Artículos SCI
2011
2011
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Well-defined negatively charged gold carbonyls on Au/SiO2
Chakarova, K., Mihaylov, M., Ivanova, S., Centeno, M.A., Hadjiivanov, K.Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 115 (2011) 21273-21282
Show abstract ▽
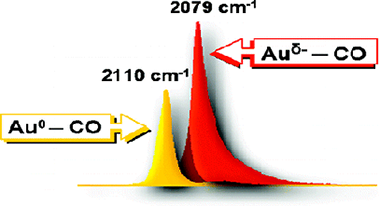
A Au/SiO2 sample was prepared by ammonia-assisted grafting using HAuCl4 as a gold precursor. Gold on the sample evacuated at 673 K is essentially in metallic form: adsorption of CO at 100 K results in formation of Au0-CO species (IR band at 2122 cm-1 shifting to 2103 cm-1 at high coverage). Coadsorption of CO and O2 even at ambient temperature leads to creation of Auδ+ sites and oxidation of CO. On the contrary, increase of the contact time between CO and the sample leads to a gradual reduction of Au0 to Au δ- species. The process is slightly favored by the presence of water and strongly enhanced in the presence of hydrogen. Back oxidation of Auδ- to Au0 and to Auδ+ occurs in the presence of oxygen. The Auδ- sites strongly adsorb CO and form different interconverting carbonyls observed in the 2080-2050 cm -1 region. On the basis of adsorption of CO-13CO and CO-13C18O isotopic mixtures, it is concluded that all Auδ--CO species are linear, and probably ordered structures are formed. Intensity transfer phenomena are nicely monitored during adsorption of CO isotopic mixtures. The eventual role of negatively charged gold in catalysis is discussed.
Noviembre, 2011 | DOI: 10.1021/jp2070562
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Comments on "an essay on contact angle measurements": Determination of surface roughness and modeling of the wetting behavior
Terriza, A; Alvarez, R; Yubero, F; Borras, A; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARPlasma Processes and Polymers, 8 (2011) 998-1002
Show abstract ▽
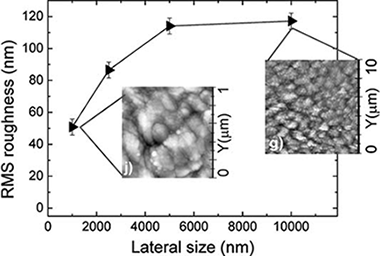
This commentary addresses the problem of determining surface roughness values and their use to assess the wetting behavior of surfaces. For very rough surfaces it is shown that depending on the observation scale by atomic force microscopy (AFM) quite different RMS roughness values can be obtained and that only the values taken at saturation can be used for properly describing the roughness of the examined materials. This effect has clear consequences when trying to apply wetting models to account for the influence of roughness on contact angles. These ideas are discussed with examples taken from rough polymer surfaces subjected to plasma etching. Debate - Discussion: To account for the wetting behavior of real surfaces within the Wenzel and similar models only surface roughness values determined at saturation can be used. This implies to check different observation areas by AFM and to choose the RMS roughness values once a maximum value of this parameter has been reached.
Noviembre, 2011 | DOI: 10.1002/ppap.201100081
Reactividad de Sólidos
Formation of the complete range of Ti5Si3-xGex solid solutions via mechanically induced self-sustained reactions
José M. Córdoba, Ernesto Chicardi, Miguel A. Avilés, Francisco J. GotorIntermetallics, 19 (2011) 1688-1692
Show abstract ▽
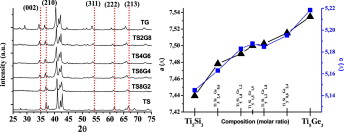
The complete range of Ti5Si3–Ti5Ge3 solid solutions was synthesised from elemental mixtures of Ti, Si, and Ge under an inert atmosphere via mechanically induced self-sustaining reactions (MSR). The stoichiometry of Ti5Si3−xGex solid solutions was controlled by adjusting the Si/Ge ratio of the initial mixture. The chemical composition and lattice parameters of the materials confirmed that Ti5Si3–Ti5Ge3 solid solutions with good chemical homogeneity could be produced via MSR.
Noviembre, 2011 | DOI: 10.1016/j.intermet.2011.07.005
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Soft plasma processing of organic nanowires: a route for the fabrication of 1D organic heterostructures and the template synthesis of inorganic 1D nanostructures
Maria Alcaire, Juan R. Sanchez-Valencia, Francisco J. Aparicio, Zineb Saghi, Juan C. Gonzalez-Gonzalez, Angel Barranco, Youssef Oulad Zian, Agustin R. Gonzalez-Elipe, Paul Midgley, Juan P. Espinos, Pierangelo Groening and Ana BorrasNanoscale, 3 (2011) 4554-4559
Show abstract ▽
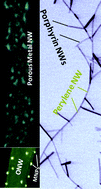
Hierarchical (branched) and hybrid metal-NPs/organic supported NWs are fabricated through controlled plasma processing of metalloporphyrin, metallophthalocyanine and perylene nanowires. The procedure is also applied for the development of a general template route for the synthesis of supported metal and metal oxide nanowires.
Noviembre, 2011 | DOI: 10.1039/C1NR11001B
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Structure and Chemical State of Octadecylamine Self-Assembled Monolayers on Mica
Benitez, JJ; San-Miguel, MA; Dominguez-Meister, S; Heredia-Guerrero, JA; Salmeron, MJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 115 (40) (2011) 19716-19723
Show abstract ▽
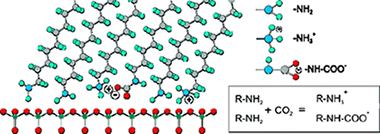
Structural and chemical data on n-octadecylamine self-assembled monolayers on mica (ODA/mica SAMs) have been obtained from ATR-FTIR and XPS spectroscopies. The analysis of the methylene modes concludes that alkylamine molecules are arranged in a rigid and well-ordered packing. Besides, the magnitude of the splitting of the methylene scissoring deflection is consistent with a molecular tilted configuration within the self-assembled layer, as already reported from topographic AFM data. Molecular dynamics simulations have supported this conclusion. XPS has revealed the presence of an important fraction of protonated amino groups (-NH3+) even in freshly prepared ODA/mica SAMs in air at RT. Two sources of protonation are proposed: (i) the acid-base reaction of (-NH2) end groups with the water adlayer on the surface of hydrophilic mica and (ii) the formation of an alkylamonium alkylcarbamate by a fast reaction with the atmospheric CO2 dissolved in such water adlayer. Though the water induced amino protonation is hypothetical, the presence of carbamate is univocally confirmed by ATR-FTIR. Upon extended contact with air (ripening) the conformational ordering in ODA/mica SAMs is slightly improved. Besides, further amino group protonation takes place with no additional carbamate formation. The process is described by a tentative mechanism in which protons are transferred from water molecules at the edges of SAMs islands to the inside. On the other side, carbamation is hindered by the steric effect of CO2 molecules trying to penetrate the close packed structure of octadecylamine molecules.
Octubre, 2011 | DOI: 10.1021/jp203871g
- ‹ anterior
- 346 of 422
- siguiente ›














