Artículos SCI
2014
2014
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Improved H2 production of Pt-TiO2/g-C3N4-MnOx composites by an efficient handling of photogenerated charge pairs
Obregon, S; Colon, GApplied Catalysis B: Environmental, 144 (2014) 775-782
Show abstract ▽
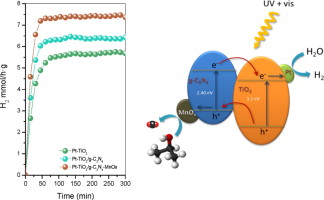
Pt-TiO2/g-C3N4-MnOx hybrid structures are synthesized by means of a simple impregnation method of Pt-TiO2 and g-C3N4-MnOx. From the wide structural and surface characterization we have stated that TiO2/g-C3N4 composites are formed by an effective covering of g-C3N4 by TiO2. The modification of composite by Pt and/or MnOx leads to improved photoactivities for phenol degradation reaction. Moreover, enhanced photoactivities have been obtained for composites systems for H2 evolution reaction. The notably photocatalytic performance obtained was related with the efficient separation of charge pairs in this hybrid heterostructure.
Enero, 2014 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.07.034
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Effect of gold on a NiLaO3 perovskite catalyst for methane steam reforming
Palma, S; Bobadilla, LF; Corrales, A; Ivanova, S; Romero-Sarria, F; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis B: Environmental, 144 (2014) 846-854
Show abstract ▽
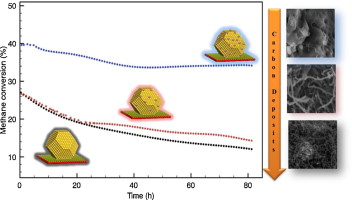
The effect of gold addition to a supported Ni SRM catalyst has been studied in this work in order to determine the influence of gold on both the amount and type of carbon species formed during the reaction. The structure of the support, a mixed La–Al perovskite, determines the catalyst reducibility and Ni particle size. Gold addition affects the metal particle size increasing metal dispersion on increasing the gold content. Therefore, although gold blocks step Ni sites, the more active sites for Csingle bondH activation, and increases electron density on nickel, the higher dispersion results in an apparently higher activity upon gold addition. Moreover, gold addition increases the catalyst stability by decreasing the rate of growth of carbon nanotubes.
Enero, 2014 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.07.055
Reactividad de Sólidos
Effect of tantalum content on the microstructure and mechanical behavior of cermets based on (TixTa1−x)(C0.5N0.5) solid solutions
Chicardi, E; Torres, Y; Cordoba, JM; Hvizdos, P; Gotor, FJMaterials & Design, 53 (2014) 435-444
Show abstract ▽
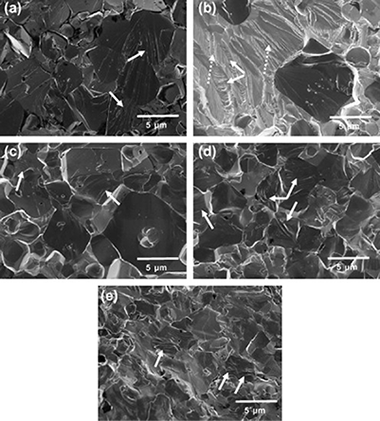
Titanium–tantalum carbonitride, (Ti, Ta)(C, N), based cermets with different Ti and Ta contents were prepared using a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction and then densified using a pressureless sintering process. Complete microstructural and mechanical characterizations were performed on the materials, which revealed that the size of the carbonitride ceramic particle was significantly reduced when the Ta content was increased. The flexural strength and fracture toughness were measured using the ball on three balls test and the indentation microfracture test, respectively. The strength profile was analyzed under the framework of Weibull theory. The change in the mechanical properties as a function of the Ta content was correlated with the normalized microstructural parameters, such as the binder mean free path. The decrease in toughness and flexural strength was attributed to the presence of intermetallic compounds in the binder phase, which was also corroborated by the nanoindentation tests.
Enero, 2014 | DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2013.07.039
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
On the kinetic and thermodynamic electron temperatures in non-thermal plasmas
Alvarez, R; Cotrino, J; Palmero, AEPL (Europhysic Letters), 105 (2014)
Show abstract ▽
The framework to describe the out-of-equilibrium free electrons in cold plasmas is developed assuming the electron entropy is defined through the Boltzmann H-theorem. Our theory explains why the Saha-Boltzmann relation among higher-lying excited states by means of the electron kinetic temperature is fulfilled, even when free electrons are far from equilibrium. The thermodynamic electron temperature, pressure and chemical potential have been introduced through the derivatives of the electron entropy. It is demonstrated that under usual conditions in cold plasmas, e.g. when the electron distribution function possesses the Maxwellian, Druyvestein or Kappa functional forms, kinetic and thermodynamic electron temperatures yield the same value.
Enero, 2014 | DOI: 10.1209/0295-5075/105/15001
2013
2013
Reactividad de Sólidos
Bio-inspired mechanochemical synthesis of semiconductor nanomaterial using eggshell membrane
Balaz, M; Balaz, P; Sayagues, MJ; Zorkovska, AMaterials Science in Semiconductor Processing, 16 (2013) 1899-1903
Show abstract ▽
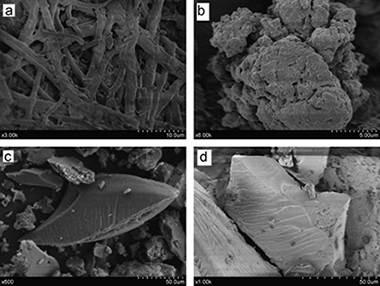
Eggshell membrane and lead acetate were successfully used as precursors for the mechanochemical synthesis of lead sulphide nanocrystals with crystallite sizes ∼8 nm. XRD, specific surface area measurements, SEM and EDX were used to characterise the synthesised material. The mechanochemical synthesis follows three-step mechanism. The “fish-like” grains with sizes around 30 μm were obtained.
Diciembre, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.mssp.2013.06.024
- ‹ anterior
- 288 of 420
- siguiente ›














