Artículos SCI
2013
2013
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Growth regimes of porous gold thin films deposited by magnetron sputtering at oblique incidence: from compact to columnar microstructures
Alvarez, R; Garcia-Martin, JM; Macias-Montero, M; Gonzalez-Garcia, L; Gonzalez, JC; Rico, V; Perlich, J; Cotrino, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Palmero, ANanotechnology, 24 (2013) 045604
Show abstract ▽
Growth regimes of gold thin films deposited by magnetron sputtering at oblique angles and low temperatures are studied from both theoretical and experimental points of view. Thin films were deposited in a broad range of experimental conditions by varying the substrate tilt angle and background pressure, and were analyzed by field emission scanning electron microscopy and grazing-incidence small-angle x-ray scattering techniques. Results indicate that the morphological features of the films strongly depend on the experimental conditions, but can be categorized within four generic microstructures, each of them defined by a different bulk geometrical pattern, pore percolation depth and connectivity. With the help of a growth model, a microstructure phase diagram has been constructed where the main features of the films are depicted as a function of experimentally controllable quantities, finding a good agreement with the experimental results in all the studied cases.
Febrero, 2013 | DOI: 10.1088/0957-4484/24/4/045604
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Thermopower of Bio-SiC and SiC/Si ecoceramics prepared from sapele tree wood
Smirnov, IA; Smirnov, BI; Orlova, TS; Sulkovski, C; Misiorek, H; Muha, J; Jezowski, A; Ramirez-Rico, J; Martinez-Fernandez, JPhysics of the Solid State, 55 (2013) 54-59
Show abstract ▽
The thermopower coefficients of bio-SiC and SiC/Si ecoceramics prepared from sapele tree wood have been measured in the temperature interval 5–300 K. The measurements have been performed both along and perpendicular to empty (bio-SiC), as well as empty and partially silicon-filled (SiC/Si) channels in the samples. In bio-SiC, a contribution to thermopower associated with electron drag by phonons has been shown to exist within the temperature interval 5–200 (250) K. No such effect is realized in SiC/Si. This is assumed to derive from the presence in this material of heavily doped silicon embedded in SiC channels and the dominant part it plays in the behavior of the thermopower of this ceramics. The results obtained for the thermopower are compared with the available data for bio-SiC prepared from white eucalyptus tree wood and heavily doped bismuth.
Febrero, 2013 | DOI: 10.1134/S1063783413010307
Reactividad de Sólidos
Comments on “Thermal decomposition of pyridoxine: an evolved gas analysis-ion attachment mass spectrometry study”. About the application of model-fitting methods of kinetic analysis to single non-isothermal curves
Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Perejon, A; Criado, JMRapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry, 27 (2013) 500-502
Show abstract ▽
Reactividad de Sólidos
Clarifications regarding the use of model-fitting methods of kinetic analysis for determining the activation energy from a single non-isothermal curve
Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Perejon, A; Criado, JMChemistry Central Journal, 7 (2013) 25
Show abstract ▽
Background
This paper provides some clarifications regarding the use of model-fitting methods of kinetic analysis for estimating the activation energy of a process, in response to some results recently published in Chemistry Central journal.
Findings
The model fitting methods of Arrhenius and Savata are used to determine the activation energy of a single simulated curve. It is shown that most kinetic models correctly fit the data, each providing a different value for the activation energy. Therefore it is not really possible to determine the correct activation energy from a single non-isothermal curve. On the other hand, when a set of curves are recorded under different heating schedules are used, the correct kinetic parameters can be clearly discerned.
Conclusions
Here, it is shown that the activation energy and the kinetic model cannot be unambiguously determined from a single experimental curve recorded under non isothermal conditions. Thus, the use of a set of curves recorded under different heating schedules is mandatory if model-fitting methods are employed.
Febrero, 2013 | DOI: 10.1186/1752-153X-7-25
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Multiple Zeolite Structures from One Ionic Liquid Template
Blanes, JMM; Szyja, BM; Romero-Sarria, F; Centeno, MA; Hensen, EJM; Odriozola, JA; Ivanova, SChemistry-A European Journal, 19 (2013) 2122-2130
Show abstract ▽
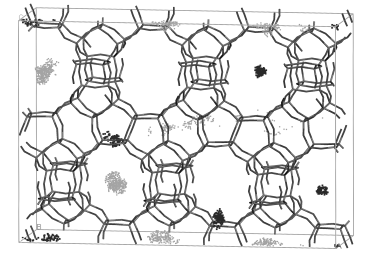
This study reports the use of 1-butyl-3-methyl imidazolium methanesulfonate ionic liquid as a template in the synthesis of zeolites. It is found that the silicon source determines the formation of beta (BEA), mordenite framework inverted (MFI), or analcime (ANA) zeolites. Depending on this source, different preorganized complexes are obtained that drive the formation of the different zeolite structures. In the presence of ethanol, the ionic liquid form preorganized complexes that drive the formation of MFI. In its absence, BEA is obtained. Whereas, the large amount of sodium present when using sodium metasilicate leads to ANA formation. A molecular simulation study of the relative stability of the template-framework system and location of the template provides further insight into the mechanism of synthesis.
Febrero, 2013 | DOI: 10.1002/chem.201202556
- ‹ anterior
- 313 of 422
- siguiente ›














