Artículos SCI
2013
2013
Reactividad de Sólidos
Spark plasma sintering of TixTa1−xC0.5N0.5-based cermets: Effects of processing conditions on chemistry, microstructure and mechanical properties
Cordoba, Jose M.; Chicardi, Ernesto; Poyato, Rosalia; Gotor, Francisco J.; Medri, Valentina; Guicciardi, Stefano; Melandri, CesareChemical Engineering Journal, 230 (2013) 558-566
Show abstract ▽
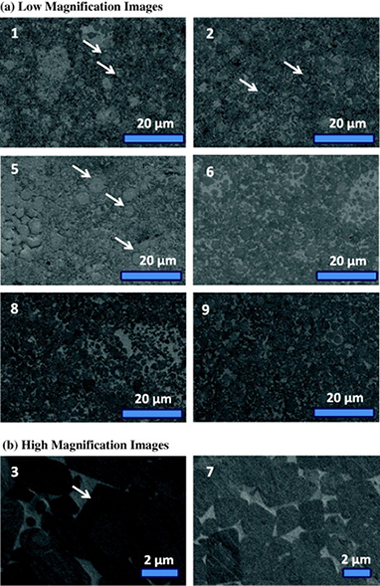
Nanometric powdered TixTa1−xC0.5N0.5-based cermets were fabricated using a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction and consolidated by spark plasma sintering. Highly dense cermets were obtained, and their chemistry, microstructure and mechanical properties were characterised by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, image analysis, microindentation and nanoindentation. The microhardness was found to depend directly on the contiguity and size of the ceramic hard particles. The samples synthesised at the lowest temperature (1150 °C) exhibited more homogeneous microstructures and smaller ceramic particles and the best combination of microhardness and fracture toughness.
Agosto, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2013.06.104
Reactividad de Sólidos
Enhanced general analytical equation for the kinetics of the thermal degradation of poly(lactic acid) driven by random scission
Carrasco, F; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perejon, A; Santana, OO; Maspoch, MLPolymer Testing, 32 (2013) 937-945
Show abstract ▽
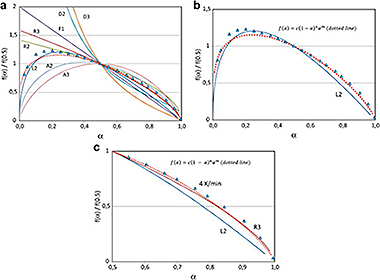
An enhanced general analytical equation has been developed in order to evaluate the kinetic parameters of the thermal degradation of poly(lactic acid) (PLA) at various linear heating rates and at constant rate conditions. This improvement consisted of replacing the n-order conversion function by a modified form of the Sestak-Berggren equation f(α) = c(1−α)nαm, which led to better adjustment of experimental data, and also adequately represented the conventional mechanisms for solid-state processes. The kinetic parameters so obtained have been compared to those determined by conventional differential and isoconversional methods. Given that the thermal degradation of PLA has been argued to be caused by random chain scission reactions of ester groups, the conversion function (α) = 2(α1/2−α), corresponding to a random scission mechanism, has been tested.
Agosto, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.polymertesting.2013.04.013
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Characterisation of Co@Fe3O4 core@shell nanoparticles using advanced electron microscopy
Knappett, BR; Abdulkin, P; Ringe, E; Jefferson, DA; Lozano-Perez, S; Rojas, TC; Fernandez, A; Wheatley, AEHNanoscale, 5 (2013) 5765-5772
Show abstract ▽
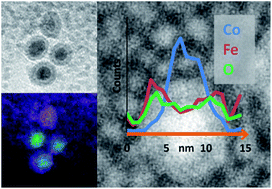
Cobalt nanoparticles were synthesised via the thermal decomposition of Co2(CO)8 and were coated in iron oxide using Fe(CO)5. While previous work focused on the subsequent thermal alloying of these nanoparticles, this study fully elucidates their composition and core@shell structure. State-of-the-art electron microscopy and statistical data processing enabled chemical mapping of individual particles through the acquisition of energy-filtered transmission electron microscopy (EFTEM) images and detailed electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS) analysis. Multivariate statistical analysis (MSA) has been used to greatly improve the quality of elemental mapping data from core@shell nanoparticles. Results from a combination of spatially resolved microanalysis reveal the shell as Fe3O4 and show that the core is composed of oxidatively stable metallic Co. For the first time, a region of lower atom density between the particle core and shell has been observed and identified as a trapped carbon residue attributable to the organic capping agents present in the initial Co nanoparticle synthesis.
Julio, 2013 | DOI: 10.1039/C3NR33789H
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Liquids Analysis with Optofluidic Bragg Microcavities
Oliva-Ramirez, M; Gonzalez-Garcia, L; Parra-Barranco, J; Yubero, F; Barranco, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 5 (2013) 6743-650
Show abstract ▽
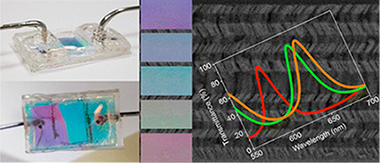
Porous Bragg microcavities formed by stacking a series of porous nanocolumnar layers with alternate low (SiO2) and high (TiO2) refractive index materials have been prepared by physical vapor deposition at glancing angles (GLAD). By strictly controlling the porosity and refractive index of the individual films, as well as the relative orientation of the nanocolumns from one layer to the next, very porous and nondispersive high optical quality microcavities have been manufactured. These photonic structures have been implemented into responsive devices to characterize liquids, mixtures of liquids, or solutions flowing through them. The large displacements observed in the optical spectral features (Bragg reflector gap and resonant peak) of the photonic structures have been quantitatively correlated by optical modeling with the refractive index of the circulating liquids. Experiments carried out with different glucose and NaCl solutions and mixtures of water plus glycerol illustrate the potentialities of these materials to serve as optofluidic devices to determine the concentration of solutions or the proportion of two phases in a liquid mixture.
Julio, 2013 | DOI: 10.1021/am401685r
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Monolayer arrangement of fatty hydroxystearic acids on graphite: Influence of hydroxyl groups
Medina, S; Benitez, JJ; Castro, MA; Cerrillos, C; Millan, C; Alba, MDThin Solid Films, 539 (2013) 194-200
Show abstract ▽
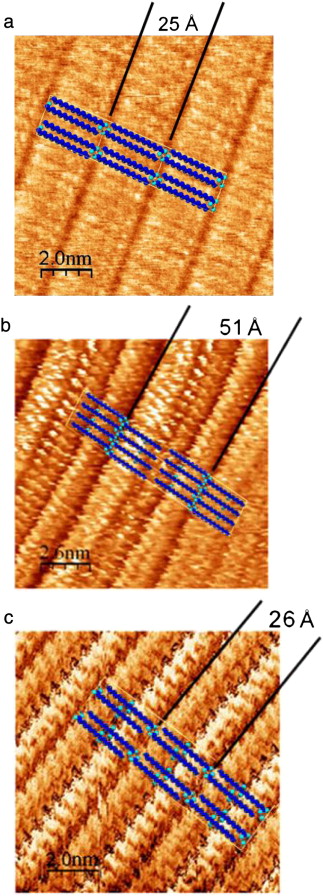
Previous studies have indicated that long-chain linear carboxylic acids form commensurate packed crystalline monolayers on graphite even at temperatures above their melting point. This study examines the effect on the monolayer formation and structure of adding one or more secondary hydroxyl, functional groups to the stearic acid skeleton (namely, 12-hydroxystearic and 9,10-dihydroxystearic acid). Moreover, a comparative study of the monolayer formation on recompressed and monocrystalline graphite has been performed through X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Scanning Tunneling Microscopy (STM), respectively. The Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) and XRD data were used to confirm the formation of solid monolayers and XRD data have provided a detailed structural analysis of the monolayers in good correspondence with obtained STM images. DSC and XRD have demonstrated that, in stearic acid and 12-hydroxystearic acid adsorbed onto graphite, the monolayer melted at a higher temperature than the bulk form of the carboxylic acid. However, no difference was observed between the melting point of the monolayer and the bulk form for 9,10-dihydroxystearic acid adsorbed onto graphite. STM results indicated that all acids on the surface have a rectangular p2 monolayer structure, whose lattice parameters were uniaxially commensurate on the a-axis. This structure does not correlate with the initial structure of the pure compounds after dissolving, but it is conditioned to favor a) hydrogen bond formation between the carboxylic groups and b) formation of hydrogen bonds between secondary hydroxyl groups, if spatially permissible. Therefore, the presence of hydroxyl functional groups affects the secondary structure and behavior of stearic acid in the monolayer.
Julio, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.tsf.2013.05.053
- ‹ anterior
- 300 of 422
- siguiente ›














