Artículos SCI
2013
2013
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
In situ imaging and strain determination during fracture in a SiC/SiC ceramic matrix composite
Ramirez-Rico, J; Stolzenburg, F; Almer, JD; Routbort, JL; Singh, D; Faber, KTScripta Materialia, 69 (2013) 497-500
Show abstract ▽

A combined imaging and microdiffraction technique using high-energy synchrotron X-rays is described and used to reveal microstructure, damage and strain evolution around notches in SiC/SiC composites. This technique allows for monitoring the material for cracks while loading and mapping the strain distribution in fibers and matrix with a resolution of tens of microns. We show that at current resolutions this technique is capable of measuring the strain distribution near crack tips in ceramic matrix composites and observe load transfer effects.
Octubre, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2013.05.032
Reactividad de Sólidos
Evidence of nanograin cluster coalescence in spark plasma sintered α-Al2O3
Morales-Rodriguez, A; Poyato, R; Gallardo-Lopez, A; Munoz, A; Dominguez-Rodriguez, AScripta Materialia, 69 (2013) 529-532
Show abstract ▽
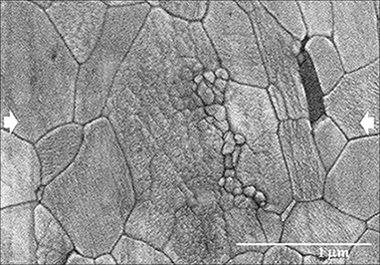
The aim of this study is to elucidate the coarsening kinetics involved during densification of fine-grained pure α-alumina by spark plasma sintering. Low temperature and short dwell time sintering conditions were used to preserve the nanocrystalline structure of the starting commercial powder (about 50 nm). Notwithstanding the above, submicron grain coarsened microstructures have been developed. The microstructure evolution of alumina under different sintering conditions points to a nanograin rotation densification mechanism as being responsible for the fast grain growth observed.
Octubre, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2013.06.019
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Gold(III) stabilized over ionic liquids grafted on MCM-41 for highly efficient three-component coupling reactions
Bobadilla, LF; Blasco, T; Odriozola, JAPhysical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 39 (2013) 16927-16934
Show abstract ▽
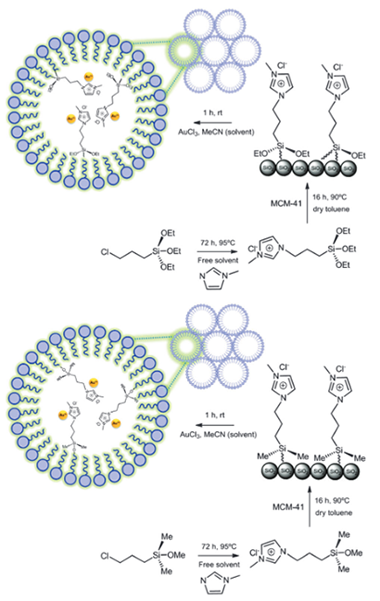
Two alkoxysilyl-modified ionic liquids (ILs) have been synthesized and further grafted onto mesoporous silica, MCM-41; these ionic liquids were used for dispersing AuCl3 catalysts that activate C–H bonds as required for the synthesis of propargylamines by coupling alkyne, aldehyde and amine (A3 coupling) species. 29Si NMR experiments demonstrate the formation of covalent bonds between alkoxysilyl-modified Bmim IL and the MCM-41 surface through silanol groups. The catalytic activities of Au(III)-supported MCM-41 and Au(III) homogeneous catalysts are lower than those obtained for the IL functionalized Au–MCM-41 solids when the same gold loading is considered. An interaction between Au(III) species and the IL is proposed for explaining the stabilization of gold(III) species. However, successive reaction cycles result in a decrease in the catalytic activity that has been explained on the basis of gold leaching.
Octubre, 2013 | DOI: 10.1039/C3CP52924J
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Thermal conductivity of wood-derived graphite and copper–graphite composites produced via electrodeposition
Johnson, MT; Childers, AS; Ramirez-Rico, J; Wang, H; Faber, KTComposites Part A: Applied Science and Manufaturing, 63 (2013) 182-189
Show abstract ▽
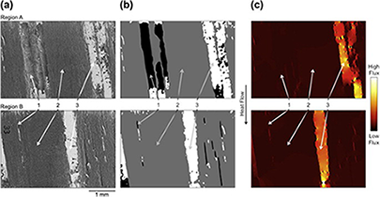
The thermal conductivity of wood-derived graphite and graphite/copper composites was studied both experimentally and using finite element analysis. The unique, naturally-derived, anisotropic porosity inherent to wood-derived carbon makes standard porosity-based approximations for thermal conductivity poor estimators. For this reason, a finite element technique which uses sample microstructure as model input was utilized to determine the conductivity of the carbon phase independent of porosity. Similar modeling techniques were also applied to carbon/copper composite microstructures and predicted conductivities compared well to those determined via experiment.
Octubre, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2013.06.009
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Role of activated carbon on the increased photocatalytic activity of AC/Bi2WO6 coupled materials
Murcia-López, S; Navío, J.A.; Hidalgo, M.C.Applied Catalysis A: General, 466 (2013) 51-59
Show abstract ▽
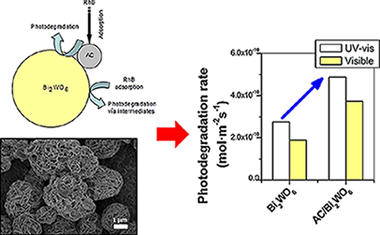
The photocatalytic activities of several Bi2WO6 and TiO2/Bi2WO6 materials with different activated carbon (AC) contents were studied for Rhodamine B (RhB) (and Phenol) photodegradation under UV–vis and vis illumination. A wide characterization of the materials was carried out. The addition of AC strongly affected the Bi2WO6 morphology although not the crystalline phase. Even in the material with the lowest AC content (2 wt% nominal content) a structure with hierarchical porosity was formed. AC presence increased the initial reaction rates in the degradation of RhB. An important improvement in the photoactivity under both UV–vis and vis illumination conditions was obtained with the lowest AC content (2 wt%) when compared to the pristine material Bi2WO6 or to the systems with higher AC additions. AC/TiO2/Bi2WO6 materials were also improved in comparison to the TiO2/Bi2WO6 heterostructure without carbon. The improvement cannot be only ascribed to adsorption capability and surface area effects. A mechanism explaining the role of AC on the photocatalytic activity improvement is proposed.
Septiembre, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2013.06.022
- ‹ anterior
- 293 of 420
- siguiente ›














