Artículos SCI
2012
2012
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
New insights into the synergistic effect in bimetallic-boron catalysts for hydrogen generation: The Co–Ru–B system as a case study
Arzac, G. M.; Rojas, T. C.; Fernandez, A.Applied Catalysis B-Environmental, 128 (2012) 39-47
Show abstract ▽
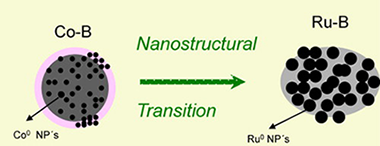
Catalysed sodium borohydride hydrolysis is a high-potential method to produce hydrogen for portable applications. Co–B catalysts are the most chosen because they are easily prepared, cheap and efficient. The addition of small amounts of Ru produces a significant enhancement in catalytic activity.
In the present work a series of Co–Ru–B catalysts with variable Ru content was prepared, isolated and characterized. The comprehension of the synergistic effect was achieved trough the incorporation of the nanostructural dimension to the study of surface and bulk chemical states of the involved atoms along the series. It was found that up to 70% (of total metal) atomic content of Ru the catalysts can be considered isostructural to the single Co–B catalyst in the nanoscale. A structural transition occurs in the case of the pure Ru–B material to produce a boron deficient material with higher nanoparticle size. This structural transition together with Co segregation and Ru dispersion play a key role when explaining a [OH−] dependent effect.
The inexistence of borate layers in Ru rich catalysts is suggestive in the research for non deactivating catalysts.
Noviembre, 2012 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.02.013
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Effect of ytterbium doping on the microstructure and plastic deformation of BaCeO3 perovskite oxide
Jimenez-Melendo, M; Vaquero-Aguilar, C; Huaman-Mamani, FAFuel Processing Technology, 103 (2012) 146-150
Show abstract ▽
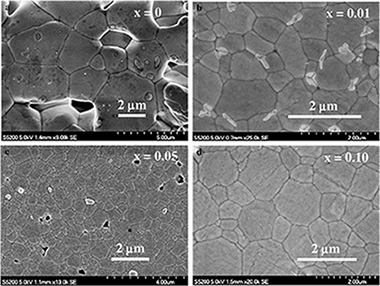
Trivalent cation-doped barium cerate perovskites are attractive materials for clean-energy applications, in particular solid oxide fuel cells, due to their singular proton conductivity in wet environments. Furthermore, these devices operate at high temperatures, where creep and other deformation processes determine the lifetime and overall performance. In this work, the structural and microstructural characteristics of undoped and ytterbium-doped (1 to 10 at.%) BaCeO 3 polycrystals produced by solid state reaction have been investigated. A single orthorhombic perovskite phase was found after sintering in air at 1500 °C for 10 h. The microstructure shows a complex evolution with doping: the average grain size firstly decreases with increasing Yb content up to 5 at.%, and then increases with further Yb additions. The high-temperature mechanical properties have been studied in compression between 1100 and 1250 °C in air at constant initial strain rate. The creep strength increases with increasing Yb content. Extended steady states of deformation were attained at lower strain rates and higher temperatures when increasing doping amount.
Noviembre, 2012 | DOI: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2011.10.005
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Preparation of nanostructured nickel aluminate spinel powder from spent NiO/Al2O3 catalyst by mechano-chemical synthesis
Nazemi, M. K.; Sheibani, S.; Rashchi, F.; Gonzalez-DelaCruz, V. M.; Caballero, A.Advanced Powder Technology, 23 (2012) 833-838
Show abstract ▽
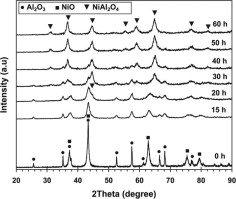
In this paper, the possibility of mechano-chemical synthesis, as a single step process for preparation of nanostructured nickel aluminate spinel powder from NiO/Al2O3 spent catalyst was investigated. Powder samples were characterized in terms of composition, morphology, structure, particle size and surface area using complementary techniques such as X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), differential thermal analysis (DTA) and volumetric adsorption of nitrogen. It was found that formation of spinel was possible after 60 h of milling with no heat treatment. Additionally, influence of mechanical activation on the heat treatment temperature was discussed. It was observed that heat treatment of 15 h milled sample at 1100 °C is enough to produce nickel aluminate spinel. A product of direct mechanical milling showed higher value of surface area (42.3 m2/g) and smaller crystallite size (12 nm) as compared to the heat treated product.
Noviembre, 2012 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apt.2011.11.004
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Gold supported on pillared clays for CO oxidation reaction: Effect of the clay aggregate size
Alvarez, A; Moreno, S; Molina, R; Ivanova, S; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAApplied Clay Science, 69 (2012) 22-29
Show abstract ▽
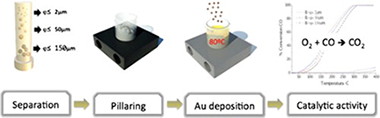
A series of 1% m/m gold particles supported on Fe, Ce and Al pillared bentonite (from Valle del Cauca, Colombia) and clay “M64” (from Tolima, Colombia) using three different fractions of aggregate sizes (≤ 2 μm, ≤ 50 μm, and ≤ 150 μm) were characterized by particle size measurements, X-ray diffraction, transmission electronic microscopy (TEM), SBET and X-ray fluorescence spectrometry (XRF) techniques. The materials tested with CO oxidation. The separation yield for each fraction depended on the type of clay. Whatever the clay or the aggregate size, the pillaring process was successfully carried out, introducing Fe, Ce and Al pillars and increasing the microporosity and the specific surface area of the material. Gold particles presented a homogenous distribution of 2–3 nm on the pillared bentonite, and of about 10 nm on the pillared clay M64. The aggregate size slightly influenced the amount of deposited gold particles and their size. All gold catalysts were active in CO oxidation, the activity depending on the nature of the clay as well as the gold loading and average gold particle size but not on the aggregate size.
Noviembre, 2012 | DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2012.07.008
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Influence of PVP in magnetic properties of NiSn nanoparticles prepared by polyol method
Bobadilla, LF; Garcia, C; Delgado, JJ; Sanz, O; Romero-Sarria, F; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAJournal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 324 (2012) 4011-4018
Show abstract ▽

The influence of PVP on the magnetic properties of NiSn nanoparticles prepared by polyol method has been studied. NiSn nanoparticles exhibit superparamagnetic behavior although there is a ferromagnetic contribution due to particles agglomerated below the blocking temperature. The particle size is controlled by the addiction of PVP in varying amounts. The addition of PVP also favours the particles isolation, narrow the particle size distribution and decrease the interparticle interaction strength increasing the superparamagnetic contribution.
Noviembre, 2012 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2012.07.005
- ‹ anterior
- 318 of 422
- siguiente ›














