Artículos SCI
2013
2013
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Gas-phase Photocatalytic Partial Oxidation of Cyclohexane to Cyclohexanol and Cyclohexanone on Au/TiO2 Photocatalysts
Sannino, D; Vaiano, V; Ciambelli, P; Murcia, JJ; Hidalgo, MC; Navio, JAJournal of Advanced Oxidation Technologies, 16 (2013) 71-82
Show abstract ▽
The heterogeneous photocatalytic partial oxidation of cyclohexane in gas-phase as an alternative green process for fine chemicals synthesis was successfully achieved on Au/TiO2 photocatalysts prepared by photodeposition technique. Different gold loadings ranging between 0.5 and 2 wt.% of photodeposited Au on TiO2 synthesized by sol-gel method were obtained by changing the concentration of gold precursor at fixed illumination intensity and time. The cyclohexane partial photoxidation was conducted in a gas-solid photocatalytic fluidized bed reactor at high illumination efficiency. Main observed reaction products were cyclohexanol, cyclohexanone and CO2. The resulting selectivity was dramatically influenced by the gold content. The reaction temperature was a critical parameter to reach the photocatalysts stability, avoiding deactivation phenomena while the tuning of Au content of the photocatalysts, resulted in the promotion of the formation of cyclohexanol or cyclohexanone with high selectivity. In particular, by increasing Au content, the process selectivity is completely reversed, passing from high cyclohexanol selectivity (75%) to high selectivity to cyclohexanone (80%). These promising results evidenced that Au/TiO2 catalysts in the selected operating conditions, are effective materials for the synthesis of cyclohexanone and cyclohexanol in gas-phase by photocatalysis, at very low reaction temperatures and without the additional step of catalyst recovering needed in the liquid partial oxidation of cyclohexane.
Enero, 2013 | DOI: 10.1515/jaots-2013-0107
Reactividad de Sólidos
Generalized master plots as a straightforward approach for determining the kinetic model: The case of cellulose pyrolysis
Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Perejon, A; Criado, JMThermochimica Acta, 552 (2013) 54-59
Show abstract ▽
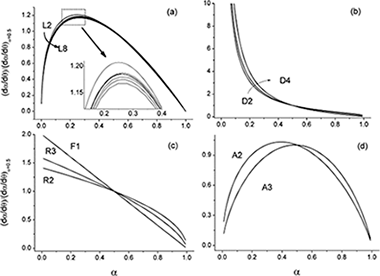
The thermal degradation of cellulose is a complex reaction and, despite the large amount of work by many investigators during the last decades, the actual understanding of the thermal decomposition kinetics is still very limited. Thus, while several mechanisms have been proposed to describe the process, the real model has not yet been clearly identified. In this paper, a set of experimental curves recorded under different heating schedules, i.e., linear heating rate, isothermal and constant rate thermal analysis (CRTA), has been analyzed using isoconversional and master plots methodology to discriminate the kinetic model followed by the reaction.
Enero, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.tca.2012.11.003
2012
2012
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Chemical–physical characterization of isolated plant cuticles subjected to low-dose γ-irradiation
Heredia-Guerrero, Jose A; de Lara, Rocio; Dominguez, Eva; Heredia, Antonio; Benavente, Juana; Benitez, Jose JChemistry and physics of lipids, 165 (2012) 803-808
Show abstract ▽
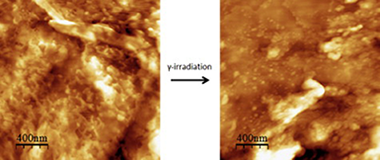
Isolated tomato fruit cuticles were subjected to low dose (80 Gy) γ-irradiation, as a potential methodology to prevent harvested fruit and vegetables spoilage. Both irradiated and non-irradiated samples have been morphologically and chemically characterized by scanning electron (SEM), atomic force (AFM), attenuated total reflectance Fourier transform infrared (ATR-FTIR) and X-ray photoelectron (XPS) spectroscopies. Additionally, electrochemical measurements comprising membrane potential and diffusive permeability were carried out to detect modifications in transport properties of the cuticle as the fruit primary protective membrane. It has been found that low dose γ-irradiation causes some textural changes on the surface but no significant chemical modification. Texture modification is found to be due to a partial removal of outermost (epicuticular) waxes which is accompanied by mild changes of electrochemical parameters such as the membrane fixed charge, cation transport number and salt permeability. The modification of such parameters indicates a slight reduction of the barrier properties of the cuticle upon low dose γ-irradiation.
Diciembre, 2012 | DOI: 10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2012.10.003
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
XPS and AES analyses of cerium conversion coatings generated on AA5083 by thermal activation
Sanchez-Amaya, JM; Blanco, G; Garcia-Garcia, FJ; Bethencourt, M; Botana, FJSurface and Coatings Technology, 213 (2012) 105-116
Show abstract ▽
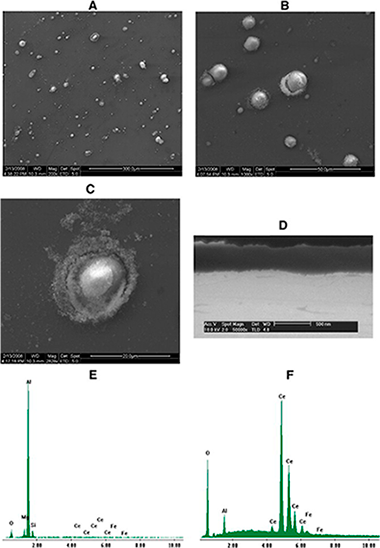
This paper describes the deep analysis of cerium conversion coatings developed with thermal activation on AA5083 under optimum processing conditions. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM), electron dispersive spectroscopy (EDX), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and Auger electron spectroscopy (AES) were employed to study these layers. Ar+ sputtering was also employed to analyse the coatings' core. Although conversion coatings based on Ce salts have been widely characterised in the literature for different aluminium alloys, the coatings developed with thermal activation on Al–Mg alloys have not been previously investigated with these techniques. SEM/EDX studies have demonstrated the existence of a heterogeneous layer formed by a film of aluminium oxide/hydroxide on the matrix as well as a series of dispersed islands of cerium deposited on the cathodic intermetallics. These results have been further confirmed by means of XPS. The XPS and AES results revealed that the outer layer comprises a mixture coating of Ce3 + (70%) and Ce4 + (30%) compounds. Although only Ce3 + compounds were detected at the inner part of the coating, possible reduction of Ce(IV) to Ce(III) due to the Ar+ beam could not be discarded. Obtained results allowed authors to confirm that the cerium conversion coatings developed have a similar structure to those previously reported for other aluminium alloys.
Diciembre, 2012 | DOI:
Reactividad de Sólidos
Bulk TiCxN1−x–15%Co cermets obtained by direct spark plasma sintering of mechanochemical synthesized powders
Borrell, A; Salvador, MD; Rocha, VG; Fernandez, A; Aviles, MA; Gotor, FJMaterials Research Bulletin, 47 (2012) 4487-4490
Show abstract ▽
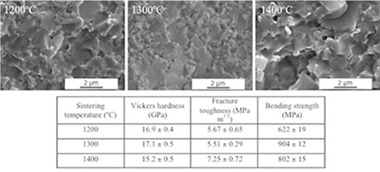
TiCxN1−x–15 wt.%Co cermets were obtained by a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction (MSR) and sintered by spark plasma sintering (SPS) technique at different temperatures (1200–1400 °C) for 1 min in vacuum under a uniaxial load of 80 MPa. The evolution of microstructure and mechanical properties was investigated. SPS allowed high densification with limited grain growth at a relatively low temperature. Material sintered at 1300 °C showed a good combination of mechanical properties with Vickers hardness of 17.1 ± 0.5 GPa, fracture toughness of 5.51 ± 0.29 MPa m1/2 and bending strength of 904 ± 12 MPa. Lower sintering temperature resulted in a decrease in bending strength due to poor cohesion between the ceramic and binder phases. An increase in sintering temperature would allow tailoring the cermet microstructure and, therefore, adjusting the Vickers hardness/fracture toughness relation.
Diciembre, 2012 | DOI: 10.1016/j.materresbull.2012.09.066
- ‹ anterior
- 316 of 422
- siguiente ›














