Artículos SCI
2011
2011
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Nitridation of nanocrystalline TiO2 thin films by treatment with ammonia
Romero-Gomez, P; Rico, V; Espinos, JP; Gonzalez-Elipe, AR; Palgrave, RG; Egdell, RGThin Solid Films, 519 (2011) 3587-3595
Show abstract ▽
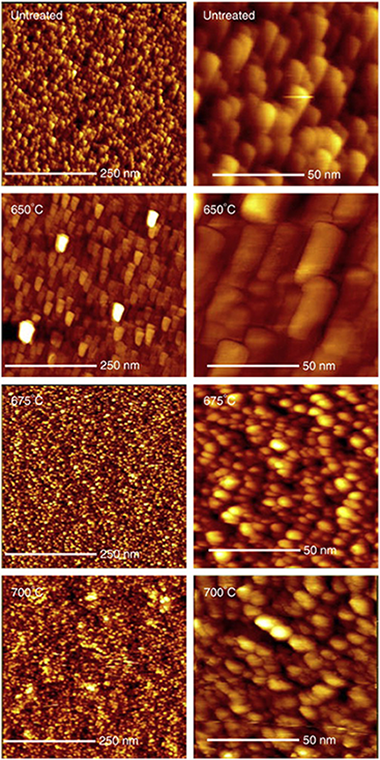
Nanocrystalline anatase (TiO2) thin films prepared by a physical vapour deposition method were nitrided by annealing in flowing NH3 at temperatures ranging between 650 °C and 700 °C. It was established that there was a narrow window of temperatures which allowed both incorporation of interstitial nitrogen into the films with retention of the anatase phase without chemical reduction and preservation of the characteristic nanocrystalline morphology. These optimally modified films responded to visible light in photowetting tests and showed the ability to degrade an organic dye under visible light irradiation.
Marzo, 2011 | DOI: 10.1016/j.tsf.2011.01.267
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Gold nanoparticles on yttrium modified titania: Support properties and catalytic activity
Plata, JJ; Marquez, AM; Sanz, JF; Avellaneda, RS; Romero-Sarria, F; Dominguez, MI; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JATopics in Catalysis, 54 (2011) 219-228
Show abstract ▽
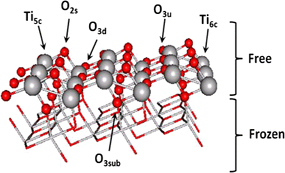
A series of titanium oxide catalysts modified with yttrium has been prepared by sol-gel method and their structural properties have been studied. The incorporation of yttrium in the titania lattice favors the formation of oxygen vacancies while at low Y loadings the anatase structure is preserved. The catalytic activity of these solids for CO oxidation is found to be significantly dependent on their physical properties. In particular the amount of dopant controls the number of surface oxygen vacancies created as well as the gold particle size, which directly affects the catalytic activity. Also, a linear relationship between the catalytic activity and the band gap values, which depend on the Y loading, is observed. Density functional theory based calculations show that Y atoms are incorporated at the TiO2 surface at substitutional positions only, while the preferred oxygen vacancies arise by removing the bridge surface oxygen atoms. These O-vacancies are the preferential adsorption sites for Au atoms and nanoparticles, acting as nucleation centers that favor the dispersion of the catalyst active phase over the support surface. In agreement with experiment, Y doping is found to decrease the band gap of the support due to a destabilization of the valence band of the oxide. © 2011 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC 2011.
Marzo, 2011 | DOI: 10.1007/s11244-011-9639-4
Materiales Coloidales
Tuning from blue to magenta the up-converted emissions of YF3:Tm3+/Yb3+ nanocrystals
Quintanilla, M; Nunez, NO; Cantelar, E; Ocana, M; Cusso, FNanoscale, 3 (2011) 1046-1052
Show abstract ▽
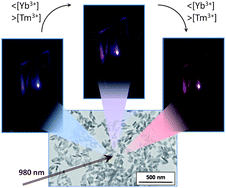
Monodisperse YF3:Tm3+/Yb3+ nanocrystals have been synthesized to explore the visible up-converting properties under near infrared (975 nm) excitation. It has been found that the nanoparticles exhibit intense red up-converted emissions, in addition to the characteristic UV and blue Tm3+-bands. It is demonstrated that, by carefully selecting Tm3+ and Yb3+ contents, the relative intensity of the different emissions can be changed producing an overall emission colour that can be tuned from blue to magenta.
Marzo, 2011 | DOI: 10.1039/c0nr00676a
Reactividad de Sólidos
Mechanochemical synthesis of visible light sensitive titanium dioxide photocatalyst
Šubrt, J., Criado, J.M., Szatmáry, L., Diánez-Millán, M.J., Murafa, N., Pérez-Maqueda, L.A., Brezová, V.International Journal of Photoenergy, 2011 (2011) Article number 156941
Show abstract ▽

Phase transition of anatase nanoparticles into the phases TiO2-II and rutile under grinding was studied. The addition of ammonium carbamate to the reaction mixture inhibits the phase conversion and the cold welding of particles. The UV-visible absorption spectrum showed narrowing the band gap width after grinding with an ammonium carbamate additive resulting in shift of the light absorption of the ground sample towards the visible region. By EPR, intensive formation of OH• radical at irradiation of the sample with both UV (λ > 300 nm) and visible (λ > 435 nm) light was observed. High photocatalytic activity of the ground sample in visible light region was demonstrated also by measurement of kinetics of the photocatalytic decomposition of 4-chlorophenol.
Marzo, 2011 | DOI: 10.1155/2011/156941
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Creep behavior of TiCxN1-x-CoTi cermets synthesized by mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction
Morales-Rodriguez, A; Gallardo-Lopez, A; Dominguez-Rodriguez, A; Cordoba, JM; Aviles, MA; Gotor, FJJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 31 (2011) 299-302
Show abstract ▽
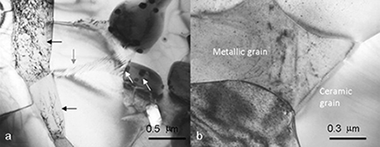
The plastic flow of TiCxN1-x-CoTi cermets has been investigated by uniaxial compression tests carried out in argon atmosphere at temperatures between 1100 and 1200°C. Two different cermets, with 5wt.% W or WC content as sintering additives, have been explored to assess the influence of the sintering additives on creep. The microstructural observations of deformed samples and the mechanical results indicate that the hard phase (ceramic grains) controls the plastic deformation. The stress exponent changes from 1 to 2 with increasing strain rate, suggesting a transition in the deformation mechanism from diffusional creep to grain boundary sliding; both with similar activation energy values of about 400kJ/mol. This value of activation energy agrees with C diffusion in the carbonitride grains as the strain rate controlling mechanism.
Marzo, 2011 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2010.10.007
- ‹ anterior
- 359 of 422
- siguiente ›














