Artículos SCI
2013
2013
Materiales Avanzados
Planning collection and solid waste flow (construction and demolition, concrete, ceramics and others) by utilizing a computerized tool for sustainable management
Garzon, E; Sanchez-Soto, PJBoletin de la Sociedad Española de Cerámica y Vidrio, 5 (2013) V-XIV (Notas Técnicas)
Show abstract ▽
Se presenta un procedimiento para la planificación de recogida y flujo de los residuos sólidos (de construcción y demolición, hormigón, cerámica, vidrio y otros) basado en la utilización de una herramienta informatizada, para conseguir una optimización de su gestión. Dicho procedimiento parte de normativa establecida según un Plan Director Territorial de la Gestión de Residuos Sólidos Urbanos (RSU) aprobado en una Comunidad Autónoma, en este caso se particulariza a la de Andalucía, tomando como ejemplo el volumen de residuos que se producen en una colectividad de tamaño medio (provincia de Almería), siendo extensible a otras mayores en población y territorio, disponiendo de datos actualizados.
El procedimiento utiliza una herramienta informática de gran difusión en el mundo, como es Google Earth y, de este modo, genera un número de “Centros deTransferencia” con objeto de minimizar el gasto de transporte, partiendo de una premisa previa en cuanto a distancia entre núcleos poblacionales y centros de tratamiento. Los Centros generados con la aplicación del procedimiento se pueden visualizar en un mapa topográfico, con áreas de influencia y vías de acceso a los mismos y se le pueden asociar una serie de datos tabulados con información adicional de utilidad. El procedimiento propuesto se va retroalimentando de manera constante con datos reales e información de campo, permitiendo a las empresas que producen residuos de distinta tipología como son los residuos de construcción y demolición principalmente, pero también hormigón, cerámica, vidrio, mezclas de todos ellos, residuos clasificados como peligrosos e incluso de otros materiales, a la propia administración y a la sociedad, en general, conocer las tasas de cada planta de tratamiento y qué se hace con los residuos entregados para contribuir a la reducción del impacto medioambiental de los mismos y a su gestión sostenible.
Septiembre, 2013 | DOI: 10.3989/cyv.2013.v52.i5
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Enhancement of visible light-induced surface photo-activity of nanostructured N–TiO2 thin films modified by ion implantation
Romero-Gomez, P; Lopez-Santos, C; Borras, A; Espinos, JP; Palmero, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARChemical Physics Letters, 582 (2013) 95-99
Show abstract ▽
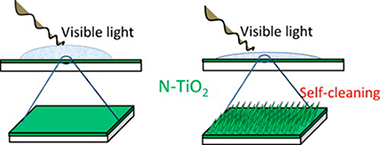
This work reports the morphological and chemical modifications induced in TiO2 thin films by bombardment with high energy N+ ions at different temperatures and their different photo-activity responses after implantation under visible and UV light illumination. When implanted samples are illuminated with visible light, no dye photo-decolouration takes place despite that light transformed the surfaces from hydrophobic to hydrophilic. In agreement with the Wenzel model of wetting, correlation is found between visible light photo-activity and film morphology. We conclude that the photo-activity response can be separated into shallow and Schottky barrier photo-activity, this latter involving a thicker layer of material.
Septiembre, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cplett.2013.07.025
Reactividad de Sólidos
Hallmarks of mechanochemistry: from nanoparticles to technology
Balaz, P; Achimovicova, M; Balaz, M; Billik, P; Cherkezova-Zheleva, Z; Criado, JM; Delogu, F; Dutkova, E; Gaffet, E; Gotor, FJ; Kumar, R; Mitov, I; Rojac, T; Senna, M; Streletskii, A; Wieczorek-Ciurowa, KChemical Society Reviews, 42 (2013) 7571-7637
Show abstract ▽
The aim of this review article on recent developments of mechanochemistry (nowadays established as a part of chemistry) is to provide a comprehensive overview of advances achieved in the field of atomistic processes, phase transformations, simple and multicomponent nanosystems and peculiarities of mechanochemical reactions. Industrial aspects with successful penetration into fields like materials engineering, heterogeneous catalysis and extractive metallurgy are also reviewed. The hallmarks of mechanochemistry include influencing reactivity of solids by the presence of solid-state defects, interphases and relaxation phenomena, enabling processes to take place under non-equilibrium conditions, creating a well-crystallized core of nanoparticles with disordered near-surface shell regions and performing simple dry time-convenient one-step syntheses. Underlying these hallmarks are technological consequences like preparing new nanomaterials with the desired properties or producing these materials in a reproducible way with high yield and under simple and easy operating conditions. The last but not least hallmark is enabling work under environmentally friendly and essentially waste-free conditions (822 references).
Septiembre, 2013 | DOI: 10.1039/C3CS35468G
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Role of activated carbon on the increased photocatalytic activity of AC/Bi2WO6 coupled materials
Murcia-López, S; Navío, J.A.; Hidalgo, M.C.Applied Catalysis A: General, 466 (2013) 51-59
Show abstract ▽
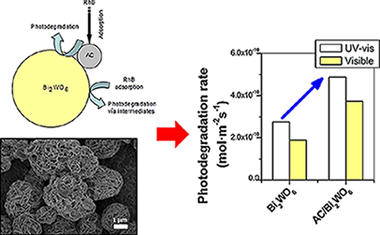
The photocatalytic activities of several Bi2WO6 and TiO2/Bi2WO6 materials with different activated carbon (AC) contents were studied for Rhodamine B (RhB) (and Phenol) photodegradation under UV–vis and vis illumination. A wide characterization of the materials was carried out. The addition of AC strongly affected the Bi2WO6 morphology although not the crystalline phase. Even in the material with the lowest AC content (2 wt% nominal content) a structure with hierarchical porosity was formed. AC presence increased the initial reaction rates in the degradation of RhB. An important improvement in the photoactivity under both UV–vis and vis illumination conditions was obtained with the lowest AC content (2 wt%) when compared to the pristine material Bi2WO6 or to the systems with higher AC additions. AC/TiO2/Bi2WO6 materials were also improved in comparison to the TiO2/Bi2WO6 heterostructure without carbon. The improvement cannot be only ascribed to adsorption capability and surface area effects. A mechanism explaining the role of AC on the photocatalytic activity improvement is proposed.
Septiembre, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2013.06.022
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Hydrogen production using Pt-loaded TiO2 photocatalysts
Melian, EP; Lopez, CR; Mendez, AO; Diaz, OG; Suarez, MN; Rodriguez, JMD; Navio, JA; Hevia, DFInternational Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 38 (2013) 11737-11748
Show abstract ▽
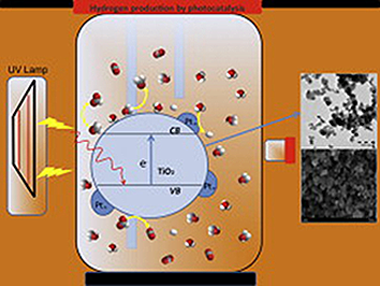
A series of synthesised TiO2-based and commercial photocatalysts were modified by Pt photodeposition and a study made of their photocatalytic activity in hydrogen production. The modified commercial photocatalysts were Evonik P25, Kronos vlp7000 and Hombikat UV-100, and the other modified photocatalysts were synthesised by our group using sol–gel and sol–gel hydrothermal processes (SG400, SG750 and HT). Pt weight percentages used in the study were 0.5, 1.0 and 2.1 wt.% (Pt/TiO2). The photocatalysts were extensively characterised by X-ray diffraction (XRD), UV–vis diffuse reflectance, Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) surface area measurement, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM–EDX), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and laser light dispersion. Methanol (25% vol.) was used as sacrificial agent over the 8 h of the hydrogen production tests and measurements were taken of the final concentrations of formaldehyde and formic acid as well as initial and final TOC. Photoactivity of all photocatalysts increased in the presence of Pt. The most efficient of the synthesised photocatalysts was SG750 and of the commercial photocatalysts P25. Maximum production of SG750 was 1846 μmol h−1 at 1.0 wt.% Pt and its production per surface unit was notably higher than that of P25.
Septiembre, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.07.006
- ‹ anterior
- 296 of 421
- siguiente ›














