Artículos SCI
2011
2011
Reactividad de Sólidos
Mechanochemical synthesis of visible light sensitive titanium dioxide photocatalyst
Šubrt, J., Criado, J.M., Szatmáry, L., Diánez-Millán, M.J., Murafa, N., Pérez-Maqueda, L.A., Brezová, V.International Journal of Photoenergy, 2011 (2011) Article number 156941
Show abstract ▽

Phase transition of anatase nanoparticles into the phases TiO2-II and rutile under grinding was studied. The addition of ammonium carbamate to the reaction mixture inhibits the phase conversion and the cold welding of particles. The UV-visible absorption spectrum showed narrowing the band gap width after grinding with an ammonium carbamate additive resulting in shift of the light absorption of the ground sample towards the visible region. By EPR, intensive formation of OH• radical at irradiation of the sample with both UV (λ > 300 nm) and visible (λ > 435 nm) light was observed. High photocatalytic activity of the ground sample in visible light region was demonstrated also by measurement of kinetics of the photocatalytic decomposition of 4-chlorophenol.
Marzo, 2011 | DOI: 10.1155/2011/156941
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
A comparative study of the role of additive in the MgH2 vs. the LiBH4–MgH2 hydrogen storage system
A. Fernández, E. Deprez, O. FriedrichsInternational Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 36 (2011) 3932-3940
Show abstract ▽
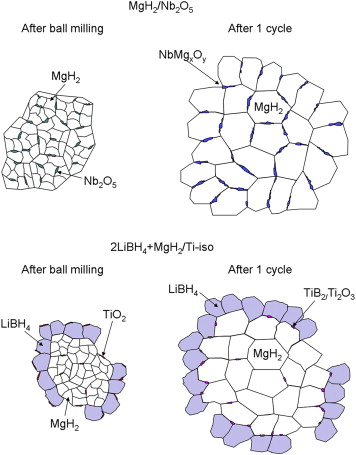
The objective of the present work is the comparative study of the behaviour of the Nb- and Ti-based additives in the MgH2 single hydride and the MgH2 + 2LiBH4 reactive hydride composite. The selected additives have been previously demonstrated to significantly improve the sorption reaction kinetics in the corresponding materials. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD), X-Ray Absorption Spectroscopy (XAS), X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) and Electron Microscopy (TEM) analysis were carried out for the milled and cycled samples in absence or presence of the additives. It has been shown that although the evolution of the oxidation state for both Nb- and Ti-species are similar in both systems, the Nb additive is performing its activity at the surface while the Ti active species migrate to the bulk. The Nb-based additive is forming pathways that facilitate the diffusion of hydrogen through the diffusion barriers both in desorption and absorption. For the Ti-based additive in the reactive hydride composite, the active species are working in the bulk, enhancing the heterogeneous nucleation of MgB2 phases during desorption and producing a distinct grain refinement that favours both sorption kinetics. The results are discussed in regards to possible kinetic models for both systems.
Marzo, 2011 | DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2010.12.112
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Gold nanoparticles on yttrium modified titania: Support properties and catalytic activity
Plata, JJ; Marquez, AM; Sanz, JF; Avellaneda, RS; Romero-Sarria, F; Dominguez, MI; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JATopics in Catalysis, 54 (2011) 219-228
Show abstract ▽
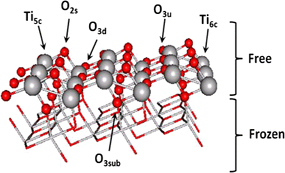
A series of titanium oxide catalysts modified with yttrium has been prepared by sol-gel method and their structural properties have been studied. The incorporation of yttrium in the titania lattice favors the formation of oxygen vacancies while at low Y loadings the anatase structure is preserved. The catalytic activity of these solids for CO oxidation is found to be significantly dependent on their physical properties. In particular the amount of dopant controls the number of surface oxygen vacancies created as well as the gold particle size, which directly affects the catalytic activity. Also, a linear relationship between the catalytic activity and the band gap values, which depend on the Y loading, is observed. Density functional theory based calculations show that Y atoms are incorporated at the TiO2 surface at substitutional positions only, while the preferred oxygen vacancies arise by removing the bridge surface oxygen atoms. These O-vacancies are the preferential adsorption sites for Au atoms and nanoparticles, acting as nucleation centers that favor the dispersion of the catalyst active phase over the support surface. In agreement with experiment, Y doping is found to decrease the band gap of the support due to a destabilization of the valence band of the oxide. © 2011 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC 2011.
Marzo, 2011 | DOI: 10.1007/s11244-011-9639-4
Materiales Nanoestructurados y Microestructura
Endurance of TiAlSiN coatings: Effect of Si and bias on wear and adhesion
Philippon, D; Godinho, V; Nagy, PM; Delplancke-Ogletree, MP; Fernandez, AWear, 270 (2011) 541-549
Show abstract ▽
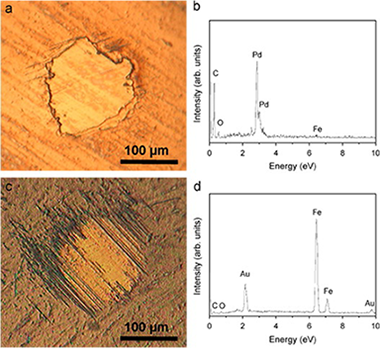
In this work, the endurance of TiAlSiN nanocomposite thin films subjected to tribological solicitation is studied. These coating were deposited on M2 steel substrate by magnetron sputtering. Dry sliding experiments were conducted at ambient temperature against WC-Co ball. Coefficients of friction, wear rates and endurances were correlated with the composition, microstructure, mechanical properties, residual stress and adhesion of the coatings. The hardness and elastic modulus were found dependent not only on the composition but also on the residual stress induced by the deposition process. Friction coefficient was found to be independent on Si content while the wear rate is strongly reduced for higher Si contents. The formation of a nanocomposite microstructure, the amount of amorphous Si-based phase and both, wear resistance and adhesion are shown as the critical factors to determine the endurance of the coating.
Marzo, 2011 | DOI: 10.1016/j.wear.2011.01.009
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Selective CO removal over Au/CeFe and CeCu catalysts in microreactors studied through kinetic analysis and CFD simulations
Arzamendi, G; Uriz, I; Dieguez, PM; Laguna, OH; Hernandez, WV; Alvarez, A; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JA; Montes, M; Gandia, LMChemical Engineering Journal, 167 (2011) 588-596
Show abstract ▽
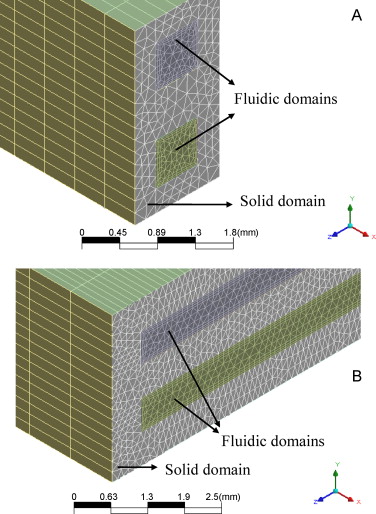
A kinetic study of the preferential oxidation of CO in H2 rich streams (CO-PrOx) over a cerium-copper oxide (CeCu) and a gold catalyst supported on cerium-iron oxide (Au/CeFe) is presented. The gold catalyst is very active but the CeCu oxide is more selective. A kinetic model describing the CO-PrOx system with CO2 and H2O in the feed has been formulated considering the oxidation of CO and H2 and the reverse water-gas shift reaction. The rate equations have been implemented in computational fluid dynamics codes to study the influence of the operating variables on the CO-PrOx in microchannels and microslits. The CeCu catalyst is the only one capable of achieving final CO contents below 10-100ppmv. Due to the opposite effect of temperature on activity and selectivity there is an optimal temperature at which the CO content is minimal over CeCu. This temperature varies between 170 and 200°C as the GHSV increases from 10,000 to 50,000h-1. Simulations have evidenced the very good heat transfer performance of the microdevices showing that the CO-PrOx temperature can be controlled using air as cooling fluid although the inlet temperature and flow rate should be carefully controlled to avoid reaction extinction. Both microchannels and microslits behaved similarly. The fact that the microslits are much easier to fabricate may be an interesting advantage in favour of that geometry in this case. © 2010 Elsevier B.V.
Marzo, 2011 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2010.08.083
- ‹ anterior
- 358 of 422
- siguiente ›














