Artículos SCI
2011
2011
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Creep behavior of TiCxN1-x-CoTi cermets synthesized by mechanically induced self-sustaining reaction
Morales-Rodriguez, A; Gallardo-Lopez, A; Dominguez-Rodriguez, A; Cordoba, JM; Aviles, MA; Gotor, FJJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 31 (2011) 299-302
Show abstract ▽
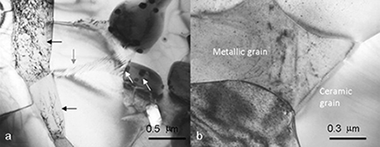
The plastic flow of TiCxN1-x-CoTi cermets has been investigated by uniaxial compression tests carried out in argon atmosphere at temperatures between 1100 and 1200°C. Two different cermets, with 5wt.% W or WC content as sintering additives, have been explored to assess the influence of the sintering additives on creep. The microstructural observations of deformed samples and the mechanical results indicate that the hard phase (ceramic grains) controls the plastic deformation. The stress exponent changes from 1 to 2 with increasing strain rate, suggesting a transition in the deformation mechanism from diffusional creep to grain boundary sliding; both with similar activation energy values of about 400kJ/mol. This value of activation energy agrees with C diffusion in the carbonitride grains as the strain rate controlling mechanism.
Marzo, 2011 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2010.10.007
Reactividad de Sólidos - Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Design and testing of a microchannel reactor for the PROX reaction
Cruz, S; Sanz, O; Poyato, R; Laguna, OH; Echave, FJ; Almeida, LC; Centeno, MA; Arzamendi, G; Gandia, LM; Souza-Aguiar, EF; Montes, M; Odriozola, JAChemical Engineering Journal, 167 (2011) 634-642
Show abstract ▽
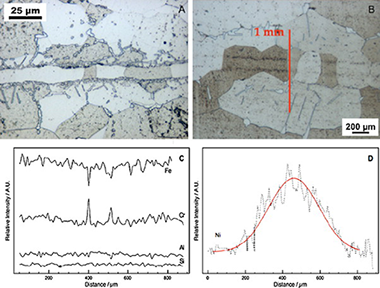
The different steps for manufacturing a microchannel reactor for the PROX reaction are discussed. Transient Liquid Phase bonding (TLP) using a Ni-B-Si amorphous melt spun is used for joining micromilled Al-alloyed ferritic stainless steel plates followed by recrystallization at 1200°C for 5h. A CuOx-CeO2 catalyst synthesized by the coprecipitation method was washcoated on the microchannel block resulting in a homogenous 20-30μm thick layer. The catalytic activity for CO-PROX reaction is similar in both the powder catalyst and the microchannel coated reactor but the selectivity is higher in the microchannel reactor. © 2010 Elsevier B.V.
Marzo, 2011 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2010.08.088
Reactividad de Sólidos
Kinetic Analysis of Complex Solid-State Reactions. A New Deconvolution Procedure
Antonio Perejón, Pedro E. Sánchez-Jiménez, José M. Criado, and Luis A. Pérez-MaquedaJournal of Physical Chemistry B, 2011, 115 (8), pp 1780–1791
Show abstract ▽
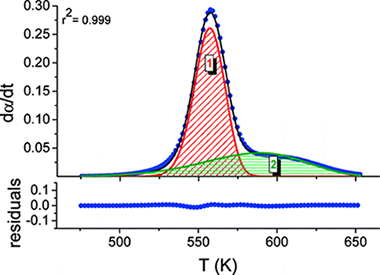
The kinetic analysis of complex solid-state reactions that involve simultaneous overlapping processes is challenging. A method that involves the deconvolution of the individual processes from the overall differential kinetic curves obtained under linear heating rate conditions, followed by the kinetic analysis of the discrete processes using combined kinetic analysis, is proposed. Different conventional mathematical fitting functions have been tested for deconvolution, paying special attention to the shape analysis of the kinetic curves. It has been shown that many conventional mathematical curves such as the Gaussian and Lorentzian ones fit kinetic curves inaccurately and the subsequent kinetic analysis yields incorrect kinetic parameters. Alternatively, other fitting functions such as the Fraser-Suzuki one properly fit the kinetic curves independently of the kinetic model followed by the reaction and their kinetic parameters, and moreover, the subsequent kinetic analysis yields the correct kinetic parameters. The method has been tested with the kinetic analysis of complex processes, both simulated and experimental.
Marzo, 2011 | DOI: 10.1021/jp110895z
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Lateral and in-depth distribution of functional groups on diamond-like carbon after oxygen plasma treatments
Lopez-Santos, C; Yubero, F; Cotrino, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARDiamond and Related Materials, 20 (2011) 49-56
Show abstract ▽
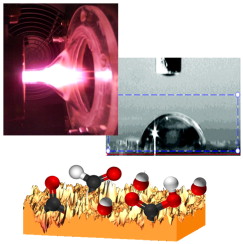
A diamond like carbon material has been exposed to a low pressure microwave and atmospheric pressure plasma of oxygen to enhance its hydrophilicity and surface energy. For comparison, data are also reported after activation with a beam of neutral atoms of oxygen. The surface incorporation of oxygenated functional groups and the determination of the in-depth distribution of this element have been analysed by means of the X ray photoemission spectroscopy (XPS). Atomic force microscopy (AFM) has been used to get information of the surface topography and, by recording friction maps of the surface, the lateral distribution of oxygenated functional groups formed after the different activation treatments. Differences in surface composition, topography and in-depth and lateral distribution of oxygen have been correlated with the intrinsic characteristics of the activation plasma processes.
Febrero, 2011 | DOI: 10.1016/j.diamond.2010.11.024
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Influence of OH− concentration on the illitization of kaolinite at high pressure
M. Mantovani, A. Escudero, A.I. Becerro,Applied Clay Science, 51 (2011) 220-225
Show abstract ▽
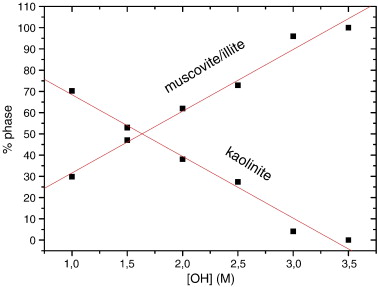
The products of hydrothermal reactions of kaolinite at 300 °C and 1000 bars were studied in KOH solutions covering an OH− concentration, [OH−], of 1 M to 3.5 M. XRD patterns indicated a notable influence of the [OH−] on the reaction. At [OH] ≥ 3 M, the only stable phase was muscovite/illite. The content of muscovite/illite was calculated from the analysis of the diagnostic 060 reflections of kaolinite and muscovite/illite. The results showed a linear dependence of kaolinite and muscovite/illite contents with [OH−]. 27Al MAS NMR spectroscopy revealed the formation of small nuclei of K-F zeolite at high [OH−]. Finally, modelling of the 29Si MAS NMR spectra indicated that the Si/Al ratio of the muscovite/illite formed was very close to that of muscovite, at least in the mineral formed at low [OH−]. In good agreement with the XRD data, the quantification of the reaction products by 29Si MAS NMR indicated a linear decrease of the kaolinite content with increasing OH− concentration.
Febrero, 2011 | DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2010.11.021
- ‹ anterior
- 360 of 422
- siguiente ›














