Artículos SCI
2013
2013
Reactividad de Sólidos
Influence of the milling parameters on the mechanical work intensity in planetary mills
Gotor, FJ; Achimovicova, M; Real, C; Balaz, PPowder Technology, 233 (2013) 1-7
Show abstract ▽
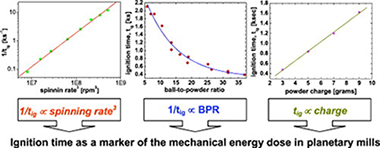
The formation of ZnSe via a mechanically-induced self-sustaining reaction (MSR) from a Zn/Se mixture showed that only size reduction and mixing of the reactants without product formation occurred during the induction period prior to ignition. Therefore, all mechanical energy supplied by the planetary mill during this time, called the ignition time (tig), was used exclusively in the activation of the reactants. This system was chosen to study the dependence of tig on the main parameters characterising the milling intensity of planetary mills. The variation of the ignition time with the process conditions reflected changes in the mechanical dose rate of the planetary mill. A direct relationship between the inverse of the ignition time and the power of the planetary mill was established, which allows the validation of theoretical models proposed in the literature for the energy transfer in milling devices and the comparison of milling equipment efficiencies.
Enero, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.powtec.2012.08.031
Reactividad de Sólidos
Mechanochemical synthesis of Sb2S3 and Bi2S3 nanoparticles
Dutkova, E; Takacs, L; Sayagues, MJ; Balaz, P; Kovac, J; Satka, AChemical Engineering Science, 85 (2013) 25-29
Show abstract ▽
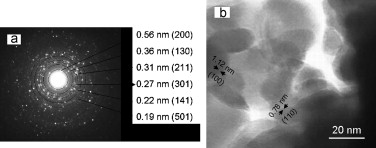
The mechanochemical synthesis of Sb2S3 and Bi2S3 nanoparticles has been studied, starting from the corresponding metals and sulfur and using high-energy mechanochemical processing in a planetary laboratory mill. XRD, specific surface area measurement, SEM and TEM (HRTEM) with ED were used for the characterization of the nanoparticles. The XRD patterns confirmed the production of Sb2S3 (JCPDS 42–1393, orthorhombic) and Bi2S3 (JCPDS 17–320, orthorhombic) nanopowders. The transformation is about three times faster in the Bi–S than in the Sb–S system. The kinetics of the reaction has been determined from XRD line intensities. The grain size is about 30 nm for Sb2S3 and 24 nm for Bi2S3. The particles are highly agglomerated due to their nanometer size consequent large specific surface area. Unlike more conventional methods, mechanochemical synthesis is a simple and fast alternative for the preparation of these nanopowders that can be carried out at ambient temperature and atmospheric pressure.
Enero, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ces.2012.02.028
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Small Pt nanoparticles on the TiO2 (110)–(1 × 2) surface
Sanchez-Sanchez, C; Martin-Gago, JA; Lopez, MFSurface Science, 607 (2013) 159-163
Show abstract ▽
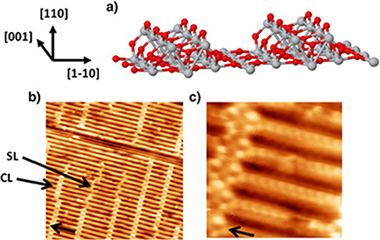
Scanning tunnelling microscopy (STM) has been used to study the initial stages of Pt deposition on the TiO2 (110)–(1 × 2) surface. Experimental STM images recorded for Pt coverage of 0.1 and 0.4 ML, suggest a Volmer-Weber growth. For low coverage and RT deposition, small clusters homogeneously distributed on the surface terraces are observed. However, after annealing at 825 K, material agglomeration, with nucleation mainly at the cross-links, is observed as a consequence of Pt diffusion on the surface. Finally, the structure of small clusters has been determined, in good agreement with previous theoretical calculations.
Enero, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.susc.2012.08.028
Materiales Coloidales
Synthesis and Properties of Multifunctional Tetragonal Eu:GdPO4 Nanocubes for Optical and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Applications
Rodriguez-Liviano, S; Becerro, AI; Alcantara, D; Grazu, V; de la Fuente, JM; Ocana, MInorganic Chemistry, 52 (2013) 647-654
Show abstract ▽
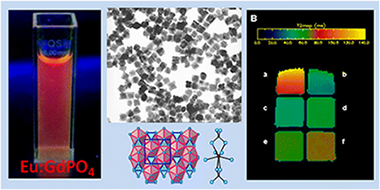
A simple and fast (7 min) procedure for synthesis of gadolinium phosphate nanocubes (edge = 75 nm) based on the microwave-assisted heating at 120 °C of gadolinium acetylacetonate and phosphoric acid solutions in buthylene glycol is reported. These nanocubes were highly crystalline and crystallized into a tetragonal structure, which has not been ever reported for pure gadolinium phosphate. Determination of such crystal structure has been carried out here for the first time in the literature by means of powder X-ray diffraction. The developed synthesis procedure was also successful for preparation of multifunctional europium(III)-doped the gadolinium phosphate nanocubes, which were nontoxic for cells and exhibited strong red luminescence under UV illumination and high transverse relaxivity (r2) values. These properties confer them potential applications as biolabels for in vitro optical imaging and as negative contrast agent for magnetic resonance imaging.
Enero, 2013 | DOI: 10.1021/ic3016996
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Strong quantum confinement effects in SnS nanocrystals produced by ultrasound-assisted method
Azizian-Kalandaragh, Y; Khodayari, A; Zeng, ZP; Garoufalis, CS; Baskoutas, S; Gontard, LCJournal of Nanoparticle Research, 15 (2013) 1388
Show abstract ▽
Nanocrystalline SnS powder has been prepared using tin chloride (SnCl2) as a tin ion source and sodium sulfide (Na2S) as a sulfur ion source with the help of ultrasound irradiation at room temperature. The as-synthesized SnS nanoparticles were quantitatively analyzed and characterized in terms of their morphological, structural, and optical properties. The detailed structural and optical properties confirmed the orthorhombic SnS structure and a strongly blue shifted direct band gap (1.74 eV), for synthesized nanoparticles. The measured band gap energy of SnS nanoparticles is in a fairly good agreement with the results of theoretical calculations of exciton energy based on the potential morphing method in the Hartree–Fock approximation.
Enero, 2013 | DOI: 10.1007/s11051-012-1388-1
- ‹ anterior
- 314 of 422
- siguiente ›














