Artículos SCI
2013
2013
Materiales Avanzados
Historic preservation, GIS, & rural development: The case of Almería province, Spain
Cano, M; Garzon, E; Sanchez-Soto, PJApplied Geograhpy, 42 (2013) 34-47
Show abstract ▽
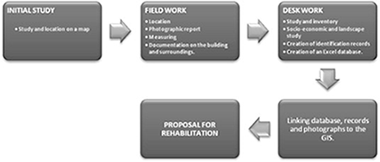
A computerized database was created, based on a Geographic Information System (GIS), with hyperlinks to the website for a Rural Development Association (Almería province, Andalusia, Spain). Thus, a catalogue of traditional rural buildings in this particular area was compiled, identifying and characterizing each one, establishing criteria for a dynamic and rational selection. The purpose to select this example was to facilitate their management by public organizations or private individuals, for their reuse, restoration or both. The cataloguing and promotion of rural architecture will contribute to creating jobs by stimulating new economic activity, such as the promotion of cultural tourism, while preserving a valuable source of information on rural culture, recovering local construction techniques, encouraging a sense of community, and making villages and rural areas more attractive to visitors. The assessment of the rehabilitation potential of rural buildings in this region has helped to establish a priority order for their reuse, and so an intervention map has been devised in terms of a “Decision Index” corresponding to each considered building.
Agosto, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apgeog.2013.04.014
Propiedades mecánicas, modelización y caracterización de cerámicos avanzados
High temperature plasticity in yttria stabilised tetragonal zirconia polycrystals (Y-TZP)
Dominguez-Rodriguez, A; Gomez-Garcia, D; Wakai, FInternational Materials Reviews, 58 (2013) 399-417
Show abstract ▽
The literature data on the superplastic deformation of high purity yttria stabilised tetragonal zirconia polycrystals is reviewed in detail. It is shown that, based on the existence of a threshold stress, the single mechanism of grain boundary sliding (GBS) accommodated by diffusional processes can explain the superplasticity of these materials over all the ranges of temperature, stress, grain size, and surrounding atmosphere that have been studied. The origin of the threshold stress and its quantitative dependence on temperature and grain size is explained in terms of the segregation of yttrium atoms at the grain boundaries. A new model for GBS accommodated by lattice or grain-boundary diffusion is presented which can explain the transition of the stress exponent from 2 to 1.
Agosto, 2013 | DOI: 10.1179/1743280413Y.0000000018
Materiales para Bioingeniería y Regeneración Tisular
Tuning of Cell–Biomaterial Anchorage for Tissue Regeneration
Leal-Egana, Aldo; Diaz-Cuenca, Aranzazu; Boccaccini, Aldo RAdvanced Materials, 25 (2013) 4049-4057
Show abstract ▽
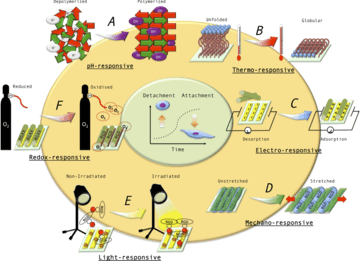
Which mechanisms mediate cell attachment to biomaterials? What role does the surface charge or wettability play on cell–material anchorage? What are the currently investigated strategies to modify cell–matrix adherence spatiotemporally? Considering the development of scaffolds made of biocompatible materials to temporarily replace the structure and/or function of the extracellular matrix, focus is given to the analysis of the specific (i.e., cell adhesive peptide sequences) and unspecific (i.e., surface charge, wettability) mechanisms mediating cell-matrix interactions. Furthermore, because natural tissue regeneration is characterized by the dynamic attachment/detachment of different cell populations, the design of advanced scaffolds for tissue engineering, based in the spatiotemporal tuning of cell–matrix anchorage is discussed.
Agosto, 2013 | DOI: 10.1002/adma.201301227
Reactividad de Sólidos
Studies of isothermal crystallisation kinetics of sunflower hard stearin-based confectionery fats
Bootello, MA; Hartel, RW; Levin, M; Martinez-Blanes, JM; Real, C; Garces, R; Martinez-Force, E; Salas, JJFood Chemistry, 139 (2013) 184-195
Show abstract ▽
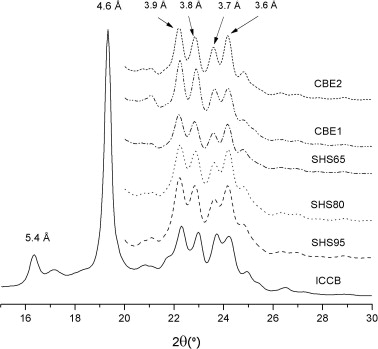
The crystallisation and polymorphic properties of three sunflower hard stearins (SHSs) and cocoa butter equivalents (CBEs) formulated by blending SHSs and palm mid fraction (PMF) were studied and compared with those from cocoa butter (CB), to explore their possibilities as confectionery fats. The isothermal crystallisation kinetics of these fats were examined by pNMR and DSC at three different temperatures. All samples studied displayed a two-step crystallisation profile that could be fitted to an exponential-Gompertz equation. Stop-and-return DSC studies showed that SHSs and CBEs exhibited different crystallisation mechanisms according to their triacylglycerol composition, with a quick formation of metastable crystals, followed by a polymorphic transition to the more stable β or β′ forms. X-ray diffraction (XRD) was used to investigate the polymorphic forms of tempered SHSs and CBEs in the long term. In all cases the resulting fats displayed short spacing patterns associated with β polymorphism. These formulations based on SHSs and PMF met all the requirements to be considered as CBEs; therefore they could be used as an alternative to traditional confectionery fats.
Agosto, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.11.141
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Erbium doped TiO2–Bi2WO6 heterostructure with improved photocatalytic activity under sun-like irradiation
Obregon, S; Colon, GApplied Catalysis B: Environmental, 140-141 (2013) 299-305
Show abstract ▽
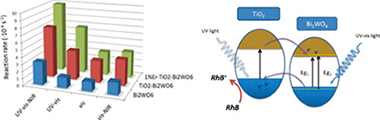
Erbium doped TiO2–Bi2WO6 have been synthesized by means of a surfactant free hydrothermal method having good photoactivities under sun-like excitation for the degradation of Rhodamine B. From the structural and morphological characterization it has been stated that the presence of Er3+ induces a progressive russelite cell contraction due to its incorporation in the Bi2WO6 lattice in substitutional sites. The best photocatalytic performance was attained for the samples with 1 at% of Er. From the study of the photocatalytic activity under different irradiation conditions it can be inferred that Er3+ presence induces a significant improvement of the photoactivity in the UV range. The evolution of band-gap values seems to be similarly related with the reaction rate progression. Thus, the higher band-gap values in lower Er doped systems would be the cause of a better electron hole separation under UV irradiation.
Agosto, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.04.014
- ‹ anterior
- 298 of 421
- siguiente ›














