Artículos SCI
2014
2014
Reactividad de Sólidos
CdSe@ZnS nanocomposites prepared by a mechanochemical route: No release of Cd2+ ions and negligible in vitro cytotoxicity
Balaz, P; Sayagues, MJ; Balaz, M; Zorkovska, A; Hronec, P; Kovac, J; Kovac, J; Dutkova, E; Mojzisova, G; Mojzis, JMaterials Research Bulletin, 49 (2014) 302-309
Show abstract ▽
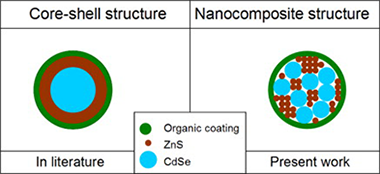
CdSe@ZnS nanocomposites have been prepared by a two-step solid state mechanochemical synthesis. CdSe prepared from Cd and Se elements in the first step was mixed with zinc acetate and sodium sulphide in the second step of milling to prepare a CdSe@ZnS nanocomposite. In the third step, the obtained nanocomposite was coated with l-cysteine to prepare a biocompatible system. The crystallite size of the new type of nanocomposite was 20–35 nm for cubic CdSe and 3–8 nm for hexagonal ZnS as calculated from XRD, TEM and SEM data. The synthesised samples show good crystallinity and have been tested for dissolution and cytotoxicity. The dissolution of cadmium from CdSe@ZnS was less than 0.05 μg mL−1, whereas a value of 0.8 μg mL−1 was measured for CdSe alone. The binding of ZnS with CdSe in the nanocomposite practically eliminated the release of cadmium into solution. As a consequence, a very low cytotoxic activity has been evidenced for CdSe@ZnS. The nanocomposites coated with l-cysteine have a great potential as fluorescent labels in biomedical engineering.
Enero, 2014 | DOI: 10.1016/j.materresbull.2013.08.070
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Nanoindentation of nanocolumnar TiO2 thin films with single and stacked zig-zag layers
Jimenez-Pique, E; Gonzalez-Garcia, L; Rico, VJ; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARThin Solid Films, 550 (2014) 444-449
Show abstract ▽
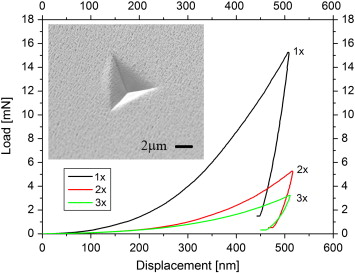
This paper reports a systematic analysis of the mechanical properties of nanocolumnar TiO2 thin films prepared by evaporation at a glancing geometry. A systematic study of the mechanical properties is carried out by comparing the hardness and the Young's modulus determined by nanoindentation for thin films prepared at different deposition angles and characterized by a tilted nanocolumnar structure and others where the nanocolumns are perpendicular to the substrate or are arranged as zig-zag stacked layers. A correlation between mechanical properties and glazing angle geometry is proposed. Differences in the results are discussed in view of the cross section images obtained by focused ion beam and of the deformed areas. Zig-zagged layers present lower values of hardness and Young's modulus due to the collapse of the angles of the columns, but at the same time this configuration impedes the appearance of fracture or delamination, as observed for tilted columns.
Enero, 2014 | DOI: 10.1016/j.tsf.2013.10.022
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Interaction of Hydrated Cations with Mica-n (n = 2, 3 and 4) Surface
Pavon, E; Castro, MA; Cota, A; Osuna, FJ; Pazos, MC; Alba, MDJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 118 (2014) 2115-2121
Show abstract ▽

High charged swelling micas, with layer charge between 2 and 4, have been found to readily swell with water, and complete cation exchange (CEC) can be achieved. Because of their high CEC, applications like radioactive cation fixation or removal of heavy metal cations from wastewater were proposed. Their applicability can be controlled by the location of the interlayer cation in a confined space with a high electric field. In synthetic brittle micas, the interlayer cation has a low water coordination number; therefore, their coordination sphere would be completed by the basal oxygen of the tetrahedral layer as inner-sphere complexes (ISC). However, no direct evidence of these complexes formation in brittle micas has been reported yet. In this contribution, we mainly focus on the understanding the mechanisms that provoke the formation of ISC in high charge swelling micas, Mica-n. A whole series of cations (X) were used to explore the influence of the charge and size of the interlayer cation. Three brittle swelling micas, Mica-n (n = 4, 3 and 2), were selected in order to analyze the influence of the layer charge in the formation of ISC. The contribution of the ISC has been analyzed thorough the evolution of the 060 reflection and the changes in the short-range order of the tetrahedral cations will be followed 29Si and 27Al MAS NMR. The results showed that ISC was favored in X-Mica-4 and that provoked a high distortion angle between the Si–Al tetrahedra. When the content of aluminum decreases, the electrostatic forces between the layers are relaxed, and the hydrated cations did not interact so strongly with the tetrahedral sheet, having the opportunity to complete their hydration sphere.
Enero, 2014 | DOI: 10.1021/jp4110695
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Panchromatic porous specular back reflectors for efficient transparent dye solar cells
Lopez-Lopez, C; Colodrero, S; Miguez, HPhysical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 16 (2014) 663-668
Show abstract ▽
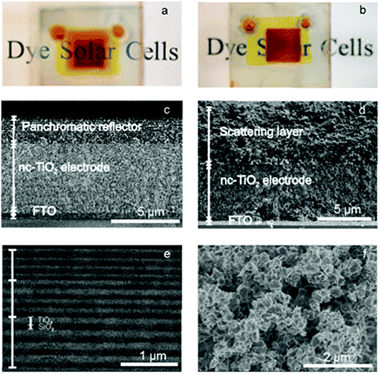
A panchromatic specular reflector based dye solar cell is presented herein. Photovoltaic performance of this novel design is compared to that of cells in which standard diffuse scattering layers are integrated. The capability of the proposed multilayer structures to both emulate the broad band reflection of diffuse scattering layers of standard thickness (around 5 microns) and give rise to similarly high light harvesting and power conversion efficiencies, yet preserving the transparency of the device, is demonstrated. Such white light reflectors are comprised of stacks of different porous optical multilayers, each one displaying a strong reflection in a complementary spectral range, and are designed to leave transmittance unaltered in a narrow red-frequency range in which the sensitized electrode shows negligible absorption, thus allowing us to see through the cell. The reflectance bandwidth achieved is three times as broad as the largest bandwidth previously achieved using any photonic structure integrated into a dye solar cell.
Enero, 2014 | DOI: 10.1039/C3CP53939C
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Improved H2 production of Pt-TiO2/g-C3N4-MnOx composites by an efficient handling of photogenerated charge pairs
Obregon, S; Colon, GApplied Catalysis B: Environmental, 144 (2014) 775-782
Show abstract ▽
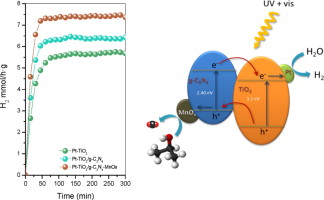
Pt-TiO2/g-C3N4-MnOx hybrid structures are synthesized by means of a simple impregnation method of Pt-TiO2 and g-C3N4-MnOx. From the wide structural and surface characterization we have stated that TiO2/g-C3N4 composites are formed by an effective covering of g-C3N4 by TiO2. The modification of composite by Pt and/or MnOx leads to improved photoactivities for phenol degradation reaction. Moreover, enhanced photoactivities have been obtained for composites systems for H2 evolution reaction. The notably photocatalytic performance obtained was related with the efficient separation of charge pairs in this hybrid heterostructure.
Enero, 2014 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.07.034
- ‹ anterior
- 287 of 420
- siguiente ›














