique Angles
Alvarez, R; Garcia-Martin, JM; Lopez-Santos, MC; Rico, V; Ferrer, FJ; Cotrino, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Palmero, APlasma Processes and Polymers, 11 (2014) 571-576
Show abstract ▽
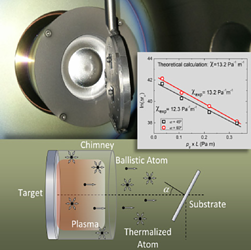
We describe here the deposition of thin films using magnetron sputtering at oblique angles. General relations between the deposition rates of the films and experimental parameters, such as gas pressure or substrate tilt angles, are deduced and experimentally tested. The model also permits the direct determination of the thermalization mean free path of the sputtered particles in the plasma gas, a key parameter defining the balance between ballistic and diffusive flows in the deposition reactor. The good agreement between experimental and calculated results supports the validity of our description, which becomes a useful tool to explain the main features of the magnetron sputtering deposition of thin films at oblique angles.
Junio, 2014 | DOI: 10.1002/ppap.201300201
Reactividad de Sólidos
Processing and characterisation of cermet/hardmetal laminates with strong interfaces
Gotor, FJ; Bermejo, R; Cordoba, JM; Chicardi, E; Medri, V; Fabbriche, DD; Torres, YMaterials & Design, 58 (2014) 226-233
Show abstract ▽
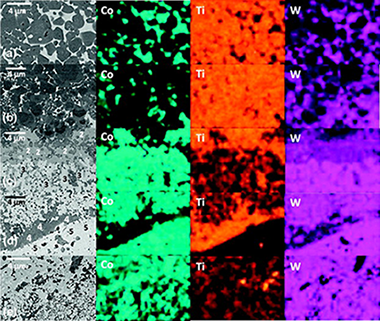
Cemented carbides and cermets are potential materials for high speed machining tools. However, cemented carbides are not chemically stable at high temperature and cermets present poor fracture toughness. Novel cermet/hardmetal multilayer systems show a huge potential for this intended application. It would be possible to achieve the right balance of the required thermomechanical properties using cermet as temperature protective outer layers and hardmetal as reinforcement layers. In this work, preliminary results on the microstructural and mechanical characterisation of a multilayer TiCxN1−x–Co/WC–Co composite densified by hot pressing are presented, with special attention to the properties of the interface. Microstructural observations revealed the existence of strong bonding interfaces between cermet and hardmetal layers due to chemical interaction during the sintering process. As a consequence, owing to the different coefficient of thermal expansion between cermet and hardmetal, a tensile and compressive biaxial residual stress of σres,Cermet ≈ +260 ± 50 MPa and σres,WC–Co ≈ −350 ± 70 MPa was estimated in the corresponding layers. Microindentation cracks introduced in the cermet layers (the less toughness material) and propagated transversely to the layers were arrested at the interface, showing the combined effect of toughness and compressive stresses on crack shielding.
Junio, 2014 | DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2014.01.076
Reactividad de Sólidos
Effect of high SWNT content on the room temperature mechanical properties of fully dense 3YTZP/SWNT composites
Poyato, R; Gallardo-Lopez, A; Gutierrez-Mora, F; Morales-Rodriguez, A; Munoz, A; Dominguez-Rodriguez, AJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 34 (2014) 1571-1579
Show abstract ▽
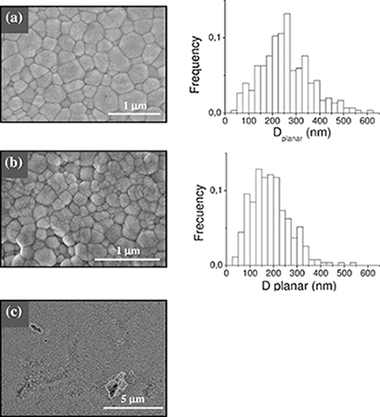
This paper is devoted to correlate the microstructure and room temperature mechanical properties of single-wall carbon nanotube (SWNT) reinforced 3 mol% yttria stabilized tetragonal zirconia with high SWNT content (2.5, 5 and 10 vol%). Fully dense composites were prepared by using a combination of aqueous colloidal powder processing and Spark Plasma Sintering. SWNTs were located at the ceramic grain boundaries and they were not damaged during the sintering process. The weak interfacial bonding between SWNTs and ceramic grains together with the detachment of SWNTs within thick bundles have been pointed out as responsible for the decrease of hardness and fracture toughness of the composites in comparison with the monolithic 3YTZP ceramic.
Junio, 2014 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2013.12.024
- ‹ anterior
- 274 of 420
- siguiente ›














