Artículos SCI
2012
2012
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Influence of plasma-generated negative oxygen ion impingement on magnetron sputtered amorphous SiO2 thin films during growth at low temperatures
Macias-Montero, M; Garcia-Garcia, FJ; Alvarez, R; Gil-Rostra, J; Gonzalez, JC; Cotrino, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Palmero, AJournal of Applied Physics, 111 (2012) 054312 (6 pages)
Show abstract ▽
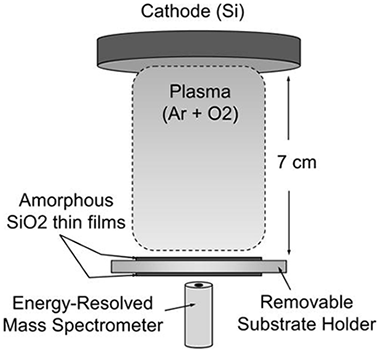
Growth of amorphous SiO2 thin films deposited by reactive magnetron sputtering at low temperatures has been studied under different oxygen partial pressure conditions. Film microstructures varied from coalescent vertical column-like to homogeneous compact microstructures, possessing all similar refractive indexes. A discussion on the process responsible for the different microstructures is carried out focusing on the influence of (i) the surface shadowing mechanism, (ii) the positive ion impingement on the film, and (iii) the negative ion impingement. We conclude that only the trend followed by the latter and, in particular, the impingement of O- ions with kinetic energies between 20 and 200 eV, agrees with the resulting microstructural changes. Overall, it is also demonstrated that there are two main microstructuring regimes in the growth of amorphous SiO2 thin films by magnetron sputtering at low temperatures, controlled by the amount of O2 in the deposition reactor, which stem from the competition between surface shadowing and ion-induced adatom surface mobility.
Marzo, 2012 | DOI: 10.1063/1.3691950
Reactividad de Sólidos
Inverse core-rim microstructure in (Ti,Ta)(C,N)-based cermets developed by a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction
Chicardi, E; Cordoba, JM; Sayagues, MJ; Gotor, FJInternational Journal of Refractory Metals & Hard Materials, 31 (2012) 39-46
Show abstract ▽
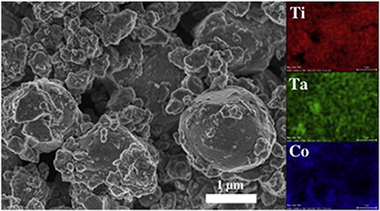
Cermets with a nominal composition (Tia(0.8)Ta(0.2)C(0.5)N(0.5)-20 wt.% Co) were synthesised by a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction (MSR) process from stoichiometric elemental powder blends. The MSR allowed the production of a complex (Ti,Ta)(C,N) solid solution, which was the raw material used for the sintering process. The pressureless sintering process was performed at temperatures between 1400 degrees C and 1600 degrees C in an inert atmosphere. The microstructural characterisation showed a complex microstructure composed of a ceramic phase with an unusual inverse core-rim structure and a Ti-Ta-Co intermetallic phase that acted as the binder.
Marzo, 2012 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2011.09.003
Reactividad de Sólidos
Thermal behaviour of ground and unground acid leached vermiculite
Perez-Maqueda, LA; Maqueda, C; Perez-Rodriguez, JL; Subrt, J; Cerny, Z; Balek, VJournal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 107 (2012) 431-438
Show abstract ▽
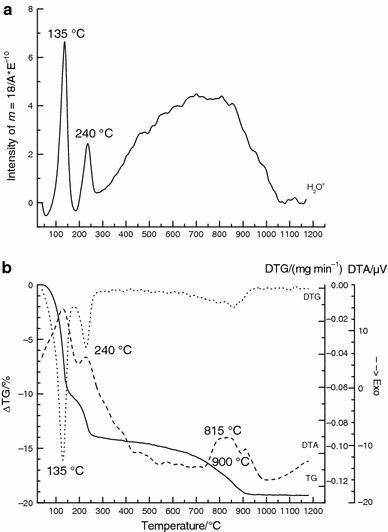
Acid leaching of vermiculite is an interesting procedure to prepare high surface area porous silica. Thermal behaviour of unground and ground vermiculite leached with HCl solutions has been studied by TG, DTA, ETA and high temperature XRD. Important differences have been observed in the thermal behaviour of unground and ground vermiculite after the acid treatments. Thus, for the acid-treated unground vermiculite, dehydrated vermiculite, enstatite and cristobalite were formed during the heating, while for the acid-treated ground vermiculite only iron oxides and cristobalite phases were observed. Structural modifications due to acid treatment were responsible for changes in the transport properties determined by ETA for the vermiculite samples.
Febrero, 2012 | DOI: 10.1007/s10973-011-1480-2
Operando DRIFTS study of the redox and catalytic properties of CuO/Ce1−xTbxO2−δ (x = 0–0.5) catalysts: evidence of an induction step during CO oxidation
Martinez-Arias, A.; Hungria, A. B.; Fernandez-Garcia, M.; Iglesias-Juez, A.; Soria, J.; Conesa, J. C.; Anderson, J. A.; Munuera, G.Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 14 (2012) 2144-2151
Show abstract ▽
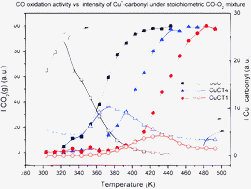
Catalysts of 1 wt% copper oxide supported on cerium oxide or cerium–terbium mixed oxides are comparatively examined with respect to their redox and catalytic properties for CO oxidation. Characterization of the catalysts had shown that they contain highly dispersed CuO-type entities on the corresponding nanostructured fluorite supports with copper dispersion increasing with increasing amounts of terbium in the support. In contrast, the CO oxidation catalytic activity decreases with increasing amounts of terbium in the support. On the basis of operando-DRIFTS experiments, one of the factors that could explain such behaviour is related to the greater difficulty in generating reduced copper sites active for the reaction in the presence of terbium, which in turn is evidenced to constitute an induction stage. Analysis of the redox properties is complemented by XPS which confirms the greater resistance to copper reduction in the presence of terbium.
Febrero, 2012 | DOI: 10.1039/C1CP23298C
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Public concern over ecotoxicology risks from nanomaterials: Pressing need for research-based information
Lapresta-Fernandez, A; Fernandez, A; Blasco, JEnvironment International, 39 (2012) 148-149
Show abstract ▽
- ‹ anterior
- 337 of 422
- siguiente ›














