Artículos SCI
2012
2012
Materiales Coloidales
Synthesis and Structure Resolution of RbLaF4
Rollet, AL; Allix, M; Veron, E; Deschamps, M; Montouillout, V; Suchomel, MR; Suard, E; Barre, M; Ocana, M; Sadoc, A; Boucher, F; Bessada, C; Massiot, D; Fayon, FInorganic Chemistry, 51 (2012) 2272-2282
Show abstract ▽
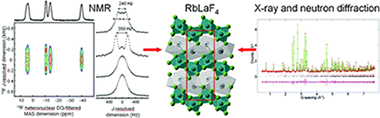
The synthesis and structure resolution of RbLaF4 are described. RbLaF4 is synthesized by solid-state reaction between RbF and LaF3 at 425 degrees C under a nonoxidizing atmosphere. Its crystal structure has been resolved by combining neutron and synchrotron powder diffraction data refinements (Pnma, a = 6.46281(2) angstrom, b = 3.86498(1) angstrom, c = 16.176:29(4) angstrom, Z = 4). One-dimensional Rb-87, La-139, and F-19 MAS NMR spectra have been recorded and are in agreement with the proposed structural model. Assignment of the F-19 resonances is performed on the basis of both F-19-La-139 J-coupling multiplet patterns observed in a heteronudear DQ-filtered J-resolved spectrum and F-19-Rb-87 HMQC MAS experiments. DFT calculations of both the F-19 isotropic chemical shieldings and the Rb-87, La-139 electric field gradient tensors using the GIPAW and PAW methods implemented in the CASTEP code are in good agreement with the experimental values and support the proposed structural model. Finally, the conductivity of RbLaF4 and luminescence properties of Eu-doped LaRbF4 are investigated.
Marzo, 2012 | DOI: 10.1021/ic202301e
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Quantification of low levels of fluorine content in thin films
Ferrer, FJ; Gil-Rostra, J; Terriza, A; Rey, G; Jimenez, C; Garcia-Lopez, J; Yubero, FNuclear Instruments & Methods in Physics Research Section B-Beam Interactions with Materials and Atoms, 274 (2012) 65-69
Show abstract ▽
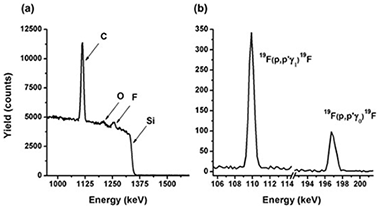
Fluorine quantification in thin film samples containing different amounts of fluorine atoms was accomplished by combining proton-Rutherford Backscattering Spectrometry (p-RBS) and proton induced gamma-ray emission (PIGE) using proton beams of 1550 and 2330 keV for p-RBS and PIGE measurements, respectively. The capabilities of the proposed quantification method are illustrated with examples of the analysis of a series of samples of fluorine-doped tin oxides, fluorinated silica, and fluorinated diamond-like carbon films. It is shown that this procedure allows the quantification of F contents as low as 1 at.% in thin films with thicknesses in the 100-400 nm range.
Marzo, 2012 | DOI: 10.1016/j.nimb.2011.11.042
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Influence of plasma-generated negative oxygen ion impingement on magnetron sputtered amorphous SiO2 thin films during growth at low temperatures
Macias-Montero, M; Garcia-Garcia, FJ; Alvarez, R; Gil-Rostra, J; Gonzalez, JC; Cotrino, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Palmero, AJournal of Applied Physics, 111 (2012) 054312 (6 pages)
Show abstract ▽
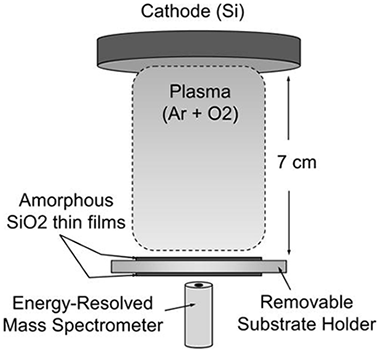
Growth of amorphous SiO2 thin films deposited by reactive magnetron sputtering at low temperatures has been studied under different oxygen partial pressure conditions. Film microstructures varied from coalescent vertical column-like to homogeneous compact microstructures, possessing all similar refractive indexes. A discussion on the process responsible for the different microstructures is carried out focusing on the influence of (i) the surface shadowing mechanism, (ii) the positive ion impingement on the film, and (iii) the negative ion impingement. We conclude that only the trend followed by the latter and, in particular, the impingement of O- ions with kinetic energies between 20 and 200 eV, agrees with the resulting microstructural changes. Overall, it is also demonstrated that there are two main microstructuring regimes in the growth of amorphous SiO2 thin films by magnetron sputtering at low temperatures, controlled by the amount of O2 in the deposition reactor, which stem from the competition between surface shadowing and ion-induced adatom surface mobility.
Marzo, 2012 | DOI: 10.1063/1.3691950
Reactividad de Sólidos
Inverse core-rim microstructure in (Ti,Ta)(C,N)-based cermets developed by a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction
Chicardi, E; Cordoba, JM; Sayagues, MJ; Gotor, FJInternational Journal of Refractory Metals & Hard Materials, 31 (2012) 39-46
Show abstract ▽
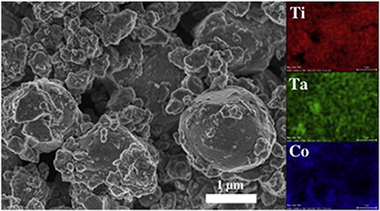
Cermets with a nominal composition (Tia(0.8)Ta(0.2)C(0.5)N(0.5)-20 wt.% Co) were synthesised by a mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction (MSR) process from stoichiometric elemental powder blends. The MSR allowed the production of a complex (Ti,Ta)(C,N) solid solution, which was the raw material used for the sintering process. The pressureless sintering process was performed at temperatures between 1400 degrees C and 1600 degrees C in an inert atmosphere. The microstructural characterisation showed a complex microstructure composed of a ceramic phase with an unusual inverse core-rim structure and a Ti-Ta-Co intermetallic phase that acted as the binder.
Marzo, 2012 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2011.09.003
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
CO-Induced Morphology Changes in Zn-Modified Ceria: A FTIR Spectroscopic Study
Penkova, A; Laguna, OH; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 116 (2012) 5747-5756
Show abstract ▽
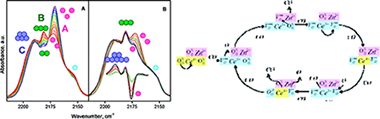
A FTIR study of the CO adsorption on a Zn-modified ceria is presented. The results indicate that at lower activation temperatures only Ce 4+ carbonyls were detected, which were reduced with the increase of the activation temperature. At higher activation temperatures, up to three Zn 2+ carbonyls were also identified according to the arrangement of the Zn 2+ cations. The consecutive CO adsorptions demonstrated an irreversible modification of the surface, resulting in an agglomeration of the zinc cations. A stepwise conversion of the isolated Zn 2+ carbonyls into carbonyls of the closely situated zinc cations followed by formation of bigger zinc oxide clusters was observed. The carbon monoxide coordinated on the isolated Zn 2+ cations at the interface with ceria reacts with the lattice oxygen leading to formation of oxygen vacancies. An insight into the origin of the activation during the CO oxidation process is proposed.
Marzo, 2012 | DOI: 10.1021/jp210996b
- ‹ anterior
- 336 of 422
- siguiente ›














