Artículos SCI
2011
2011
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Interaction of Eu-isotopes with saponite as a component of the engineered barrier
María D. Alba, Miguel A. Castro, P. Chaín, Santiago Hurtado, M. Mar Orta, M. Carolina Pazos and María VillaApplied Clay Science, 52 (2011) 253-257
Show abstract ▽

Bentonite is accepted as the best clay material in the engineered barrier of deep geological repositories (DGRs) for radioactive waste disposal. In recent years, the interactions between a wide range of rare-earth (REE) cations and smectites have been studied. A combined study of stable europium and radioactive isotopes is reported here. Saponite was subjected to hydrothermal reactions with stable and radioactive (152Eu) europium ions under subcritical conditions. The structural changes of saponite were evaluated by XRD and SEM. The effect of temperature and reaction time on the changes was quantified by measuring 152Eu through gamma spectrometry. The reaction between europium and saponite was a first-order reaction. The presence of Eu in the precipitate in an amount much higher than the cation exchange capacity of saponite confirmed participation of chemical reactions or surface adsorption in the europium immobilization, even at temperatures as low as 150 °C. The reaction rate constant indicated that an 8- to 9-month period was needed for the completion, without significant changes, of the europium/saponite chemical reaction under the subcritical conditions of 200 °C and 350 °C.
Mayo, 2011 | DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2011.02.027
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Supported plasma-made 1D heterostructures: Perspectives and applications
Borras, A; Macias-Montero, M; Romero-Gomez, P; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARJournal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 44 (2011) 174016
Show abstract ▽
Plasma-related methods have been widely used in the fabrication of carbon nanotubes and nanofibres (NFs) and semiconducting inorganic nanowires (NWs). A natural progression of the research in the field of 1D nanostructures is the synthesis of multicomponent NWs and NFs. In this paper we review the state of the art of the fabrication by plasma methods of 1D heterostructures including applications and perspectives. Furthermore, recent developments on the use of metal seeds (Ag, Au, Pt) to obtain metal@oxide nanostructures are also extensively described. Results are shown for various metal substrates, either metal foils or supported nanoparticles/thin films of the metal where the effects of the size, surface coverage, percolation degree and thickness of the metal seeds have been systematically evaluated. The possibilities of the process are illustrated by the preparation of nanostructured films and supported NFs of different metal@oxides (Ag, Au and SiO2, TiO2, ZnO). Particularly, in the case of silver, the application of an oxygen plasma treatment prior to the deposition of the oxide was critical for efficiently controlling the growth of the 1D heterostructures. A phenomenological model is proposed to account for the thin-film nanostructuring and fibre formation by considering basic phenomena such as stress relaxation, inhomogeneities in the plasma sheath electrical field and the local disturbance of the oxide growth.
Mayo, 2011 | DOI: 10.1088/0022-3727/44/17/174016
Reactividad de Sólidos
Constant rate thermal analysis for thermal stability studies of polymers
Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Perejon, A; Criado, JMPolymer Degradation and Stability, 96 (2011) 974-981
Show abstract ▽
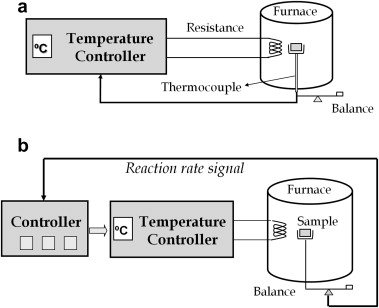
This paper explores the relationship between the shapes of temperature-time curves obtained from experimental data recorded by means of constant rate thermal analysis (CRTA) and the kinetic model followed by the thermal degradation reaction. A detailed shape analysis of CRTA curves has been performed as a function of the most common kinetic models. The analysis has been validated with simulated data, and with experimental data recorded from the thermal degradation of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), poly(1,4-butylene terephthalate) (PBT), polyethylene (PE) and poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC). The resulting temperature-time profiles indicate that the studied polymers decompose through phase boundary, random scission, diffusion and nucleation mechanisms respectively. The results here presented demonstrate that the strong dependence of the temperature-time profile on the reaction mechanism would allow the real kinetic model obeyed by a reaction to be discerned from a single CRTA curve.
Mayo, 2011 | DOI: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2011.01.027
Materiales Ópticos Multifuncionales
Analysis of artificial opals by scanning near field optical microscopy
Barrio, J; Lozano, G; Lamela, J; Lifante, G; Dorado, LA; Depine, RA; Jaque, F; Miguez, HJ. Appl. Phys., 109 (2011) 083514(5 pages)
Show abstract ▽
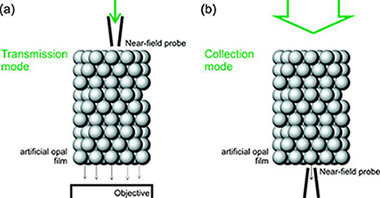
Herein we present a detailed analysis of the optical response of artificial opal films realized employing a near-field scanning optical microscope in collection and transmission modes. Near-field patterns measured at the rear surface when a plane wave impinges on the front face are presented with the finding that optical intensity maps present a clear correlation with the periodic arrangement of the outer surface. Calculations based on the vector Korringa-Kohn-Rostoker method reproduce the different profiles experimentally observed as well as the response to the polarization of the incident field. These observations constitute the first experimental confirmation of the collective lattice resonances that give rise to the optical response of these three dimensional periodic structures in the high-energy range.
Abril, 2011 | DOI: 10.1063/1.3573777
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Structural, chemical surface and transport modifications of regenerated cellulose dense membranes due to low-dose γ-radiation
Vazquez, MI; Heredia-Guerrero, JA; Galan, P; Benitez, JJ; Benavente, JMaterials Chemistry and Physics, 126 (2011) 734-740
Show abstract ▽
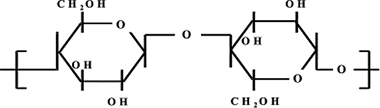
Modifications caused in commercial dense regenerated cellulose (RC) flat membranes by low-dose γ-irradiation (average photons energy of 1.23 MeV) are studied. Slight structural, chemical and morphological surface changes due to irradiation in three films with different RC content were determined by ATR-FTIR, XRD, XPS and AFM. Also, the alteration of their mechanical elasticity has been studied. Modification of membrane performance was determined from solute diffusion coefficient and effective membrane fixed charge concentration obtained from NaCl diffusion measurements. Induced structural changes defining new and effective fracture propagation directions are considered to be responsible for the increase of fragility of irradiated RC membranes. The same structural changes are proposed to explain the reduction of the membrane ion permeability through a mechanism involving either ion pathways elongation and/or blocking.
Abril, 2011 | DOI: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2010.12.051
- ‹ anterior
- 356 of 422
- siguiente ›














