Artículos SCI
2014
2014
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Surface Oxygen Vacancies in Gold Based Catalysts for CO Oxidation
Romero-Sarria, F; Plata, JJ; Laguna, OH; Marquez, AM; Centeno, MA; Sanz, JF; Odriozola, JARSC Advances, 4 (2014) 13145-13152
Show abstract ▽
Experimental catalytic activity measurements, Diffuse Reflectance Infrared Fourier Spectroscopy, and Density Functional Theory calculations are used to investigate the role and dynamics of surface oxygen vacancies in the CO oxidation with O2 catalyzed by Au nanoparticles supported on a Y-doped TiO2 catalyst. Catalytic activity measurements show that the CO conversion is improved in a second cycle of reaction if the reactive flow is composed by CO and O2 (and inert) while if water is present in the flow, the catalyst shows a similar behaviour in two successive cycles. DRIFTS-MS studies indicate the occurrence of two simultaneous phenomena during the first cycle in dry conditions: the surface is dehydroxylated and a band at 2194 cm-1 increases (proportionally to the number of surface oxygen vacancies). Theoretical calculations were conducted in order to explain these observations. On one hand, the calculations show that there is a competition between gold nanoparticles and OH to occupy the surface oxygen vacancies and that the adsorption energy of gold on these sites increases as the surface is being dehydroxylated. On another hand, these results evidence that a strong electronic transfer from the surface to the O2 molecule is produced after its adsorption on the Au/TiO2 perimeter interface (activation step), leaving the gold particle in a high oxidation state. This explains the appearance of a band at a wavenumber unusually high for the CO adsorbed on oxidized gold particles (2194 cm-1) when O2 is present in the reactive flow. These simultaneous phenomena indicate that a gold redispersion on the surface occurs under reactive flow in dry conditions generating small gold particles very actives at low temperature. This fact is notably favoured by the presence of surface oxygen vacancies that improve the surface dynamics. The obtained results suggest that the reaction mechanism proceeds through the formation of a peroxo-like complex formed after the electronic transfer from the surface to the gas molecule.
Abril, 2014 | DOI: 10.1039/c3ra46662k
Materiales Coloidales
Synthesis and luminescence of uniform europium-doped bismuth fluoride and bismuth oxyfluoride particles with different morphologies
A. Escudero; E. Moretti; M. OcañaCrysEngComm, 16 (2014) 3274-3283
Show abstract ▽
Facile synthesis routes have been developed for the preparation of uniform cubic bismuth fluoride and bismuth oxyfluoride particles. The synthesis methods are based on homogeneous precipitation reactions at 120 °C in solutions of bismuth nitrate and sodium tetrafluoroborate precursors in polyol-based solvents. Both the nature of the solvent and the heating modes (conventional or microwave-assisted heating) have a remarkable effect on the morphology and crystallinity of the resulting particles. Thus, polycrystalline spheres of α-BiF3 with a mean diameter ranging from 1.2 to 2 μm could be obtained by heating solutions with the appropriate reagent concentrations in a mixture of ethylene glycol and glycerol (1 : 1 by volume) using a conventional oven, whereas octahedral single crystals of α-BiOyF3−2y with mean edges ranging from 250 nm to 920 nm precipitated when using a diethylene glycol–water mixture (8 : 2 in volume) as solvent and a microwave reactor for heating. To explain these different morphological and structural features, the mechanism of formation of such particles was investigated. Both kinds of particles were also doped with Eu3+, and both the morphological and luminescence properties of the resulting materials were evaluated. It was found that the luminescence intensity of the europium-doped α-BiOyF3−2y nanoparticles was higher than that of the europium-doped α-BiF3 sub-micrometric spheres, which was associated with the higher crystallinity of the former. Moreover, the presence of oxygen in the europium-doped α-BiOyF3−2y samples permits the excitation of the europium cations through an Eu–O energy transfer process, which results in a much higher luminescence intensity with respect to that corresponding to the direct excitation of the europium cations. Finally, the effect of the amount of dopant on the luminescence properties of the phosphors was also evaluated.
Abril, 2014 | DOI: 10.1039/C3CE42462F
Reactividad de Sólidos
Chemical and electrical properties of LSM cathodes prepared by mechanosynthesis
Moriche, R.; Marrero-López, D.; Gotor, F.J.; Sayagués, M.J.Journal of Power Sources, 252 (2014) 43-50
Show abstract ▽

Mechanosynthesis of La1−xSrxMnO3 (x = 0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75 and 1) was carried out at room temperature from stoichiometric mixtures of La2O3, Mn2O3 and SrO, obtaining monophasic powders with the perovskite structure. Physical properties of these materials and their chemical compatibility with the electrolyte yttria stabilized zirconia (YSZ), which depend strongly on the La/Sr ratio, were evaluated to corroborate availability to be implemented as cathode material in solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs). Electrical conductivity values in air ranged between 100 and 400 S cm−1 in the temperature range of 25–850 °C. Samples presented low reactivity with YSZ in the working temperature range (600–1000 °C) maintaining the grain size small enough to preserve the catalytic activity for oxygen reduction.
Abril, 2014 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2013.11.093
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Tuning the transmittance and the electrochromic behavior of CoxSiyOz thin films prepared by magnetron sputtering at glancing angle
Gil-Rostra, J; Garcia-Garcia, F; Yubero, F; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARSolar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 123 (2014) 130-138
Show abstract ▽
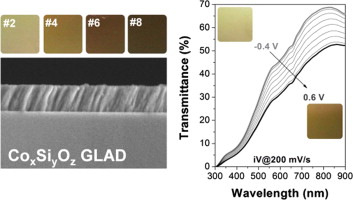
This work reports the synthesis and the characterization of amorphous CoxSiyOz thin films prepared by magnetron sputtering from a single cathode. Porous layers with outstanding electrochromic properties are obtained at room temperature in one step by performing the deposition at a glancing angle configuration. The electrochromic behavior of these layers in a basic aqueous medium was dependent on the Co/Si ratio in the films and in all cases was characterized by a fast response, a high coloration efficiency and a complete reversibility after several hundred cycles. A characteristic feature of these electrochromic layers is that, for a similar thickness, the range of transmittance modulation can be tuned by changing the Co/Si ratio in the films and, specifically for films with a high concentration of silicon, to change their aspect from an almost transparent to a full colored state.
Abril, 2014 | DOI: 10.1016/j.solmat.2013.12.020
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Understanding the Role of the Cosolvent in the Zeolite Template Function of Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquid
Ayala, R; Ivanova, S; Blanes, JMM; Romero-Sarria, F; Odriozola, JAJournal of Physical Chemistry B, 118 (2014) 3650–3660
Show abstract ▽
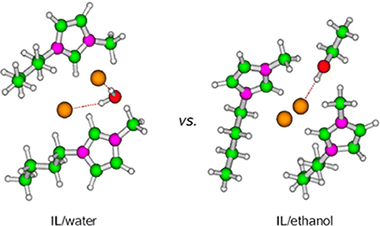
In this work, a study for understanding the role played by [ClBmim], [BF4Bmim], [PF6Bmim], and [CH3SO3Bmim] ionic liquids (ILs) in the synthesis of zeolites is presented. The use of [ClBmim] and [CH3SO3Bmim] ILs, as reported earlier [ Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 2122] led to the formation of MFI or BEA type zeolites. Contrary, [BF4Bmim] and [PF6Bmim] ILs did not succeed in organizing the Si–Al network into a zeolite structure. To try to explain these results, a series of quantum mechanical calculations considering monomers ([XBmim]) and dimers ([XBmim]2) by themselves and plus cosolvent (water or ethanol) were carried out, where X ≡ Cl–, BF4–, PF6–, or CH3SO3–. Our attention was focused on the similarities and differences among the two types of cosolvents and the relation between the structure and the multiple factors defining the interactions among the ILs and the cosolvent. Although a specific pattern based on local structures explaining the different behavior of these ILs as a zeolite structuring template was not found, the calculated interaction energies involving the Cl– and CH3SO3– anions were very close and larger than those for BF4– and PF6– species. These differences in energy can be used as an argument to describe their different behavior as structure directing agents. Moreover, the topology of the cosolvent is also an ingredient to take into account for a proper understanding of the results.
Abril, 2014 | DOI: 10.1021/jp410260g
- ‹ anterior
- 279 of 420
- siguiente ›














