Artículos SCI
2011
2011
Materiales Coloidales - Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Synthesis, through pyrolysis of aerosols, of YIn1−xMnxO3 blue pigments and their efficiency for colouring glazes
M. Ocaña, J.P. Espinós, J.B. CardaDyes and Pigments, 91 (2011) 501-507
Show abstract ▽
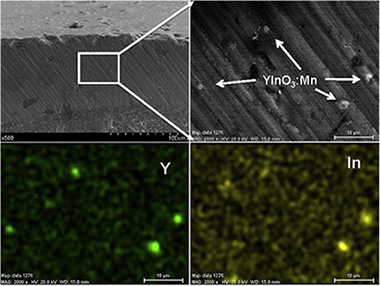
Mn-doped YInO3 blue pigments have been synthesised at a much lower temperature (1100 °C) than that required by the traditional solid state method (1400 °C). The developed procedure, which is based on the pyrolysis at 600 °C of aerosols generated from aqueous solutions of Y, In and Mn nitrates followed by an annealing treatment at 1100 °C, yields spherical pigments particles with heterogeneous size in the optimum range required for ceramic applications (<10 μm). The amount of Mn introduced in the YInO3 matrix has been systematically varied in order to evaluate the effects of the Mn content on the colour properties of the pigments. It has been found that the optimum pigment composition (bluer colour with the lowest Mn content) is given by the formula YIn0.90Mn0.10O 3. The technological performance of these YIn1-xMn xO3 blue pigments has also been evaluated by testing their efficiency for colouring ceramic glazes of different composition (boracic and plumbic) and properties, aiming to find a less toxic alternative for the Co-based pigments commonly used by the ceramic industry.
Diciembre, 2011 | DOI: 10.1016/j.dyepig.2011.03.009
Reactividad de Sólidos
An improved model for the kinetic description of the thermal degradation of cellulose
Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Perejon, A; Pascual-Cosp, J; Benitez-Guerrero, M; Criado, JMCellulose, 18 (2011) 1487-1498
Show abstract ▽
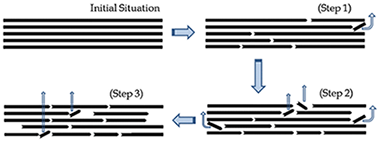
In spite of the large amount of work performed by many investigators during last decade, the actual understanding of the kinetics of thermal degradation of cellulose is still largely unexplained. In this paper, recent findings suggesting a nucleation and growth of nuclei mechanism as the main step of cellulose degradation have been reassessed and a more appropriate model involving chain scission and volatilization of fragments has been proposed instead. The kinetics of cellulose pyrolysis have been revisited by making use of a novel kinetic method that, without any previous assumptions regarding the kinetic model, allows performing the kinetic analysis of a set of experimental curves recorded under different heating schedules. The kinetic parameters and kinetic model obtained allows for the reconstruction of the whole set of experimental TG curves.
Diciembre, 2011 | DOI: 10.1007/s10570-011-9602-3
Compositional and Quantitative Microtextural Characterization of Historic Paintings by Micro-X-ray Diffraction and Raman Microscopy
Julia Romero-Pastor, Adrian Duran, Alejandro Basilio Rodríguez-Navarro, René Van Grieken, Carolina CardellAnalytical Chemistry, 83 (2011) 8420-8428
Show abstract ▽

This work shows the benefits of characterizing historic paintings via compositional and microtextural data from micro-X-ray diffraction (μ-XRD) combined with molecular information acquired with Raman microscopy (RM) along depth profiles in paint stratigraphies. The novel approach was applied to identify inorganic and organic components from paintings placed at the 14th century Islamic University—Madrasah Yusufiyya—in Granada (Spain), the only Islamic University still standing from the time of Al-Andalus (Islamic Spain). The use of μ-XRD to obtain quantitative microtextural information of crystalline phases provided by two-dimensional diffraction patterns to recognize pigments nature and manufacture, and decay processes in complex paint cross sections, has not been reported yet. A simple Nasrid (14th century) palette made of gypsum, vermilion, and azurite mixed with glue was identified in polychromed stuccos. Here also a Christian intervention was found via the use of smalt, barite, hematite, Brunswick green and gold; oil was the binding media employed. On mural paintings and wood ceilings, more complex palettes dated to the 19th century were found, made of gypsum, anhydrite, barite, dolomite, calcite, lead white, hematite, minium, synthetic ultramarine blue, and black carbon. The identified binders were glue, egg yolk, and oil.
Noviembre, 2011 | DOI: 10.1021/ac201159e
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Application of the solid state NMR to the study of the alcohol/alkane mixtures adsorption onto graphite
María D. Alba, Miguel A. Castro, Stuart M. Clarke, Santiago Medina, Loic Messe, Carmen MillánSolid State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, 40 (2011) 138-143
Show abstract ▽
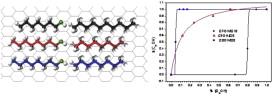
The mixing of molecules adsorbed from solution to different interfaces has both industrial and academic relevance and the mixing behaviour at the interface is a key to understanding for example, that the surface tension of a mixture of two surfactants is lower than either of the two pure materials and many other effects. In this paper, we report, for the first time, the application of Solid State NMR to the study of alkane/alcohol mixtures, in a range of relative size ratio between 0 and 0.35, adsorbed onto graphite at high, multilayer coverage. Moreover, this paper evaluated, for the first time, the utility of the combined used of 1H and 2H NMR for: (i) determining the surface composition and (ii) making a theoretical approach to the sorption isotherm. A variety of preferential adsorption behaviour is reported. Preferential adsorption of the longer molecule (decane vs. heptanol) from a mixture has been observed. However, if both components are of similar length, the alcohol is preferentially adsorbed (heptanol vs. octane and octanol vs. octane). Finally, a linear relation between the relative size ratio and the amount of alcohol at monolayer coverage is observed.
Noviembre, 2011 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ssnmr.2011.11.002
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Influence of the strong metal support interaction effect (SMSI) of Pt/TiO(2) and Pd/TiO(2) systems in the photocatalytic biohydrogen production from glucose solution
Colmenares, JC; Magdziarz, A; Aramendia, MA; Marinas, A; Marinas, JM; Urbano, FJ; Navio, JACatalysis Communications, 16 (2011) 1-6
Show abstract ▽
Two different catalysts consisting of Pt/TiO2 and Pd/TiO 2 were submitted to diverse oxidative and reductive calcination treatments and tested for photocatalytic reforming of glucose water solution (as a model of biomass component) in H2 production. Oxidation and reduction at 850°C resulted in better photocatalysts for hydrogen production than Degussa P-25 and the ones prepared at 500°C, despite the fact that the former consisted in very low surface area (6-8 m2/g) rutile titania specimens. The platinum-containing systems prepared at 850°C give the most effective catalysts. XPS characterization of the systems showed that thermal treatment at 850°C resulted in electron transfer from titania to metal particles through the so-called strong metal-support interaction (SMSI) effect. Furthermore, the greater the SMSI effect, the better the catalytic performance. Improvement in photocatalytic behavior is explained in terms of avoidance of electron-hole recombination through the electron transfer from titania to metal particles.
Noviembre, 2011 | DOI: 10.1016/j.catcom.2011.09.003
- ‹ anterior
- 344 of 422
- siguiente ›














