Artículos SCI
2011
2011
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Application of the solid state NMR to the study of the alcohol/alkane mixtures adsorption onto graphite
María D. Alba, Miguel A. Castro, Stuart M. Clarke, Santiago Medina, Loic Messe, Carmen MillánSolid State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, 40 (2011) 138-143
Show abstract ▽
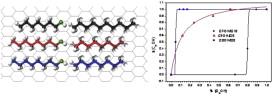
The mixing of molecules adsorbed from solution to different interfaces has both industrial and academic relevance and the mixing behaviour at the interface is a key to understanding for example, that the surface tension of a mixture of two surfactants is lower than either of the two pure materials and many other effects. In this paper, we report, for the first time, the application of Solid State NMR to the study of alkane/alcohol mixtures, in a range of relative size ratio between 0 and 0.35, adsorbed onto graphite at high, multilayer coverage. Moreover, this paper evaluated, for the first time, the utility of the combined used of 1H and 2H NMR for: (i) determining the surface composition and (ii) making a theoretical approach to the sorption isotherm. A variety of preferential adsorption behaviour is reported. Preferential adsorption of the longer molecule (decane vs. heptanol) from a mixture has been observed. However, if both components are of similar length, the alcohol is preferentially adsorbed (heptanol vs. octane and octanol vs. octane). Finally, a linear relation between the relative size ratio and the amount of alcohol at monolayer coverage is observed.
Noviembre, 2011 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ssnmr.2011.11.002
Fotocatálisis Heterogénea: Aplicaciones
Influence of the strong metal support interaction effect (SMSI) of Pt/TiO(2) and Pd/TiO(2) systems in the photocatalytic biohydrogen production from glucose solution
Colmenares, JC; Magdziarz, A; Aramendia, MA; Marinas, A; Marinas, JM; Urbano, FJ; Navio, JACatalysis Communications, 16 (2011) 1-6
Show abstract ▽
Two different catalysts consisting of Pt/TiO2 and Pd/TiO 2 were submitted to diverse oxidative and reductive calcination treatments and tested for photocatalytic reforming of glucose water solution (as a model of biomass component) in H2 production. Oxidation and reduction at 850°C resulted in better photocatalysts for hydrogen production than Degussa P-25 and the ones prepared at 500°C, despite the fact that the former consisted in very low surface area (6-8 m2/g) rutile titania specimens. The platinum-containing systems prepared at 850°C give the most effective catalysts. XPS characterization of the systems showed that thermal treatment at 850°C resulted in electron transfer from titania to metal particles through the so-called strong metal-support interaction (SMSI) effect. Furthermore, the greater the SMSI effect, the better the catalytic performance. Improvement in photocatalytic behavior is explained in terms of avoidance of electron-hole recombination through the electron transfer from titania to metal particles.
Noviembre, 2011 | DOI: 10.1016/j.catcom.2011.09.003
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Structure, Electrical Resistivity, and Thermal Conductivity of Beech Wood Biocarbon Produced at Carbonization Temperatures below 1000 degrees C
Parfen'eva, LS; Orlova, TS; Kartenko, NF; Smirnov, BI; Smirnov, IA; Misiorek, H; Jezowski, A; Muha, J; Vera, MCPhysics of the Solid State, 53 (2011) 2398-2407
Show abstract ▽
This paper reports on measurements of the thermal conductivity. and the electrical resistivity. in the temperature range 5-300 K, and, at 300 K, on X-ray diffraction studies of high-porosity (with a channel pore volume fraction of similar to 47 vol %) of the beech wood biocarbon prepared by pyrolysis (carbonization) of tree wood in an argon flow at the carbonization temperature T(carb) = 800 degrees C. It has been shown that the biocarbon template of the samples studied represents essentially a nanocomposite made up of amorphous carbon and nanocrystallites-"graphite fragments" and graphene layers. The sizes of the nanocrystallites forming these nanocomposites have been determined. The dependences rho(T) and kappa(T) have been measured for the samples cut along and perpendicular to the tree growth direction, thus permitting determination of the magnitude of the anisotropy of these parameters. The dependences rho(T) and kappa(T), which have been obtained for beech biocarbon samples prepared at T(carb) = 800 degrees C, are compared with the data amassed by us earlier for samples fabricated at T(carb) = 1000 and 2400 degrees C. The magnitude and temperature dependence of the phonon thermal conductivity of the nanocomposite making up the beech biocarbon template at T(carb) = 800 degrees C have been found.
Noviembre, 2011 | DOI: 10.1134/S1063783411110230
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Structural and catalytic properties of lanthanide (La, Eu, Gd) doped ceria
Hernandez, WY; Laguna, OH; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAJournal of Solid State Chemistry, 184 (2011) 3014-3020
Show abstract ▽
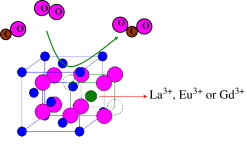
Ce0.9M0.1O2-δ mixed oxides (M=La, Eu and Gd) were synthesized by coprecipitation. Independent of the dopant cation, the obtained solids maintain the F-type crystalline structure, characteristic of CeO2 (fluorite structure) without phase segregation. The ceria lattice expands depending on the ionic radii of the dopant cation, as indicated by X-ray diffraction studies. This effect also agrees with the observed shift of the F2g Raman vibrational mode. The presence of the dopant cations in the ceria lattice increases the concentration of structural oxygen vacancies and the reducibility of the redox pair Ce4/Ce3. All synthesized materials show higher catalytic activity for the CO oxidation reaction than that of bare CeO2, being Eu-doped solid the one with the best catalytic performances despite of its lower surface area.
Noviembre, 2011 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jssc.2011.09.018
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Influence of Al2O3 reinforcement on precipitation kinetic of Cu–Cr nanocomposite
S. Sheibani, A. Ataie, S. Heshmati-Manesh, A. Caballero, J.M. CriadoThermochimica Acta, 526 (2011) 222-228
Show abstract ▽
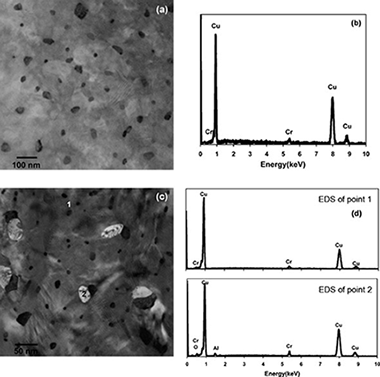
In this paper, the kinetic of precipitation process in mechanically alloyed Cu-1 wt.% Cr and Cu-1 wt.% Cr/3 wt.% Al2O3 solid solution was compared using differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), X-ray diffraction (XRD) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The ageing kinetics in Cu–Cr and Cu–Cr/Al2O3 can be described using Johnson–Mehl–Avrami (JMA) and Sestak–Berggren (SB) models, respectively. These different behaviors have been discussed in details. It was found that in presence of Al2O3 reinforcement, the ageing activation energy is decreased and the overall ageing process is accelerated. This behavior is probably due to higher dislocation density previously obtained during ball milling and Al2O3–Cu interface. TEM observations confirm that Al2O3–Cu interface and structural defects act as a primary and secondary nucleation sites, respectively.
Noviembre, 2011 | DOI: 10.1016/j.tca.2011.09.024
- ‹ anterior
- 345 of 422
- siguiente ›














