Artículos SCI
2013
2013
Materiales y Procesos Catalíticos de Interés Ambiental y Energético
Improved photocatalytic activity of g-C3N4/TiO2 composites prepared by a simple impregnation method
Miranda, C; Mansilla, H; Yanez, J; Obregon, S; Colon, GJournal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 253 (2013) 16-21
Show abstract ▽
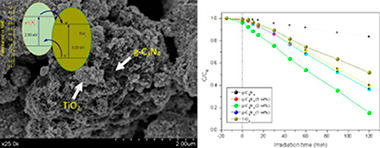
g-C3N4 and TiO2 hybrid structures are synthesized by means of a simple impregnation method having good photoactivities for the degradation of phenol under UV irradiation. From the wide structural and surface characterization we have stated that the presence of g-C3N4 notably affect the surface feature of TiO2 (surface area and pore size distribution). Enhanced photoactivities have been obtained for composites systems. The best result was obtained for 2 wt% loading of g-C3N4 leading to a 70% of improvement with respect to bare TiO2 in the reaction rate. The effective charge carrier separation was proposed as the responsible of such improved photoactivity.
Febrero, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2012.12.014
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Laser induced enhancement of dichroism in supported silver nanoparticles deposited by evaporation at glancing angles
Filippin, AN; Borras, A; Rico, VJ; Frutos, F; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARNanotechnology, 24 (2013) 045301
Show abstract ▽
Silver nanoparticles (NPs) depicting well defined surface plasmon resonance (SPR) absorption were deposited on flat substrates by physical vapor deposition in a glancing angle configuration. The particles were characterized by scanning electron microscopy and atomic force microscopy and their optical properties examined by UV–vis absorption spectroscopy using linearly polarized light. It was found that, depending on the amount of deposited silver and the evaporation angle, part of the 'as-prepared' samples present NPs characterized by an anisotropic shape and a polarization dependent SPR absorption and different colors when using polarized white light at 0° and 90°. Low-power irradiation of these materials with an infrared Nd-YAG nanosecond laser in ambient conditions produced an enhancement in such dichroism. At higher powers, the dichroism was lost and the SPR bands shifted to lower wavelengths as a result of the reshaping of the silver NPs in the form of spheres. The possible factors contributing to the observed changes in dichroism are discussed.
Febrero, 2013 | DOI: 10.1088/0957-4484/24/4/045301
Reactividad de Sólidos
Kinetic approach to partially overlapped thermal decomposition processes
Koga, N; Goshi, Y; Yamada, S; Perez-Maqueda, LAJournal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 111 (2013) 1463-1474
Show abstract ▽
Practical usefulness of the kinetic deconvolution for partially overlapped thermal decomposition processes of solids was examined by applying to the co-precipitated basic zinc carbonate and zinc carbonate. Comparing with the experimental deconvolutions by thermoanalytical techniques and mathematical deconvolutions using different statistical fitting functions, performance of the kinetic deconvolution based on an accumulative kinetic equation for the independent processes overlapped partially was evaluated in views of the peak deconvolution and kinetic evaluation. Two-independent kinetic processes of thermal decompositions of basic zinc carbonate and zinc carbonate were successfully deconvoluted by means of the thermoanalytical measurements in flowing CO2 and by applying sample controlled thermal analysis (SCTA). The deconvolutions by the mathematical curve fittings using different fitting functions and subsequent formal kinetic analysis provide acceptable values of the mass-loss fractions and apparent activation energies of the respective reaction processes, but the estimated kinetic model function changes depending on the fitting functions employed for the peak deconvolution. The mass-loss fractions and apparent kinetic parameters of the respective reaction processes can be optimized simultaneously by the kinetic deconvolution based on the kinetic equation through nonlinear least square analysis, where all the parameters indicated acceptable correspondences to those estimated through the experimental and mathematical deconvolutions. As long as the reaction processes overlapped are independent kinetically, the simple and rapid procedure of kinetic deconvolution is useful as a tool for characterizing the partially overlapped kinetic processes of the thermal decomposition of solids.
Febrero, 2013 | DOI: 10.1007/s10973-012-2500-6
Preferential oxidation of CO in excess H2 over CuO/CeO2 catalysts: Characterization and performance as a function of the exposed face present in the CeO2 support
Gamarra, D; Camara, AL; Monte, M; Rasmussen, SB; Chinchilla, LE; Hungria, AB; Munuera, G; Gyorffy, N; Schay, Z; Corberan, VC; Conesa, JC; Martinez-Arias, AApplied Catalysis B: Environmental, 130-131 (2013) 224-238
Show abstract ▽
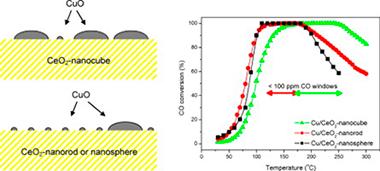
A series of oxidised copper-cerium nanostructured catalysts prepared by impregnation of copper over ceria supports synthesized by different methods (hydrothermal with varying preparation parameters, microemulsion/precipitation), in order to achieve different specific morphologies (nanocubes, nanorods and nanospheres), have been examined with respect to their catalytic properties for preferential oxidation of CO in excess H2 (CO-PROX). The catalysts have been characterized in detail by XRD, Raman, SBET measurement, HREM, XPS, TPR and EPR, which allows establishing a model of structural characteristics of the catalysts. The characterization results have been correlated with analysis of CO-PROX catalytic properties by means of catalytic activity measurements complemented by operando-DRIFTS. Structural dependence of the CO oxidation reaction on the dispersed copper oxide entities as a function of the exposed face present at the surface of the different ceria supports is revealed. An important overall enhancement of the CO-PROX performance is detected for the sample supported on ceria nanocubes which is proposed to be a consequence of the interaction between copper oxide and (1 0 0) faces of the ceria support.
Febrero, 2013 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2012.11.008
Reactividad de Sólidos
Clarifications regarding the use of model-fitting methods of kinetic analysis for determining the activation energy from a single non-isothermal curve
Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Perejon, A; Criado, JMChemistry Central Journal, 7 (2013) 25
Show abstract ▽
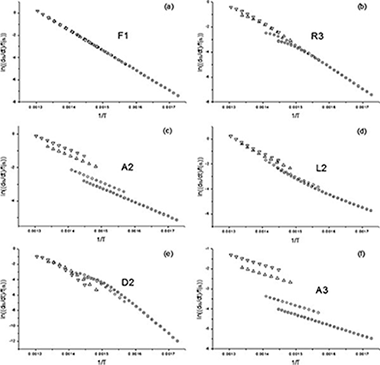
Background
This paper provides some clarifications regarding the use of model-fitting methods of kinetic analysis for estimating the activation energy of a process, in response to some results recently published in Chemistry Central journal.
Findings
The model fitting methods of Arrhenius and Savata are used to determine the activation energy of a single simulated curve. It is shown that most kinetic models correctly fit the data, each providing a different value for the activation energy. Therefore it is not really possible to determine the correct activation energy from a single non-isothermal curve. On the other hand, when a set of curves are recorded under different heating schedules are used, the correct kinetic parameters can be clearly discerned.
Conclusions
Here, it is shown that the activation energy and the kinetic model cannot be unambiguously determined from a single experimental curve recorded under non isothermal conditions. Thus, the use of a set of curves recorded under different heating schedules is mandatory if model-fitting methods are employed.
Febrero, 2013 | DOI: 10.1186/1752-153X-7-25
- ‹ anterior
- 312 of 422
- siguiente ›














