Artículos SCI
2011
2011
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Comparative investigation of Al- and Cr-doped TiSiCN coatings
D.V. Shtansky, K.A. Kuptsov, Ph.V. Kiryukhantsev-Korneev, A.N. Sheveiko, A. Fernandez and M.I. PetrzhikSurface and Coatings Technology, 205 (2011) 4640-4648
Show abstract ▽
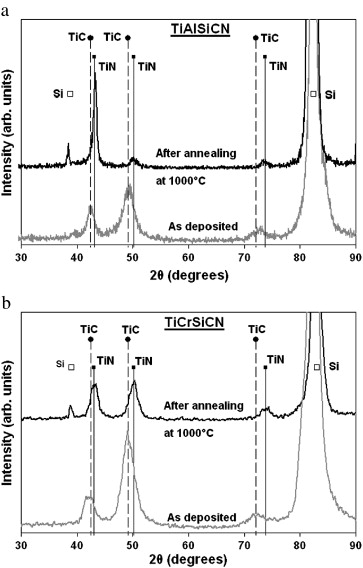
The aim of this work was a comparative investigation of the structure and properties of Al- and Cr-doped TiSiCN coatings deposited by magnetron sputtering of composite TiAlSiCN and TiCrSiCN targets produced by self-propagating high-temperature synthesis method. Based on X-ray diffraction, scanning and transmission electron microscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, and Raman spectroscopy data, the Al- and Cr-doped TiSiCN coatings possessed nanocomposite structures (Ti,Al)(C,N)/a-(Si,C) and (Ti,Cr)(C,N)/a-SiCxNy/a-C with cubic crystallites embedded in an amorphous matrix. To evaluate the thermal stability and oxidation resistance, the coatings were annealed either in vacuum at 1000, 1100, 1200, and 1300°C or in air at 1000°C for 1h. The results obtained show that the hardness of the Al-doped TiSiCN coatings increased from 41 to 46GPa, reaching maximum at 1000°C, and then slightly decreased to 38GPa at 1300°C. The Cr-doped TiSiCN coatings demonstrated high thermal stability up to 1100°C with hardness above 34GPa. Although both Al- and Cr-doped TiSiCN coatings possessed improved oxidation resistance up to 1000°C, the TiAlSiCN coatings were more oxidation resistant than their TiCrSiCN counterparts. The TiCrSiCN coatings showed better tribological characteristics both at 25 and 700°C and superior cutting performance compared with the TiAlSiCN coatings.
Junio, 2011 | DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2011.04.012
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Surface-functionalized fluorescent silica nanoparticles for the detection of ATP
Moro, AJ; Schmidt, J; Doussineau, T; Lapresta-Fernandez, A; Wegener, J; Mohr, GJChemical Communications, 47 (2011) 6066-6068
Show abstract ▽
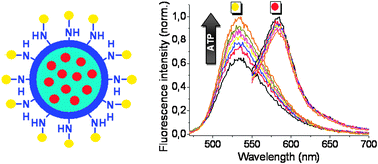
The design of two-dyed fluorescent silica nanoparticles for ATP detection is presented. The indicator dye possesses a dipicolyl-amine (DPA) unit complexed with Zn(ii) as a receptor function for ATP while a rhodamine derivative is used as the reference dye. The nanoparticles were fully characterized regarding analytical performance, morphology and cytocompatibility.
Junio, 2011 | DOI: 10.1039/C1CC10419E
Natural earth pigments from Roman and Arabic wall paintings revealed by spectroscopic techniques
Garofano, I., Duran, A., Perez-Rodriguez, J.L., Robador, M.D.Spectroscopy Letters, 44 (2011) 560-565
Show abstract ▽
Full identification of pigments used in wall paintings by Romans and Arabs that were recently discovered was achieved by the combined application of several spectroscopy methods. Identification of pigments was provided by the use of micro-Raman and FT-IR spectroscopy, while UV-Visible spectroscopy and chromatic studies permitted the authors to identify slight variations of hue attributed to mixtures of pigments. Natural earths and minerals were detected as the main pigments employed by both civilizations, although some differences were found between them. Red ochre, vermilion, yellow ochre, Egyptian blue, green earth, calcite, carbon, and possibly ivory blacks were identified in the Roman paintings. Only hematite and calcite were observed in the Arabic fragments.
Junio, 2011 | DOI: 10.1080/00387010.2011.610655
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Electrical properties of biomorphic SiC ceramics and SiC/Si composites fabricated from medium density fiberboard
T.S. Orlova, V.V. Popov, J. Quispe Cancapa, D. Hernández Maldonado, E. Enrique Magarino, F.M. Varela Feria, A. Ramírez de Arellano, J. Martínez FernándezJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 31 (2011) 1317-1323
Show abstract ▽

A study has been made of the dependences of the electrical resistivity and the Hall coefficient on the temperature in the range 1.8–1300 K and on magnetic fields of up to 28 kOe for the biomorphic SiC/Si (MDF-SiC/Si) composite and biomorphic porous SiC (MDF-SiC) based upon artificial cellulosic precursor (MDF – medium density fiberboards). It has been shown that electric transport in MDF-SiC is effected by carriers of n-type with a high concentration of ∼1020 cm−3 and a low mobility of ∼0.4 cm2 V−1 s−1. The specific features in the conductivity of MDF-SiC are explained by quantum effects arising in disordered systems and requiring quantum corrections to conductivity. The TEM studies confirmed the presence of disordering structural features (nanocrystalline regions) in MDF-SiC. The conductivity of MDF-SiC/Si composite originates primarily from Si component in the temperature range 1.8–500 K and since ∼500 to 600 K the contribution of MDF-SiC matrix becomes dominant.
Junio, 2011 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2010.06.015
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Compressive strength degradation in ZrB2-based ultra-high temperature ceramic composites
Ramirez-Rico, J; Bautista, MA; Martinez-Fernandez, J; Singh, MJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 31 (2011) 1345-1352
Show abstract ▽
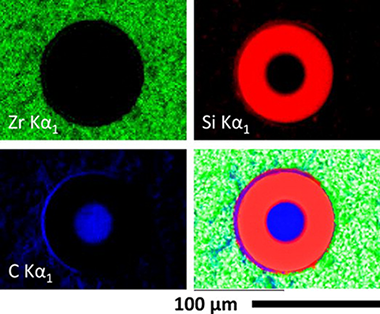
The high temperature compressive strength behavior of zirconium diboride (ZrB2)-silicon carbide (SiC) particulate composites containing either carbon powder or SCS-9a silicon carbide fibers was evaluated in air. Constant strain rate compression tests have been performed on these materials at room temperature, 1400, and 1550°C. The degradation of the mechanical properties as a result of atmospheric air exposure at high temperatures has also been studied as a function of exposure time. The ZrB2-SiC material shows excellent strength of 3.1±0.2GPa at room temperature and 0.9±0.1GPa at 1400°C when external defects are eliminated by surface finishing. The presence of C is detrimental to the compressive strength of the ZrB2-SiC-C material, as carbon burns out at high temperatures in air. As-fabricated SCS-9a SiC fiber reinforced ZrB2-SiC composites contain significant matrix microcracking due to residual thermal stresses, and show poor mechanical properties and oxidation resistance. After exposure to air at high temperatures an external SiO2 layer is formed, beneath which ZrB2 oxidizes to ZrO2. A significant reduction in room temperature strength occurs after 16-24h of exposure to air at 1400°C for the ZrB2-SiC material, while for the ZrB2-SiC-C composition this reduction is observed after less than 16h. The thickness of the oxide layer was measured as a function of exposure time and temperatures and the details of oxidation process has been discussed.
Junio, 2011 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2010.05.020
- ‹ anterior
- 354 of 422
- siguiente ›














