Artículos SCI
2013
2013
Reactividad de Sólidos
Arsenic sorption by nanocrystalline magnetite: An example of environmentally promising interface with geosphere
Bujnakova, Z; Balaz, P; Zorkovska, A; Sayagues, MJ; Kovac, J; Timko, MJournal of Hazardous Materials, 262 (2013) 1204-1212
Show abstract ▽
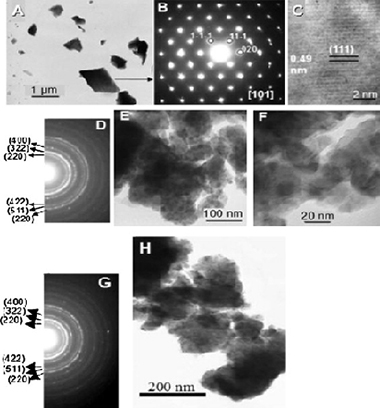
In this paper, the sorption of arsenic onto nanocrystalline magnetite mineral Fe3O4 was studied in a model system. Nanocrystalline magnetite was produced by mechanical activation in a planetary ball mill from natural microcrystalline magnetite. As a consequence of milling, the specific surface area increased from 0.1 m2/g to 11.9 m2/g and the surface site concentration enhanced from 2.2 sites/nm2 to 8.4 sites/nm2. These changes in surface properties of magnetite lead to the enhancement of arsenic removal from model system. The best sorption ability was achieved with magnetite sample activated for 90 min. In this case the sample was able to absorb around 4 mg/g. The structural changes of magnetite were also observed and the new hematite phase was detected after 120 min of milling. A good correlation between the decreasing particle size, increasing specific surface area and reduction of saturation magnetization was found. In desorption study, KOH and NaOH were found as the best eluents where more than 70% of arsenic was released back into the solution. The principal novelty of the paper is that mineral magnetite, truly one nature's gift can be used after “smart” milling (mechanical activation) as an effective arsenic sorbent.
Noviembre, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.03.007
Materiales Coloidales
Synthesis of metallic silver nanoparticles and silver organometallic nanodisks mediated by extracts of Capsicum annuum var. aviculare (piquin) fruits
Mendoza-Resendez, R; Nunez, NO; Barriga-Castro, ED; Luna, CRSC Advances, 43 (2013) 20765-20771
Show abstract ▽
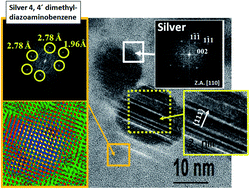
Silver-based nanostructures were prepared through reduction/oxidation reactions of aqueous silver nitrate solutions mediated by extracts of red fruits of the piquin pepper (Capsicum annuum var. aviculare) at room temperature. Detailed morphological and microstructural studies using X-ray diffraction, conventional and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy and selected area electron diffraction revealed that the product was constituted by three kinds of nanoparticles. One of them was composed of twinned metallic silver nanoparticles with a size of few nanometers. Other kind of particles was ultrafine disk-like single crystals of silver 4,4′-dimethyldiazoaminobenzene, being in our best knowledge the first time that this compound is reported in the form of nanoparticles. Both kinds of nanoparticles experienced processes of self-assembly and subsequent grain growth to form the third kind of nanoparticles. Such resulting nanostructures are monocrystalline and flattened metallic silver nanoparticles that have diameters around tens of nanometers, the [112] direction perpendicular to the particle plane, and are coated by a surface organometallic layer and residues of biomolecules. The ultraviolet-visible spectrum of the biosynthesized product showed a surface plasmon resonance (SPR) extinction band with an absorbance maximum at around 400 nm, thereby confirming the presence of fine Ag particles. Studies carried out by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy indicated that the principal active compounds responsible of the reduction of the Ag ions are proteins and capsaicin (through the amino groups) and phenolic compounds (through hydroxyl groups).
Noviembre, 2013 | DOI: 10.1039/C3RA43524E
Reactividad de Sólidos
Formation mechanism of ZrB2–Al2O3 nanocomposite powder by mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction
Jalaly, M; Bafghi, MS; Tamizifar, M; Gotor, FJJournal of Materials Science, 48 (2013) 7557-7567
Show abstract ▽
ZrB2–Al2O3 nanocomposite powder was produced by aluminothermic reduction in Al/ZrO2/B2O3 system. In this research, high energy ball milling was used to produce the necessary conditions to induce a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction. The ignition time of the composite formation was found to be about 13 min. The synthesis mechanism in this system was investigated by examining the corresponding sub-reactions as well as changing the stoichiometry of reactants. Thermal behavior of the system was also studied.
Noviembre, 2013 | DOI: 10.1007/s10853-013-7571-7
Reactividad de Sólidos
Reversible reactions of Ni and Pd hydroxo pincer complexes [( iPrPCP)M-OH] with CO2: Solid-state study of the decarboxylation of the monomeric bicarbonate complexes [(i PrPCP)M-OCOOH] (M = Ni, Pd)
Martinez-Prieto, LM; Real, C; Avila, E; Alvarez, E; Palma, P; Campora, JEuropean Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 32 (2013) 5555-5566
Show abstract ▽
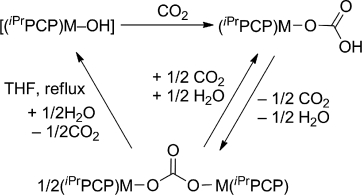
Monomeric Ni and Pd hydroxides stabilized by the iPrPCP pincer ligand react with CO2 to give labile terminal bicarbonate complexes that readily lose CO2 and water to give binuclear carbonate complexes. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) has been used to monitor the decomposition of both bicarcabonates in the solid state. When the carbonate complexes are heated under reflux in thf in the presence of water, full decarboxylation takes place, restoring the starting hydroxides and demonstrating that CO2 insertion is a fully reversible process. The decarboxylation of the nickel carbonate complex is completed more readily, suggesting that the reaction of the Pd hydroxide with CO2 is more favourable than that of its nickel counterpart. This is supported by DFT calculations, which also shows that CO2 insertion takes place through a concerted Lipscomb-type mechanism. Monomeric Ni and Pd hydroxides stabilized by the iPrPCP pincer ligand react with CO2 to give labile terminal hydrogen carbonate complexes that readily lose CO2 and water to give binuclear carbonate complexes.
Noviembre, 2013 | DOI: 10.1002/ejic.201300995
Materiales Coloidales - Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Monoclinic–Tetragonal Heterostructured BiVO4 by Yttrium Doping with Improved Photocatalytic Activity
Usai, S; Obregon, S; Becerro, AI; Colon, GJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 117 (2013) 24479-24484
Show abstract ▽
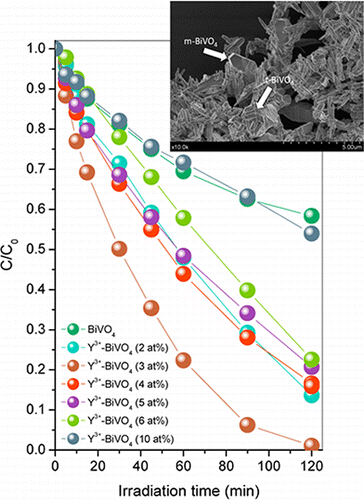
Yttrium-doped BiVO4 has been synthesized by means of a surfactant free hydrothermal method having good photoactivities under sun-like excitation for the degradation of Methylene Blue (MB). From the structural and morphological characterization it has been stated that the presence of Y3+ induces the progressive stabilization of the tetragonal phase and the slight higher surface area values. By following the tetragonal cell parameters, the substitutional incorporation of Y3+ into the BiVO4 tetragonal lattice might be considered. Best photocatalytic performances were attained for the samples with Y3+ content of 3.0 at. % for which the MB degradation rate constant appears 2-fold higher. Furthermore, photoactivities for visible-light-driven O2 evolution demonstrate that the photocatalytic performance of the best Y-doped system (initial rate of O2 evolution, 285 μmol g–1 h–1) was more than 5 times that of undoped m-BiVO4 (initial rate of O2 evolution, 53 μmol g–1 h–1). The occurrence of Y3+ doping and a monoclinic–tetragonal heterostructured BiVO4 system induces the higher photocatalytic activities. PL analysis provides a clear evidence of the lower charge carriers recombination in heterostructured yttrium-doped systems.
Octubre, 2013 | DOI: 10.1021/jp409170y
- ‹ anterior
- 291 of 420
- siguiente ›














