Artículos SCI
2013
2013
Reactividad de Sólidos
Influence of the milling parameters on the mechanical work intensity in planetary mills
Gotor, FJ; Achimovicova, M; Real, C; Balaz, PPowder Technology, 233 (2013) 1-7
Show abstract ▽
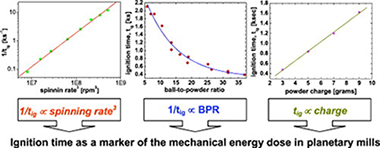
The formation of ZnSe via a mechanically-induced self-sustaining reaction (MSR) from a Zn/Se mixture showed that only size reduction and mixing of the reactants without product formation occurred during the induction period prior to ignition. Therefore, all mechanical energy supplied by the planetary mill during this time, called the ignition time (tig), was used exclusively in the activation of the reactants. This system was chosen to study the dependence of tig on the main parameters characterising the milling intensity of planetary mills. The variation of the ignition time with the process conditions reflected changes in the mechanical dose rate of the planetary mill. A direct relationship between the inverse of the ignition time and the power of the planetary mill was established, which allows the validation of theoretical models proposed in the literature for the energy transfer in milling devices and the comparison of milling equipment efficiencies.
Enero, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.powtec.2012.08.031
Materiales Coloidales
Synthesis and Properties of Multifunctional Tetragonal Eu:GdPO4 Nanocubes for Optical and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Applications
Rodriguez-Liviano, S; Becerro, AI; Alcantara, D; Grazu, V; de la Fuente, JM; Ocana, MInorganic Chemistry, 52 (2013) 647-654
Show abstract ▽
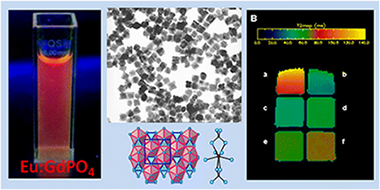
A simple and fast (7 min) procedure for synthesis of gadolinium phosphate nanocubes (edge = 75 nm) based on the microwave-assisted heating at 120 °C of gadolinium acetylacetonate and phosphoric acid solutions in buthylene glycol is reported. These nanocubes were highly crystalline and crystallized into a tetragonal structure, which has not been ever reported for pure gadolinium phosphate. Determination of such crystal structure has been carried out here for the first time in the literature by means of powder X-ray diffraction. The developed synthesis procedure was also successful for preparation of multifunctional europium(III)-doped the gadolinium phosphate nanocubes, which were nontoxic for cells and exhibited strong red luminescence under UV illumination and high transverse relaxivity (r2) values. These properties confer them potential applications as biolabels for in vitro optical imaging and as negative contrast agent for magnetic resonance imaging.
Enero, 2013 | DOI: 10.1021/ic3016996
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Tribological properties of surface-modified Pd nanoparticles for electrical contacts
Abad, MD; Sanchez-Lopez, JCWear, 297 (2013) 943-951
Show abstract ▽
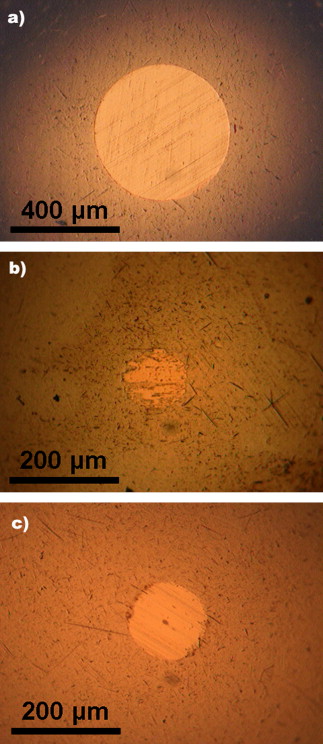
A fully comprehensive study of the tribological behavior of palladium nanoparticles (Pd NPs) capped by tetrabutylammonium chains using a ball-on-disk tribometer under different conditions of applied load, concentration, tribometer motion, linear speed and nature of the counterface is revised. A low concentration of NPs (2 wt%) in tetrabutylammonium acetate was found sufficient to improve the tribological properties due to the formation of a protective transfer film (TF) comprised of metallic Pd. The increase of the applied load (up to 20 N, 1.82 GPa of contact pressure) confirmed the excellent extreme-pressure behavior avoiding the counterfaces from severe wear. After a running-in period whose duration depends on the operating conditions, the TF build-up allows to maintain a low contact electrical resistance through the contact (<0.1 kΩ) during the entire test. When the Pd NPs are used with ceramic counterfaces, the nanoparticles increase the load-bearing capabilities and performance of the base without forming TF, likely by mixed or boundary lubrication and healing effects. Finally, the Pd NPs are demonstrated to be useful as a thin solid lubricant film in reciprocating motion yielding a comparable tribological behavior. Hence, the presented surface Pd NPs can be very helpful to extend life of sliding components due to their high strength resistance providing a gateway to electrical conduction as well.
Enero, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.wear.2012.11.009
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Strong quantum confinement effects in SnS nanocrystals produced by ultrasound-assisted method
Azizian-Kalandaragh, Y; Khodayari, A; Zeng, ZP; Garoufalis, CS; Baskoutas, S; Gontard, LCJournal of Nanoparticle Research, 15 (2013) 1388
Show abstract ▽
Nanocrystalline SnS powder has been prepared using tin chloride (SnCl2) as a tin ion source and sodium sulfide (Na2S) as a sulfur ion source with the help of ultrasound irradiation at room temperature. The as-synthesized SnS nanoparticles were quantitatively analyzed and characterized in terms of their morphological, structural, and optical properties. The detailed structural and optical properties confirmed the orthorhombic SnS structure and a strongly blue shifted direct band gap (1.74 eV), for synthesized nanoparticles. The measured band gap energy of SnS nanoparticles is in a fairly good agreement with the results of theoretical calculations of exciton energy based on the potential morphing method in the Hartree–Fock approximation.
Enero, 2013 | DOI: 10.1007/s11051-012-1388-1
Reactividad de Sólidos
Generalized master plots as a straightforward approach for determining the kinetic model: The case of cellulose pyrolysis
Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Perejon, A; Criado, JMThermochimica Acta, 552 (2013) 54-59
Show abstract ▽
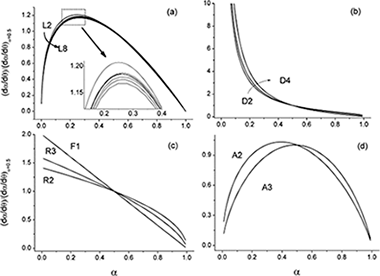
The thermal degradation of cellulose is a complex reaction and, despite the large amount of work by many investigators during the last decades, the actual understanding of the thermal decomposition kinetics is still very limited. Thus, while several mechanisms have been proposed to describe the process, the real model has not yet been clearly identified. In this paper, a set of experimental curves recorded under different heating schedules, i.e., linear heating rate, isothermal and constant rate thermal analysis (CRTA), has been analyzed using isoconversional and master plots methodology to discriminate the kinetic model followed by the reaction.
Enero, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.tca.2012.11.003
- ‹ anterior
- 315 of 422
- siguiente ›














