Artículos SCI
2013
2013
Materiales Coloidales - Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Monoclinic–Tetragonal Heterostructured BiVO4 by Yttrium Doping with Improved Photocatalytic Activity
Usai, S; Obregon, S; Becerro, AI; Colon, GJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 117 (2013) 24479-24484
Show abstract ▽
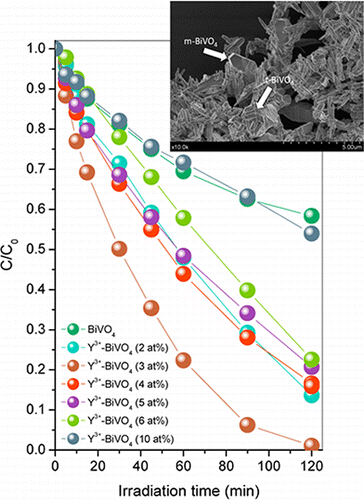
Yttrium-doped BiVO4 has been synthesized by means of a surfactant free hydrothermal method having good photoactivities under sun-like excitation for the degradation of Methylene Blue (MB). From the structural and morphological characterization it has been stated that the presence of Y3+ induces the progressive stabilization of the tetragonal phase and the slight higher surface area values. By following the tetragonal cell parameters, the substitutional incorporation of Y3+ into the BiVO4 tetragonal lattice might be considered. Best photocatalytic performances were attained for the samples with Y3+ content of 3.0 at. % for which the MB degradation rate constant appears 2-fold higher. Furthermore, photoactivities for visible-light-driven O2 evolution demonstrate that the photocatalytic performance of the best Y-doped system (initial rate of O2 evolution, 285 μmol g–1 h–1) was more than 5 times that of undoped m-BiVO4 (initial rate of O2 evolution, 53 μmol g–1 h–1). The occurrence of Y3+ doping and a monoclinic–tetragonal heterostructured BiVO4 system induces the higher photocatalytic activities. PL analysis provides a clear evidence of the lower charge carriers recombination in heterostructured yttrium-doped systems.
Octubre, 2013 | DOI: 10.1021/jp409170y
Materiales Coloidales
Crystal Structure and Luminescent Properties of Eu3+-Doped A-La2Si2O7 Tetragonal Phase Stabilized by Spray Pyrolysis Synthesis
Fernandez-Carrion, Alberto J.; Ocana, Manuel; Florian, Pierre; Garcia-Sevillano, Jorge; Cantelar, Eugenio; Fitch, Andrew N.; Suchomel, Matthew R.; Becerro, Ana I.Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 117 (2013) 20876-20886
Show abstract ▽
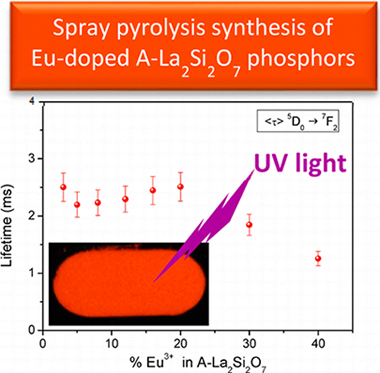
Pure A-La2Si2O7 powder has been synthesized through a spray pyrolysis method followed by calcination at 1100 degrees C for 15 h. The crystallographic structure, refined from the synchrotron powder diffraction pattern of the sample, showed tetragonal symmetry with space group P4(1), a = 6.83565(1) angstrom, and c = 24.84133(1) angstrom. The Si-29 and La-139 NMR spectra have been described here for the first time in the literature and could be simulated with four Si and four La resonances, respectively, in good agreement with the presence of four Si and four La crystallographic sites in the unit cell. The same synthesis method was 2 successful for the synthesis of Eu3+-doped A-La2Si2O7 (%Eu = 3-40). The analysis of the unit cell volumes indicated that Eu3+ replaces La3+ in the unit cell for all Eu3+ substitution levels investigated. However, anomalous diffraction data indicated that the La/Eu substitution mechanism was not homogeneous, but Eu much prefers to occupy the RE3 sites. The Eu-doped A-La2Si2O7 phosphors thus synthesized exhibited a strong orange-red luminescence after excitation at 393 nm. Lifetime measurements indicated that the optimum phosphor was that with an Eu3+ content of 20%, which showed a lifetime of 2.3 ms. The quantum yield of the latter was found to be 12% at 393 nm excitation. These experimental observations together with the high purity of the phase obtained by the proposed spray pyrolysis method make this material an excellent phosphor for optoelectronic applications.
Octubre, 2013 | DOI: 10.1021/jp407172z
Reactividad de Sólidos
Mechanosynthesis of nanocrystalline ZrB2-based powders by mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction method
Jalaly, M; Bafghi, MS; Tamizifar, M; Gotor, FJAdvances in Applied Ceramics, 112 (2013) 383-388
Show abstract ▽
Preparation of nanocrystalline ZrB2-based powder by aluminothermic and magnesiothermic reductions in M/ZrO2/B2O3 (M=Al or Mg) systems was investigated. In this research, high energy ball milling was employed to persuade necessary conditions for the occurrence of a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction (MSR). The course of MSR reactions were recorded by a noticeable pressure rise in the system during milling. Ignition times for ZrB2 formation by aluminothermic and magnesiothermic reductions were found to be 13 and 6 min, respectively. Zirconium diboride formation mechanism in both systems was explained through the analysis of the relevant sub-reactions.
Octubre, 2013 | DOI: 10.1179/1743676113Y.0000000091
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Synthesis and tribological properties of WSex films prepared by magnetron sputtering
Dominguez-Meister, S; Justo, A; Sanchez-Lopez, JCMaterials Chemistry and Physics, 142 (2013) 186-194
Show abstract ▽
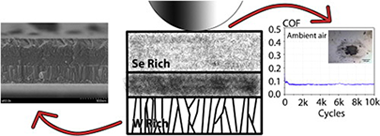
WSex films with variable Se/W ratio were deposited by non-reactive r.f. magnetron sputtering from WSe2 target changing the applied d.c. pulsed bias conditions and substrate temperature. The structural and chemical properties were measured by cross-sectional scanning electron microscopy (X-SEM), energy dispersive analysis (EDX), X-ray diffraction (XRD), Raman and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The tribological properties were measured in ambient air (RH = 30–40%) and dry nitrogen by means of a reciprocating ball-on-disk tribometer. A clear correlation was found between the Se/W ratio and the measured friction coefficient displaying values below 0.1 (in ambient air) and 0.03 (in dry N2) for ratios Se/W ≥ 0.6 as determined by electron probe microanalysis (EPMA). The results demonstrated that notable tribological results could be obtained even in ambient air (friction ≤ 0.07 and wear rate ≈10−7 mm3 Nm−1) by controlling the film microstructure and chemical composition. By incorporating carbon, wear and chemical resistance can be gained by formation of non-stoichiometric carbides and/or alloying into the defective WSex hexagonal structure. The existence of a WSe2 rich interfacial layer (either on the ball scar or embedded in the film track) was evidenced by Raman in low friction conditions. The improvement in tribological performance is therefore obtained by means of layered WSex, the formation of gradient composition from metallic W (hard) to WSe2 (lubricant) and carbon incorporation.
Octubre, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2013.07.004
Materiales Coloidales
Perfectly Transparent Sr3Al2O6 Polycrystalline Ceramic Elaborated from Glass Crystallization
Alahrache, S; Al Saghir, K; Chenu, S; Veron, E; Meneses, DD; Becerro, AI; Ocana, M; Moretti, F; Patton, G; Dujardin, C; Cusso, F; Guin, JP; Nivard, M; Sangleboeuf, JC; Matzen, G; Allix, MChemistry of Materials, 25 (2013) 4017-4024
Show abstract ▽
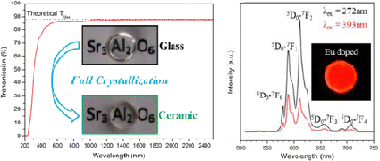
The highly visible and infrared (up to 6 mu m) transparent Sr3Al2O6 polycrystalline ceramic was obtained by full crystallization of the corresponding glass composition. The glass synthesis and the direct congruent crystallization processes are described, and the material transparency is discussed in light of its microstructure. This new transparent ceramic exhibits a high density (i.e., complete absence of porosity) and micrometer-scale crystallites with very thin grain boundaries. These microstructural characteristics, inherent to the preparation method, minimize light scattering and demonstrate the advantages of this synthesis route compared to the high-pressure process used for the few reported transparent polycrystalline materials. This Sr3Al2O6 ceramic shows a H = 10.5 GPa hardness, a E-r = 150 GPa reduced elasticity modulus, and a 9.6 x 10(-6) K-1 thermal expansion coefficient. Such a transparent strontium aluminate ceramic opens the way to a wide range of applications, especially photonics when doped by various doping agents. As examples, the luminescence of Sr3Al2O6:Eu3+ and Sr3Al2O6:Er3+, which show strong emissions in the visible and infrared ranges, respectively, is presented. Moreover, the Sr3Al2O6:Ce3+ material was found to exhibit scintillation properties under X-ray excitation. Interestingly, the analogous Sr3Ga2O6 transparent polycrystalline ceramic material could equally be prepared using the same elaboration method, although its hygroscopicity prevents the preservation of its high transparency under normal conditions. The establishment of the key factors for the transparency of this economical and innovative synthesis method should enable the prediction of new classes of technologically relevant transparent ceramics.
Octubre, 2013 | DOI: 10.1021/cm401953d
- ‹ anterior
- 292 of 420
- siguiente ›














