Artículos SCI
2012
2012
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
XPS and AES analyses of cerium conversion coatings generated on AA5083 by thermal activation
Sanchez-Amaya, JM; Blanco, G; Garcia-Garcia, FJ; Bethencourt, M; Botana, FJSurface and Coatings Technology, 213 (2012) 105-116
Show abstract ▽
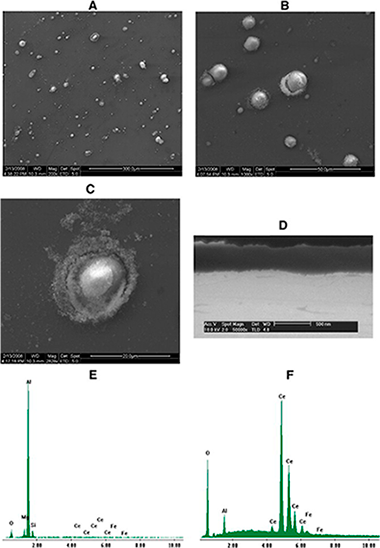
This paper describes the deep analysis of cerium conversion coatings developed with thermal activation on AA5083 under optimum processing conditions. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM), electron dispersive spectroscopy (EDX), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and Auger electron spectroscopy (AES) were employed to study these layers. Ar+ sputtering was also employed to analyse the coatings' core. Although conversion coatings based on Ce salts have been widely characterised in the literature for different aluminium alloys, the coatings developed with thermal activation on Al–Mg alloys have not been previously investigated with these techniques. SEM/EDX studies have demonstrated the existence of a heterogeneous layer formed by a film of aluminium oxide/hydroxide on the matrix as well as a series of dispersed islands of cerium deposited on the cathodic intermetallics. These results have been further confirmed by means of XPS. The XPS and AES results revealed that the outer layer comprises a mixture coating of Ce3 + (70%) and Ce4 + (30%) compounds. Although only Ce3 + compounds were detected at the inner part of the coating, possible reduction of Ce(IV) to Ce(III) due to the Ar+ beam could not be discarded. Obtained results allowed authors to confirm that the cerium conversion coatings developed have a similar structure to those previously reported for other aluminium alloys.
Diciembre, 2012 | DOI:
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Hydrogenation of 2,2,2-trifluoroacetophenone: Molecular insight into the role of solvent in enantioselection
Rosa Pereñiguez; Gianluca Santarossa; Tamas Mallat; Alfons BaikerJournal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical, 365 (2012) 39-49
Show abstract ▽
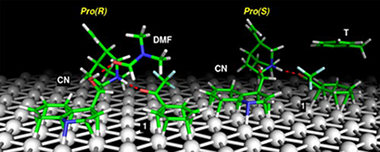
The unique solvent effect in the enantioselective hydrogenation of α-fluorinated ketones has been investigated in ten different solvents using the hydrogenation of 2,2,2-trifluoroacetophenone (1) on cinchonine (CN)-modified Pt/Al2O3 as a model reaction. Application of strongly basic solvents – but also increasing hydrogen pressure or conversion – inverted the sense of enantiodifferentiation from (S)-alcohol (expected enantiomer based on the stereochemistry of CN) to (R)-alcohol. The known formation of hemiketals was the origin of the inversion in alcohols. Considering only the non-reacting solvents and low conversions at low pressures, the best correlation was established between the enantiomeric excess and the solvent basicity represented by the H-bond acceptor ability (β). In contrast to former proposals, solvent acidity (α) did not play a significant role. The experimental results are validated by theoretical calculations. The docking of 1 to CN has been investigated in the absence of solvent and also in the presence of toluene and dimethyl formamide. Several competing docking complexes have been isolated that can coexist on the metal surface. Detailed analyses of these complexes show that their stabilities depend on the formation of enantiospecific local interactions between 1, CN, and the platinum surface. The presence of solvent interferes with these interactions, affecting the relative stability of the docking complexes. A correlation between the solvent-induced interactions at molecular level and changes in enantioselectivity is suggested.
Diciembre, 2012 | DOI: 10.1016/j.molcata.2012.08.006
Reactividad de Sólidos
Quantum-Mechanical Study on the Aquaions and Hydrolyzed Species of Po(IV), Te(IV), and Bi(III) in Water
Ayala, Regla; Manuel Martinez, Jose; Pappalardo, Rafael R.; Sanchez Marcos, EnriqueJournal of Physical Chemistry B, 116 (2012) 14903-14914
Show abstract ▽
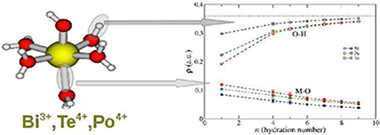
A systematic study of [M(H2O)n(OH)m]q+ complexes of Te(IV) and Bi(III) in solution has been undertaken by means of quantum mechanical calculations. The results have been compared with previous information obtained for the same type of Po(IV) complexes ( J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 487) to get insight into the similarities and differences among them from a theoretical view. The evolution of the coordination number (n + m) with the degree of hydrolysis (m) for the stable species shows a systematic decrease regardless the ion. A general behavior on the M–O distances when passing from the gas phase to solution, represented by the polarizable continuum model (PCM), is also observed: RM–O values corresponding to water molecules decrease, while those of the hydroxyl groups slightly increase. The hydration numbers of aquaions are between 8 and 9 for the three cations, whereas hydrolyzed species behave differently for Te(IV) and Po(IV) than for Bi(III), which shows a stronger trend to dehydrate with the hydrolysis. On the basis of the semicontinuum solvation model, the hydration Gibbs energies are −800 (exptl −834 kcal/mol), −1580 and −1490 kcal/mol for Bi(III), Te(IV), and Po(IV), respectively. Wave function analysis of M–O and O–H bonds along the complexes has been carried out by means of quantum theory of atoms in molecule (QTAIM). Values of electron density and its Laplacian at bond critical points show different behaviors among the cations in aquaions. An interesting conclusion of the QTAIM analysis is that the prospection of the water O–H bond is more sensitive than the M–O bond to the ion interaction. A global comparison of cation properties in solution supplies a picture where the Po(IV) behavior is between those of Te(IV) and Bi(III), but closer to the first one.
Diciembre, 2012 | DOI: 10.1021/jp309439f
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Selective photooxidation of alcohols as test reaction for photocatalytic activity
Lopez-Tenllado, F. J.; Marinas, A.; Urbano, F. J.; Colmenares, J. C.; Hidalgo, M. C.; Marinas, J. M.; Moreno, J. M.Applied Catalysis B-Environmental, 128 (2012) 150-158
Show abstract ▽
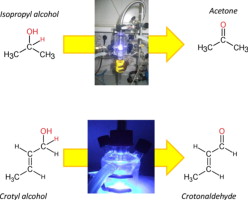
Twenty-four different titania-based systems synthesized through the sol–gel process varying the precursor (titanium isopropoxide or tetrachloride) and/or the ageing conditions (magnetic stirring, ultrasounds, microwave or reflux) were tested for liquid-phase selective photooxidation of 2-butenol (crotyl alcohol) to 2-butenal (crotonaldehyde) and gas-phase selective photooxidation of 2-propanol to acetone. To the best of our knowledge, the former process is suggested for the first time as test reaction for photocatalytic activity. Interestingly, both test reactions (despite having very different reactant/catalyst ratio and contact times) showed quite similar results in terms of influence of the precursor (titanium isopropoxide leading to better results than titanium tetrachloride) and the metals (the presence of iron, palladium or zinc being detrimental to activity whereas zirconium and especially gold improved the results as compared to pure titania). To our mind, these results give validity to both processes as test reactions for a fast screening of catalysts for photocatalytic tranformations. Finally, some gold-containing solids even improved photocatalytic activity of Degussa P25.
Noviembre, 2012 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.02.015
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
New insights into the synergistic effect in bimetallic-boron catalysts for hydrogen generation: The Co–Ru–B system as a case study
Arzac, G. M.; Rojas, T. C.; Fernandez, A.Applied Catalysis B-Environmental, 128 (2012) 39-47
Show abstract ▽
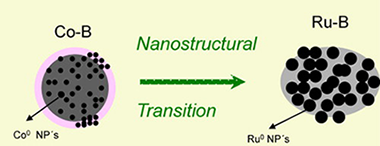
Catalysed sodium borohydride hydrolysis is a high-potential method to produce hydrogen for portable applications. Co–B catalysts are the most chosen because they are easily prepared, cheap and efficient. The addition of small amounts of Ru produces a significant enhancement in catalytic activity.
In the present work a series of Co–Ru–B catalysts with variable Ru content was prepared, isolated and characterized. The comprehension of the synergistic effect was achieved trough the incorporation of the nanostructural dimension to the study of surface and bulk chemical states of the involved atoms along the series. It was found that up to 70% (of total metal) atomic content of Ru the catalysts can be considered isostructural to the single Co–B catalyst in the nanoscale. A structural transition occurs in the case of the pure Ru–B material to produce a boron deficient material with higher nanoparticle size. This structural transition together with Co segregation and Ru dispersion play a key role when explaining a [OH−] dependent effect.
The inexistence of borate layers in Ru rich catalysts is suggestive in the research for non deactivating catalysts.
Noviembre, 2012 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.02.013
- ‹ anterior
- 317 of 422
- siguiente ›














