Artículos SCI
2013
2013
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Hydrogen production using Pt-loaded TiO2 photocatalysts
Melian, EP; Lopez, CR; Mendez, AO; Diaz, OG; Suarez, MN; Rodriguez, JMD; Navio, JA; Hevia, DFInternational Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 38 (2013) 11737-11748
Show abstract ▽
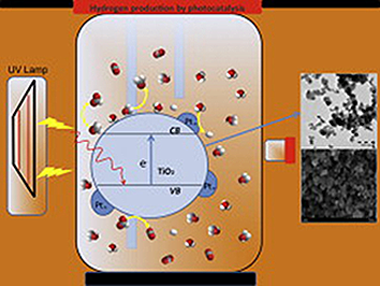
A series of synthesised TiO2-based and commercial photocatalysts were modified by Pt photodeposition and a study made of their photocatalytic activity in hydrogen production. The modified commercial photocatalysts were Evonik P25, Kronos vlp7000 and Hombikat UV-100, and the other modified photocatalysts were synthesised by our group using sol–gel and sol–gel hydrothermal processes (SG400, SG750 and HT). Pt weight percentages used in the study were 0.5, 1.0 and 2.1 wt.% (Pt/TiO2). The photocatalysts were extensively characterised by X-ray diffraction (XRD), UV–vis diffuse reflectance, Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) surface area measurement, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM–EDX), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and laser light dispersion. Methanol (25% vol.) was used as sacrificial agent over the 8 h of the hydrogen production tests and measurements were taken of the final concentrations of formaldehyde and formic acid as well as initial and final TOC. Photoactivity of all photocatalysts increased in the presence of Pt. The most efficient of the synthesised photocatalysts was SG750 and of the commercial photocatalysts P25. Maximum production of SG750 was 1846 μmol h−1 at 1.0 wt.% Pt and its production per surface unit was notably higher than that of P25.
Septiembre, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.07.006
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Structure-mediated transition in the behavior of elastic and inelastic properties of beach tree bio-carbon
Kardashev, BK; Orlova, TS; Smirnov, BI; Gutierrez, A; Ramirez-Rico, JPhysics of the Solid State, 55 (2013) 1884-1891
Show abstract ▽
Microstructural characteristics and amplitude dependences of the Young modulus E and of internal friction (logarithmic decrement δ) of bio-carbon matrices prepared from beech tree wood at different carbonization temperatures T carb ranging from 600 to 1600°C have been studied. The dependences E(T carb) and δ(T carb) thus obtained revealed two linear regions of increase of the Young modulus and of decrease of the decrement with increasing carbonization temperature, namely, ΔE ∼ AΔT carb and Δδ ∼ BΔT carb, with A ≈ 13.4 MPa/K and B ≈ −2.2 × 10−6 K−1 for T carb < 1000°C and A ≈ 2.5 MPa/K and B ≈ −3.0 × 10−7 K−1 for T carb > 1000°C. The transition observed in the behavior of E(T carb) and δ(T carb) at T carb = 900–1000°C can be assigned to a change of sample microstructure, more specifically, a change in the ratio of the fractions of the amorphous matrix and of the nanocrystalline phase. For T carb < 1000°C, the elastic properties are governed primarily by the amorphous matrix, whereas for T carb > 1000°C the nanocrystalline phase plays the dominant part. The structurally induced transition in the behavior of the elastic and microplastic characteristics at a temperature close to 1000°C correlates with the variation of the physical properties, such as electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and thermopower, reported in the literature.
Septiembre, 2013 | DOI: 10.1134/S1063783413090151
Reactividad de Sólidos
Kinetic studies in solid state reactions by sample-controlled methods and advanced analysis procedures
Perez-Maqueda, LA; Criado, JM; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perejon, AJournal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 113 (2013) 1447-1453
Show abstract ▽
A comparative study of both conventional rising temperature and sample-controlled methods, like constant rate thermal analysis (CRTA), is carried out after analyzing a set of solid state reactions using both methods. It is shown that CRTA avoids the influence of heat and mass transfer phenomena for a wide range of sample sizes leading to reliable kinetic parameters. On the other hand, conventional rising temperature methods yield α–T plots dependent on experimental conditions, even when using samples sizes smaller than 2 mg. Moreover, it is shown that the discrimination of overlapping processes is dramatically improved using sample-controlled methods instead of conventional heating procedures. An advanced method for performing the kinetic analysis of complex processes from a single CRTA experiment is proposed.
Septiembre, 2013 | DOI: 10.1007/s10973-013-3114-3
Reactividad de Sólidos
Pyrolysis kinetics of ethylene–propylene (EPM) and ethylene–propylene–diene (EPDM)
Perejon, A; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Gil-Gonzalez, E; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Criado, JMPolymer Degradation and Stability, 98 (2013) 1571-1577
Show abstract ▽
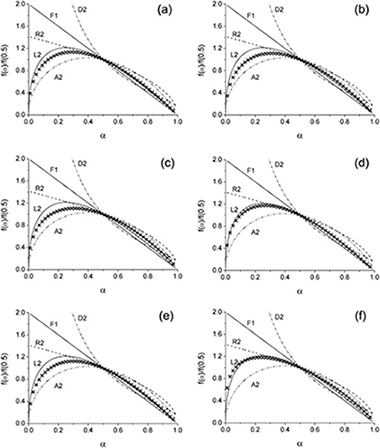
The thermal degradation kinetics of several ethylene–propylene copolymers (EPM) and ethylene–propylene–diene terpolymers (EPDM), with different chemical compositions, have been studied by means of the combined kinetic analysis. Until now, attempts to establish the kinetic model for the process have been unsuccessful and previous reports suggest that a model other than a conventional nth order might be responsible. Here, a random scission kinetic model, based on the breakage and evaporation of cleavaged fragments, is found to describe the degradation of all compositions studied. The suitability of the kinetic parameters resulting from the analysis has been asserted by successfully reconstructing the experimental curves. Additionally, it has been shown that the activation energy for the pyrolysis of the EPM copolymers decreases by increasing the propylene content. An explanation for this behavior is given. A low dependence of the EPDM chemical composition on the activation energy for the pyrolysis has been reported, although the thermal stability is influenced by the composition of the diene used.
Septiembre, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2013.06.029
Materiales Coloidales
Surface modified Eu:GdVO4 nanocrystals for optical and MRI imaging
Nuñez, Nuria O.; Rivera, Sara; Alcantara, David; de la Fuente, Jesus M.; Garcia-Sevillano, Jorge; Ocaña, ManuelDalton Transactions, 42 (2013) 10725-10734
Show abstract ▽
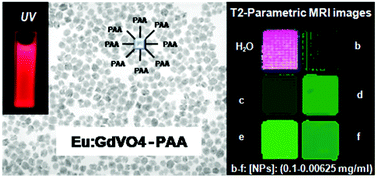
A facile solvothermal route has been developed for the preparation of europium doped gadolinium orthovanadate nanoparticles ([similar]70 nm) with tetragonal structure, based on a homogenous precipitation reaction at 120 °C from rare earth precursors (yttrium nitrate and europium nitrate) and sodium orthovanadate solutions using an ethylene glycol–water mixture as the solvent. The effects of the doping level on the luminescence properties were evaluated in order to find the optimum nanophosphors. These nanocrystals were successfully functionalized with amino (two step process) and carboxylate (one-pot process) groups provided by amino-dextran polymers (AMD) and polyacrylic acid (PAA), respectively. It was found that while the luminescent properties of both kinds of functionalized systems were similar, the colloidal stability of the PAA-modified sample was higher, because of which, it was selected to study their cytotoxicity and magnetic properties (relaxivity and phantom analyses) to assess their potentiality as multifunctional probes for both “in vitro” optical biolabels and negative contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging.
Agosto, 2013 | DOI: 10.1039/C3DT50676B
- ‹ anterior
- 297 of 421
- siguiente ›














