Artículos SCI
2011
2011
Materiales para Bioingeniería y Regeneración Tisular
Determination of Pore Size Distribution at the Cell-Hydrogel Interface
Leal-Egana, A., Dietrich-Braumann, U., Diaz-Cuenca, A., Nowicki, M., Bader, A.Journal of Nanobiotechnology, 9 (2011) Page 24
Show abstract ▽
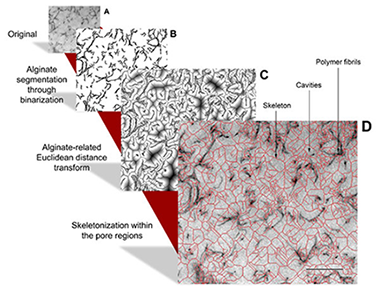
Analyses of the pore size distribution in 3D matrices such as the cell-hydrogel interface are very useful when studying changes and modifications produced as a result of cellular growth and proliferation within the matrix, as pore size distribution plays an important role in the signaling and microenvironment stimuli imparted to the cells. However, the majority of the methods for the assessment of the porosity in biomaterials are not suitable to give quantitative information about the textural properties of these nano-interfaces.
Mayo, 2011 | DOI: 10.1186/1477-3155-9-24
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Stability of Rare-Earth Disilicates: Ionic Radius Effect
Galunin, E; Alba, MD; Vidal, MJournal of the American Ceramic Society, 94 (2011) 1568–1574
Show abstract ▽
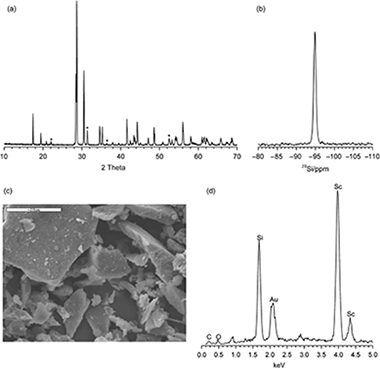
Rare-earth (RE) disilicates, of general formula RE2Si 2O7, are one of the products of the chemical reaction between RE (elements), which are actinide simulators, and the silicates used in the engineered barrier systems of deep geological repositories (DGPs). The aim of this paper is to establish the stability range of the disilicate phase as function of the nature of the RE (RE=Sc, Lu, or Y) and examine whether this phase would permit RE leaching under experimental conditions simulating those of the DGP. The β-polymorphs of the RE disilicates were synthesized by the sol-gel method and subsequently submitted to a pHstat leaching test. The rates of RE and Si leaching were measured and the transformation of the crystalline and amorphous phases was examined by X-ray powder diffraction and nuclear magnetic resonance techniques. The results indicate that the disilicate phases were stable within a wide range of pH, their stability being related to the hydrated ratio of the RE. Disilicate stability increased with the ionic radius of the RE. As a result, the Sc disilicate was stable throughout the pH range tested, whereas Y and Lu disilicate leaching was only observed at pH<4. Thus, it was confirmed that the formation of the disilicate phases could contribute to the confinement of radioactive wastes in engineered barriers.
Mayo, 2011 | DOI: 10.1111/j.1551-2916.2010.04272.x
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Structure and support induced structure disruption of soft nanoparticles obtained from hydroxylated fatty acids
Heredia-Guerrero, JA; San-Miguel, MA; Luna, M; Dominguez, E; Heredia, A; Benitez, JJSoft Matter, 7 (2011) 4357-4363
Show abstract ▽
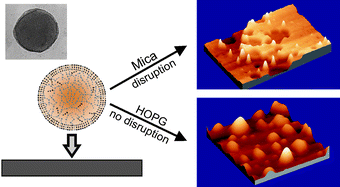
Soft and spherical nanoparticles, named as cutinsomes, have been prepared from concentrated 9(10),16-dihydroxypalmitic acid (diHPA) in aqueous solution. After isolation, cutinsomes have been chemically and structurally characterized by ATR-FTIR, TEM and dynamic atomic force microscopy (dynamic AFM). The nanoparticle can be described as a lipidic, liquid-like and mostly esterified core surrounded by a polar shell of carboxylate/carboxylic acid molecules. Molecular dynamic (MD) simulations have been used to support this model. The structural stability of soft cutinsomes has been tested by deposition on both non-polar (HOPG) and polar (mica) flat substrates. It has been found that the magnitude of the interaction between the polar shell of cutinsomes and the support determines their structure conservation or its spreading or rupture and spill out of the liquid-like content. The structural consistence of these nanoparticles as a function of the polarity of substrate is of interest in elucidating the formation mechanism of cutin, the most abundant biopolyester in nature and a very interesting biomaterial to be mimetized.
Mayo, 2011 | DOI: 10.1039/c0sm01545h
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Interplay of Resonant Cavity Modes with Localized Surface Plasmons: Optical Absorption Properties of Bragg Stacks Integrating Gold Nanoparticles
Olalla Sánchez-Sobrado, Gabriel Lozano, Mauricio E. Calvo, Ana Sánchez-Iglesias, Luis M. Liz-Marzán, Hernán MíguezAdvanced Materials, 23 (2011) 2108-2112
Show abstract ▽
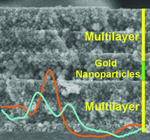
A procedure to prepare porous photonic crystal resonators containing gold nanoparticles is reported. The optical absorption of the ensemble, resulting from the excitation of the localized surface plasmon of the metallic beads, is finely tuned by a gradual shift of the cavity mode. This is achieved by infiltration of the void network with different guest compounds.
Mayo, 2011 | DOI: 10.1002/adma.201004401
Materiales para Bioingeniería y Regeneración Tisular
Hydroxyapatite Synthesis on Mesoporous Silica: A High Resolution Electron Microscopy Study
D.R. Acosta, A. Díaz-Cuenca, A.Acta Microscopica, 20 (2011) 29-35
Show abstract ▽
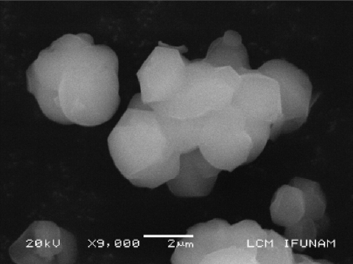
En este trabajo se presentan resultados de la síntesis de hidroxiapatita (HA) en sílice mesoporosa SBA-15. Se ha hecho un estudio de la síntesis de ambos materiales y un seguimiento del efecto del doble tratamiento térmico posterior a la síntesis. Las muestras se sometieron a distintas temperaturas de tratamiento hidrotermal entre 353 y 393 K con incrementos de 10 K durante 24 horas. En cada caso y una vez filtrado y seco el material se volvió a tratar con una calcinación a 773 K durante 10 hs. Se presentan los resultados del estudio del material compuesto SBA-15-HA por microscopia electrónica de transmisión convencional y avanzada ( STEM, Contraste Z, HREM) . El crecimiento de HA en los túneles de la matriz de sílice mesoporosa y el nivel de ocupación de los mismos aumenta con la temperatura del primer tratamiento hidrotermal y también del segundo tratamiento que favorece el sinterizado dentro de los túneles.
Mayo, 2011 | DOI:
- ‹ anterior
- 355 of 422
- siguiente ›














