Artículos SCI
2013
2013
Reactividad de Sólidos
Enhanced general analytical equation for the kinetics of the thermal degradation of poly(lactic acid) driven by random scission
Carrasco, F; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perejon, A; Santana, OO; Maspoch, MLPolymer Testing, 32 (2013) 937-945
Show abstract ▽
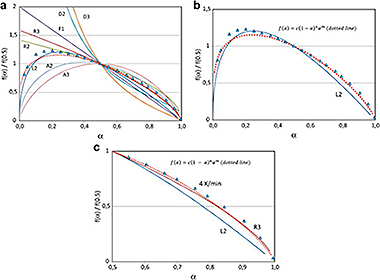
An enhanced general analytical equation has been developed in order to evaluate the kinetic parameters of the thermal degradation of poly(lactic acid) (PLA) at various linear heating rates and at constant rate conditions. This improvement consisted of replacing the n-order conversion function by a modified form of the Sestak-Berggren equation f(α) = c(1−α)nαm, which led to better adjustment of experimental data, and also adequately represented the conventional mechanisms for solid-state processes. The kinetic parameters so obtained have been compared to those determined by conventional differential and isoconversional methods. Given that the thermal degradation of PLA has been argued to be caused by random chain scission reactions of ester groups, the conversion function (α) = 2(α1/2−α), corresponding to a random scission mechanism, has been tested.
Agosto, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.polymertesting.2013.04.013
Reactividad de Sólidos
Constant rate thermal analysis for enhancing the long-term CO2 capture of CaO at Ca-looping conditions
Valverde, JM; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perejon, A; Perez-Maqueda, LAApplied Energy, 108 (2013) 108-120
Show abstract ▽
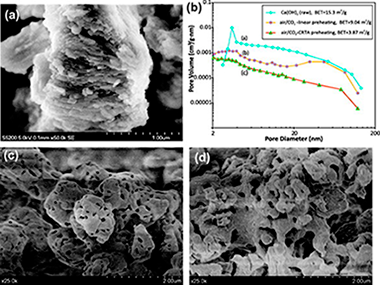
Experimental results are reported on the (Ca-looping) multicyclic CO2 capture of CaO and nanosilica/CaO composites derived from Ca(OH)2 and nanosilica/Ca(OH)2 dry mixtures subjected in situ to linear and constant rate thermal analysis (CRTA) preheating programs in either air or air/CO2 atmospheres. By means of CRTA preheating the rates of the reactions taking place during pretreatment are kept at a constant and small value along the entire process. In agreement with a pore skeleton model, previously proposed in the literature for explaining the behavior of natural limestones thermally pretreated, our results suggest that air/CO2-CRTA pretreatment yields a thermally stable hard skeleton of poorly reactive CaO on which a soft skeleton of reactive CaO would be supported. The sorbent subjected to this preheating program exhibits a reactivation in the very first carbonation/calcination cycles, after which CaO conversion decays slowly with the cycle number. In contrast, linearly or air-CRTA preheated sorbents show a significant decrease of CaO conversion within the first cycles. In the latter case, CaO multicyclic conversion fits well to a model where it is assumed that the progressive reduction of surface area as the number of carbonation/calcination cycles is increased obeys to sintering of the preheated sorbent skeleton as it is subjected to repeated calcinations during cycling. In the former case, CaO conversion data conforms to the prediction by a model in which the loss of surface area is mainly due to sintering of a nascent CaO soft skeleton regenerated in the diffusive carbonation phase, which is enhanced by the air/CO2-CRTA pretreatment. As regards the effect of nanosilica, the results indicate that it slows down CaO sintering during pretreatment, which hinders the development of a stable CaO skeleton thus hampering reactivation and stabilization of conversion. On the other hand, as CaO sintering is also lessened during looping calcination, nanosilica is useful to increase the absolute values of CaO conversion.
Agosto, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2013.03.013
Reactividad de Sólidos
Spark plasma sintering of TixTa1−xC0.5N0.5-based cermets: Effects of processing conditions on chemistry, microstructure and mechanical properties
Cordoba, Jose M.; Chicardi, Ernesto; Poyato, Rosalia; Gotor, Francisco J.; Medri, Valentina; Guicciardi, Stefano; Melandri, CesareChemical Engineering Journal, 230 (2013) 558-566
Show abstract ▽
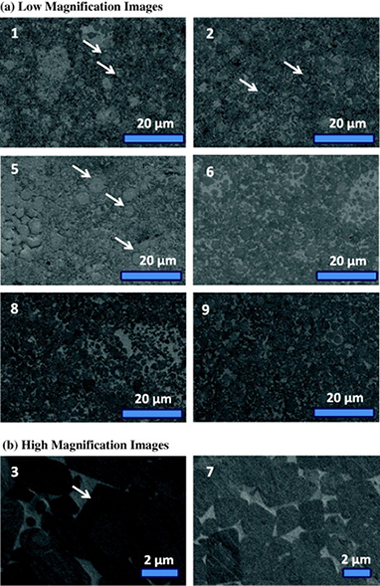
Nanometric powdered TixTa1−xC0.5N0.5-based cermets were fabricated using a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction and consolidated by spark plasma sintering. Highly dense cermets were obtained, and their chemistry, microstructure and mechanical properties were characterised by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, image analysis, microindentation and nanoindentation. The microhardness was found to depend directly on the contiguity and size of the ceramic hard particles. The samples synthesised at the lowest temperature (1150 °C) exhibited more homogeneous microstructures and smaller ceramic particles and the best combination of microhardness and fracture toughness.
Agosto, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2013.06.104
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Degradation of Rhodamine B/Phenol Mixtures in Water by Sun-Like Excitation of a Bi2WO6–TiO2 Photocatalyst
Murcia-López, S; Navío, J.A.; Hidalgo, M.C.Photochemistry and Photobiology, 89 (2013) 832-840
Show abstract ▽
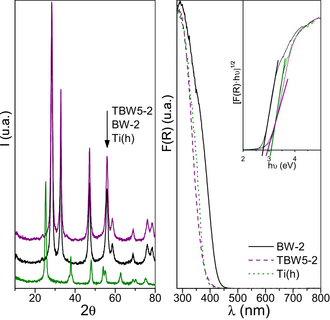
Bi2WO6 and Bi2WO6–TiO2 (5% molar Ti) nano-heterostructures were synthesized by a hydrothermal method. The properties of the synthesized catalysts were characterized, having high photoactivity for Rhodamine B degradation under sun-like illumination, explained by a synergetic mechanism previously proposed through UV and visible induced processes, in which the photosensitization effect of Rhodamine B is considered. We now report that using Phenol, a molecule which does not lead the photosensitization process, the photoactivity decreased considerably, thus emphasizing how important is the model molecule selected as degradation substrate for evaluating the photoactivity. The photocatalytic properties of the synthesized catalysts have been evaluated by exposing a mixture of Rhodamine B and Phenol in water, to different illumination conditions. It can be confirmed that the photoinduced mechanism via the photosensitization of Rhodamine B is a key factor responsible for the increase on the photocatalytic activity showed by the Bi2WO6–TiO2 compound and that the degradation mechanism of Rhodamine B is not changed by the simultaneous presence of other transparent substrate as Phenol.
Julio, 2013 | DOI: 10.1111/php.12054
Materiales Coloidales
Thermal Expansion of Rare-Earth Pyrosilicates
Fernandez-Carrion, AJ; Allix, M; Becerro, AIJournal of the American Ceramic Society, 96 (2013) 2298-2305
Show abstract ▽
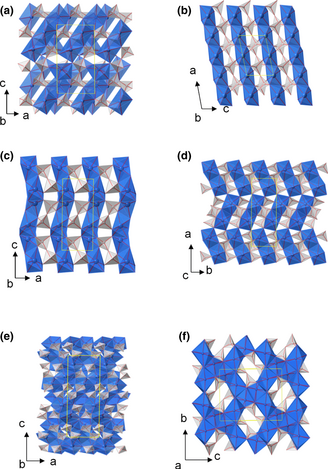
The use of RE2Si2O7 materials as environmental barrier coatings (EBCs) and in the sintering process of advanced ceramics demands a precise knowledge of the coefficient of thermal expansion of the RE2Si2O7. High-temperature X-ray diffraction (HTXRD) patterns were collected on different RE2Si2O7 polymorphs, namely A, G, α, β, γ, and δ, to determine the changes in unit cell dimensions. RE2Si2O7 compounds belonging to the same polymorph showed, qualitatively, very similar unit cell parameters behavior with temperature, whereas the different polymorphs of a given RE2Si2O7 compound exhibited markedly different thermal expansion evolution. The isotropy of thermal expansion was demonstrated for the A-RE2Si2O7 polymorph while the rest of polymorphs exhibited an anisotropic unit cell expansion with the biggest expansion directed along the REOx polyhedral chains. The apparent bulk thermal expansion coeficcients (ABCTE) were calculated from the unit cell volume expansion for each RE2Si2O7 compound. All compounds belonging to the same polymorph exhibited similar ABCTE values. However, the ABCTE values differ significantly from one polymorph to the other. The highest ABCTE values correspond to A-RE2Si2O7 compounds, with an average of 12.1 × 10−6 K−1, whereas the lowest values are those of β- and γ-RE2Si2O7, which showed average ABCTE values of ~4.0 × 10−6 K−1.
Julio, 2013 | DOI: 10.1111/jace.12388
- ‹ anterior
- 299 of 421
- siguiente ›














