Artículos SCI
2013
2013
Materiales Coloidales
Small Particle-Size Talc Is Associated with Poor Outcome and Increased Inflammation in Thoracoscopic Pleurodesis
Arellano-Orden, E; Romero-Falcon, A; Juan, JM; Jurado, MO; Rodriguez-Panadero, F; Montes-Worboys, ARespiration, 86 (2013) 201-209
Show abstract ▽
Rationale: Talc is very effective for pleurodesis, but there is concern about complications, especially acute respiratory distress syndrome. Objectives: It was the aim of this study to investigate if talc with a high concentration of small particles induces greater production of cytokines, and if pleural tumor burden has any influence on the local production and spillover of cytokines to the systemic circulation and eventual complications. Methods: We investigated 227 consecutive patients with malignant effusion submitted to talc pleurodesis. One hundred and three patients received ‘small-particle talc' (ST; containing about 50% particles <10 µm) and 124 received ‘large-particle talc' (with <20% particles <10 µm). Serial samples of both pleural fluid and blood were taken before and 3, 24, 48 and 72 h after thoracoscopy. Also, mesothelial cells were stimulated with both types of talc in vitro. Measurements and Results: Interleukin-8, tumor necrosis factor-α, vascular endothelial growth factor, basic fibroblast growth factor and thrombin-antithrombin complex were measured in all samples. Early death (<7 days after talc) occurred in 8 of 103 patients in the ST and in 1 of 124 in the ‘large-particle talc' group (p = 0.007). Patients who received ST had significantly higher proinflammatory cytokines in pleural fluid and serum after talc application, and also in supernatants of the in vitro study. Pleural tumor burden correlated positively with proinflammatory cytokines in serum, suggesting that advanced tumor states induce stronger systemic reactions after talc application. Conclusions: ST provokes a strong inflammatory reaction in both pleural space and serum, which is associated with a higher rate of early deaths observed in patients receiving it.
Septiembre, 2013 | DOI: 10.1159/000342042
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Enhancement of visible light-induced surface photo-activity of nanostructured N–TiO2 thin films modified by ion implantation
Romero-Gomez, P; Lopez-Santos, C; Borras, A; Espinos, JP; Palmero, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARChemical Physics Letters, 582 (2013) 95-99
Show abstract ▽
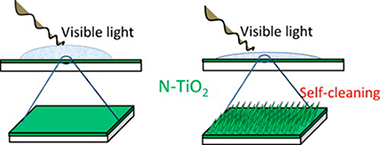
This work reports the morphological and chemical modifications induced in TiO2 thin films by bombardment with high energy N+ ions at different temperatures and their different photo-activity responses after implantation under visible and UV light illumination. When implanted samples are illuminated with visible light, no dye photo-decolouration takes place despite that light transformed the surfaces from hydrophobic to hydrophilic. In agreement with the Wenzel model of wetting, correlation is found between visible light photo-activity and film morphology. We conclude that the photo-activity response can be separated into shallow and Schottky barrier photo-activity, this latter involving a thicker layer of material.
Septiembre, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cplett.2013.07.025
Reactividad de Sólidos
Hallmarks of mechanochemistry: from nanoparticles to technology
Balaz, P; Achimovicova, M; Balaz, M; Billik, P; Cherkezova-Zheleva, Z; Criado, JM; Delogu, F; Dutkova, E; Gaffet, E; Gotor, FJ; Kumar, R; Mitov, I; Rojac, T; Senna, M; Streletskii, A; Wieczorek-Ciurowa, KChemical Society Reviews, 42 (2013) 7571-7637
Show abstract ▽
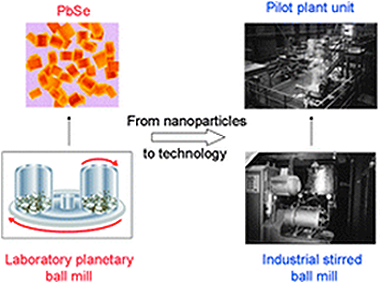
The aim of this review article on recent developments of mechanochemistry (nowadays established as a part of chemistry) is to provide a comprehensive overview of advances achieved in the field of atomistic processes, phase transformations, simple and multicomponent nanosystems and peculiarities of mechanochemical reactions. Industrial aspects with successful penetration into fields like materials engineering, heterogeneous catalysis and extractive metallurgy are also reviewed. The hallmarks of mechanochemistry include influencing reactivity of solids by the presence of solid-state defects, interphases and relaxation phenomena, enabling processes to take place under non-equilibrium conditions, creating a well-crystallized core of nanoparticles with disordered near-surface shell regions and performing simple dry time-convenient one-step syntheses. Underlying these hallmarks are technological consequences like preparing new nanomaterials with the desired properties or producing these materials in a reproducible way with high yield and under simple and easy operating conditions. The last but not least hallmark is enabling work under environmentally friendly and essentially waste-free conditions (822 references).
Septiembre, 2013 | DOI: 10.1039/C3CS35468G
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Role of activated carbon on the increased photocatalytic activity of AC/Bi2WO6 coupled materials
Murcia-López, S; Navío, J.A.; Hidalgo, M.C.Applied Catalysis A: General, 466 (2013) 51-59
Show abstract ▽
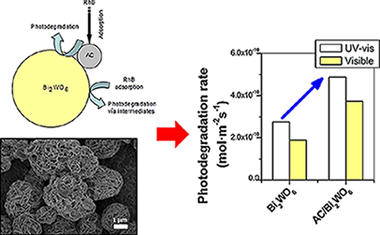
The photocatalytic activities of several Bi2WO6 and TiO2/Bi2WO6 materials with different activated carbon (AC) contents were studied for Rhodamine B (RhB) (and Phenol) photodegradation under UV–vis and vis illumination. A wide characterization of the materials was carried out. The addition of AC strongly affected the Bi2WO6 morphology although not the crystalline phase. Even in the material with the lowest AC content (2 wt% nominal content) a structure with hierarchical porosity was formed. AC presence increased the initial reaction rates in the degradation of RhB. An important improvement in the photoactivity under both UV–vis and vis illumination conditions was obtained with the lowest AC content (2 wt%) when compared to the pristine material Bi2WO6 or to the systems with higher AC additions. AC/TiO2/Bi2WO6 materials were also improved in comparison to the TiO2/Bi2WO6 heterostructure without carbon. The improvement cannot be only ascribed to adsorption capability and surface area effects. A mechanism explaining the role of AC on the photocatalytic activity improvement is proposed.
Septiembre, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2013.06.022
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
On the different photocatalytic performance of BiVO4 catalysts for Methylene Blue and Rhodamine B degradation
Obregon, S; Colon, GJournal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical, 376 (2013) 40-47
Show abstract ▽
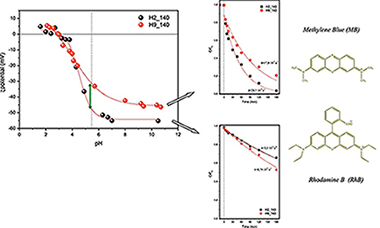
BiVO4 hierarchical structures were synthesized by means of a surfactant free hydrothermal method having good photoactivities for the degradation of Methylene Blue and Rhodamine B under UV–vis irradiation. From the structural and morphological characterization it has been stated that BiVO4 present the monoclinic crystalline phase with different morphologies depending on the pH value. For Methylene Blue the photodegradation rate is strongly affected by the crystallite size and higher (0 0 4) facet exposition. On the contrary, for Rhodamine B, the ζ-potential of the surface clearly determines the photocatalytic performance of BiVO4 catalyst.
Septiembre, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.molcata.2013.04.012
- ‹ anterior
- 295 of 421
- siguiente ›














