Artículos SCI
2011
2011
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Microstructure and chemical bonding of DLC films deposited on ACM rubber by PACVD
Martinez-Martinez, D., Schenkel, M., Pei, Y.T., Sánchez-López, J.C., De Hosson, J.T.H.M.Surface and Coatings Technology, 205 (2011) S75-S78
Show abstract ▽
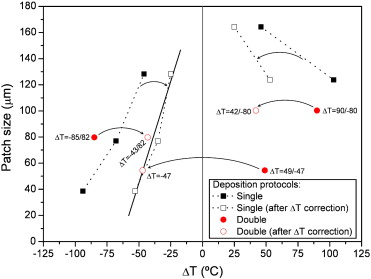
The microstructure and chemical bonding of DLC films prepared by plasma assisted chemical vapor deposition on acrylic rubber (ACM) are studied in this paper. The temperature variation produced by the ion impingement during plasma cleaning and subsequent film deposition was used to modify the film microstructure by controlling the different degrees of strain applied to the substrate. The film microstructure is studied by top view and cross sectional SEM. The observed patch sizes are correlated with the variation of temperature that occurred during deposition. Finally, the chemical bonding of the samples is studied by Raman spectroscopy. All the samples show similar spectra regardless the bias voltage used.
Julio, 2011 | DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2011.02.067
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Bacterial adherence on UHMWPE with vitamin E: an in vitro study
E. Gómez-Barrena, J. Esteban, D. Molina-Manso, H. Adames, M.J. Martínez-Morlanes, A. Terriza, F. Yubero and J. A. PuértolasJournal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine, 22 (2011) 1701-1706
Show abstract ▽
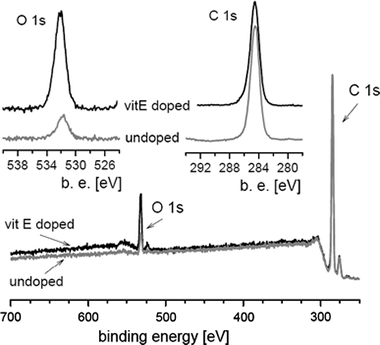
Orthopaedic materials may improve its capacity to resist bacterial adherence, and subsequent infection. Our aim was to test the bacterial adherence to alpha-tocopherol (frequently named vitamin E, VE) doped or blended UHMWPE with S. aureus and S. epidermidis, compared to virgin material. Collection strains and clinical strains isolated from patients with orthopaedic infections were used, with the biofilm-developing ability as a covariable. While collection strains showed significantly less adherence to VE-UHMWPE, some clinical strains failed to confirm this effect, leading to the conclusion that VE doped or blended UHMWPE affects the adherence of some S. epidermidis and S. aureus strains, independently of the concentration in use, but the results showed important intraspecies differences and cannot be generalized.
Julio, 2011 | DOI: 10.1007/s10856-011-4340-5
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Mechanical, microstructural and oxidation properties of reactively sputtered thin Cr-N coatings on steel
Cecchini, R., Fabrizi, A., Cabibbo, M., Paternoster, C., Mavrin, B.N., Denisov, V.N., Novikova, N.N., Haïdopoulo, M.Thin Solid Films, 519 (2011) 6515-6521
Show abstract ▽
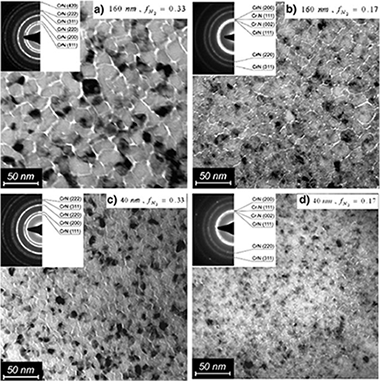
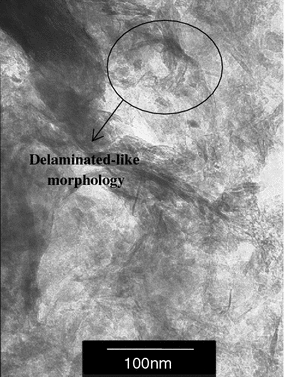
Thin (40 nm and 160 nm) CrN coatings were deposited on steel by reactive magnetron sputtering deposition, varying the N2 flow. The coatings were characterized in the as-deposited condition and after annealing in air at 500 °C for 1 h, by X-Ray Diffraction, Transmission Electron Microscopy, Raman and Fourier Transform Infrared spectroscopies. Hardness was measured by nanoindentation. Coatings have a nanocrystalline microstructure with the phase shifting from Cr2N to CrN, increasing grain size, thermal stability and resistance to oxidation with increasing N2. Also intrinsic coating hardness is influenced by both N2 flow during deposition and film thickness, as a result of changes in phase composition and microstructural properties.
Julio, 2011 | DOI: 10.1016/j.tsf.2011.04.115
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
High-stable mesoporous Ni-Ce/clay catalysts for syngas production
Daza, C.E., Gamba, O.A., Hernández, Y., Centeno, M.A., Mondragón, F., Moreno, S., Molina, R.Catalysis Letters, 141 (2011) 1037-1046
Show abstract ▽
A mesoporous-type catalytic support was synthesized through the modification of a smectite with polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) and microwaves. Texture and micro-morphology of the support was determined. Several techniques were employed in order to describe the chemical environment of active species on the surface. Ni0 particle sizes were dependent on the structural site of reducible species. High stable Ni-Ce catalysts (calcined at 800 °C) were evaluated in the CO2 reforming of methane reaction at 700 °C (WHSV = 96 L g-1 h-1, without dilution gas and pre-reduction). The catalysts have presented CH4 conversions between 40 and 65%, CO2 conversion between 35 and 65% and H2/CO ratios between 0.2 and 0.4.
Julio, 2011 | DOI: 10.1007/s10562-011-0579-1
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Solid solubility of Yb2Si2O7 in β-, γ- And δ-Y2Si2O7
Fernández-Carrión, A.J., Alba, M.D., Escudero, A., Becerro, A.I.Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 184 (2011) 1882-1889
Show abstract ▽
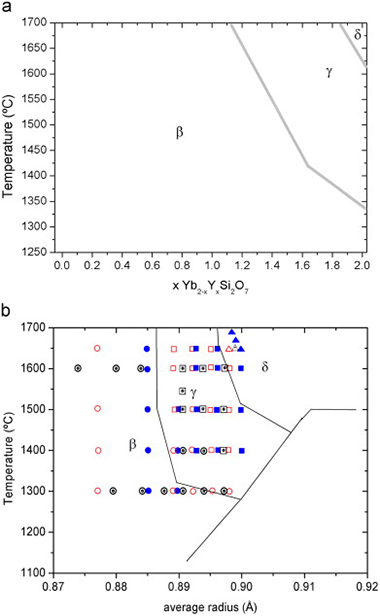
This paper examines the structural changes with temperature and composition in the Yb2Si2O7–Y2Si2O7 system; members of this system are expected to form in the intergranular region of Si3N4 and SiC structural ceramics when sintered with the aid of Yb2O3 and Y2O3 mixtures. A set of different compositions have been synthesised using the sol–gel method to obtain a xerogel, which has been calcined at temperatures between 1300 and 1650 °C during different times. Isotherms at 1300 and 1600 °C have been analysed in detail to evaluate the solid solubility of Yb2Si2O7 in β-Y2Si2O7 and γ-Y2Si2O7. Although Yb2Si2O7 shows a unique stable polymorph (β), Yb3+ is able to replace Y3+ in γ-Y2Si2O7 and δ-Y2Si2O7 at high temperatures and low Yb contents. IR results confirm the total solid solubility in the system and suggest a constant SiOSi angle of 180° in the Si2O7 unit across the system. The temperature–composition diagram of the system, obtained from powder XRD data, is dominated by the β-RE2Si2O7 polymorph, with γ-RE2Si2O7 and δ-RE2Si2O7 showing reduced stability fields. The diagram is in accordance with Felsche's diagram if average ionic radii are assumed for the members of the solid solution at any temperature, as long as the β–γ phase boundary is slightly shifted towards higher radii.
Julio, 2011 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jssc.2011.05.034
- ‹ anterior
- 351 of 422
- siguiente ›














