Artículos SCI
2011
2011
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Formation of organo-highly charged mica
Alba, M.D. , Castro, M.A., Orta, M.M., Pavón, E., Pazos, M.C., Valencia Rios, J.S.Langmuir, 16 (2011) 9711-9718
Show abstract ▽
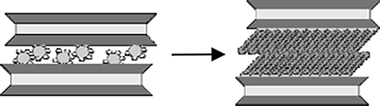
The interlayer space of the highly charged synthetic Na-Mica-4 can be modified by ion-exchange reactions involving the exchange of inorganic Na + cations by surfactant molecules, which results in the formation of an organophilic interlayer space. The swelling and structural properties of this highly charged mica upon intercalation with n-alkylammonium (RNH 3) + cations with varying alkyl chain lengths (R = C12, C14, C16, and C18) have been reported. The stability, fine structure, and evolution of gaseous species from alkylammonium Mica-4 are investigated in detail by conventional thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), in situ X-ray diffraction (XRD), and solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance (MAS NMR) techniques. The results clearly show the total adsorption of n-alkylammonium cations in the interlayer space which expands as needed to accommodate intercalated surfactants. The surfactant packing is quite ordered at room temperature, mainly involving a paraffin-type bilayer with an all-trans conformation, in agreement with the high density of the organic compounds in the interlayer space. At temperatures above 160 °C, the surfactant molecules undergo a transformation that leads to a liquid-like conformation, which results in a more disordered phase and expansion of the interlayer space.
Agosto, 2011 | DOI: 10.1021/la200942u
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Boron Compounds as Stabilizers of a Complex Microstructure in a Co-B-based Catalyst for NaBH4 Hydrolysis
Arzac, G.M., Rojas, T.C., Fernández, A.ChemCatChem, 3 (2011) 1305-1313
Show abstract ▽
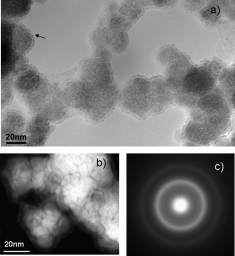
Co-B-based materials are widely used as catalysts for hydrogen generation through sodium borohydride self-decomposition. In the mid 1990s, the aqueous and organic chemistry involved in Co-B synthesis and handling was studied. Nevertheless, the exact microstructure of these catalysts has remained unsolved. Herein we present an exhaustive study which shows a new and complete microstructural view of a Co-B-based material together with the chemistry of the cobalt and boron involved. By using nanoscale-resolution microscopy and spectroscopy techniques, we have elucidated the role of boron compounds as stabilizers in a complex microstructure, which also explains its high catalytic performance and long-term stability. The catalyst is proposed to be made up of 1-3nm hcp Co0 nanoparticles embedded in amorphous CoxB (x=1, 2, 3), CoxOy, Co(BO2)2, and B2O3 phases alternatively or all together. All of these amorphous phases protect the nanocrystalline metallic core from growth and oxidation.
Agosto, 2011 | DOI: 10.1002/cctc.201100101
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Fe-doped ceria solids synthesized by the microemulsion method for CO oxidation reactions
O.H. Laguna, M.A. Centeno, M. Boutonnet, J.A. OdriozolaApplied Catalysis B: Environmental, 106 (2011) 621-629
Show abstract ▽
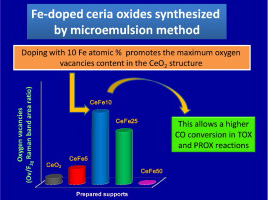
A series of Ce-Fe mixed oxides as well as the pure oxides were synthesized by the microemulsions method. The solid solution formation was established for all the Fe-doped systems and only a hardly noticeable segregation of α-Fe2O3 was appreciated for the solid with the maximum iron content (50at.% Fe). The oxygen exchange is improved for all the Fe-doped systems; however the 10at.% Fe appears as the optimal iron content for achieving the maximum oxygen vacancies concentration and the higher reducibility efficiency. The CO oxidation (TOX, PROX) is especially achieved for the solids with the lower iron contents but with a superior oxygen vacancies proportion. These Ce-Fe systems prepared from microemulsions are very attractive to be considered as supports for depositing active phases capable of enhancing oxygen exchange ability of the whole system, allowing higher CO oxidation abilities.
Agosto, 2011 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2011.06.025
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Ionic liquid protected heteropoly acids for methanol dehydration
Ivanova, S., Nitsch, X., Romero-Sarria, F., Louis, B., Centeno, M.A., Roger, A.C., Odriozola, J.A.Catalysis Today, 171 (2011) 236-241
Show abstract ▽
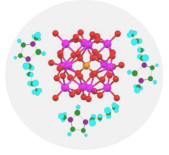
We report herein the synthesis of an organic-inorganic hybrid composed by the ionic liquid protected Keggin structure, as a precursor for acid catalyst and its subsequent application in the methanol dehydration reaction. Special attention was paid to the thermal stability of the resulted hybrids as a function of the Keggin anion. The catalytic behaviour of these new materials are also studied and compared to the metal salt Cs2HPW 12O40. The prepared hybrids are less thermally stable than the metal salt, but their partial decomposition results in very active and selective catalysts for the dehydration of methanol to dimethyl ether.
Agosto, 2011 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2011.03.077
Reactividad de Sólidos
Mechanochemical synthesis of Ti1−xZrxB2 and Ti1−xHfxB2 solid solutions
M.A. Avilés, J.M. Córdoba, M.J. Sayagués and F.J. GotorCeramics International, 37 (2011) 1895-1904
Show abstract ▽
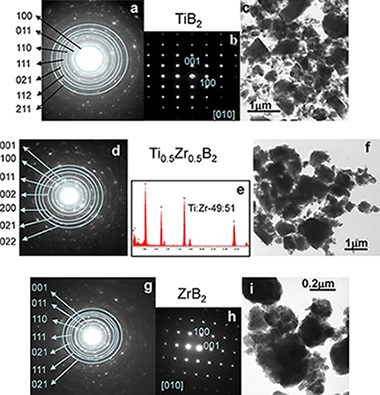
Solid solutions of TiB2-ZrB2 and TiB 2-HfB2 were obtained under an inert atmosphere by high-energy ball-milling mixtures of Ti/Zr/B and Ti/Hf/B, respectively. Milling promoted mechanically induced self-sustaining reactions (MSR), and the ignition time was dependent on the initial composition of the mixture. The stoichiometry of Ti1-xZrxB2 and Ti1-xHf xB2 solid solutions was controlled by adjusting the atomic ratio of the reactants. The solid solutions were characterised by X-ray diffraction, transmission electron microscopy, electron diffraction, and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. The results revealed that TiB2- ZrB2 possessed a nanometric microstructure and good chemical homogeneity. However, in the TiB2-HfB2 system, an inhomogeneous solid solution was obtained when a Ti-rich mixture was employed. The solid solutions showed good thermal stability; thus, can be used as raw materials for the development of technological materials for structural applications.
Agosto, 2011 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2011.02.004
- ‹ anterior
- 350 of 422
- siguiente ›














