Artículos SCI
2011
2011
Materiales Coloidales
A facile single-step procedure for the synthesis of luminescent Ln 3+:YVO4 (Ln = Eu or Er + Yb)-silica nanocomposites
Ocana, M; Cantelar, E; Cusso, FMaterials Chemistry and Physics, 125 (2011) 224-230
Show abstract ▽
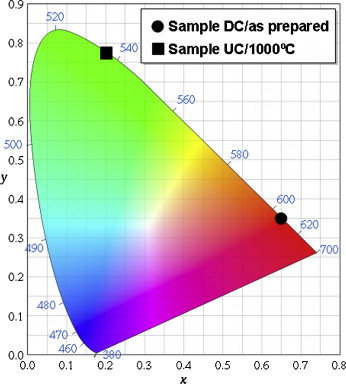
A simple and single-step method for the production of Ln-doped YVO 4 nanocrystals and their simultaneous encapsulation in a silica network based on the pyrolysis of liquid aerosols at 800 °C is reported. The procedure is illustrated for Yb,Er:YVO4-silica nanocomposites consisting of spherical particles, which present up-converted green luminescence after IR excitation whose efficiency increased on annealing up to 1000 °C due to the release of impurities (adsorbed water, and residual anions). XPS spectroscopy and TEM observations revealed that the surface of the composite particles was enriched in silica, which would facilitate their functionalisation required to use them in biological applications. The procedure can also be used to prepare other rare earth doped systems as illustrated for the case of Eu-doped YVO4/silica having down-converted red luminescence.
Enero, 2011 | DOI: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2010.09.011
Reactividad de Sólidos
Synthesis and characterization of titanium-vanadium ternary nitride (Tix V1-x N)
Roldan, MA; Alcala, MD; Ortega, A; Real, CBoletín de la Sociedad Española de Cerámica y Vidrio, 50 (2011) 31-40
Show abstract ▽
Titanium-Vanadium nitride (TiVN) has been prepared from carbothermal reduction of corresponding oxides and also by direct nitridation of a mix of two metals employing the ATVC method. The characterization of the final product by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, electron energy loss (EELS), and X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) is presented. The synthesis of the ternary nitride has been possible in all range of composition and the final product is obtained with nanometric particle size and a high microhardness after sintering.
Enero, 2011 | DOI: 10.3989/cyv.052011
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Hydrogen production by methanol steam reforming on NiSn/MgO-Al2O3 catalysts: The role of MgO addition
Penkova, A; Bobadilla, L; Ivanova, S; Dominguez, MI; Romero-Sarria, F; Roger, AC; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAApplied Catalysis A-General,392 (2011) 184-191
Show abstract ▽
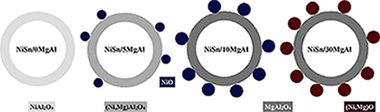
The effect of the magnesia loading on the surface structure and catalytic properties of NiSn/MgO-Al2O3 catalysts for hydrogen production by methanol steam reforming has been investigated. The catalysts have been obtained by impregnation of γ-Al2O3 by the incipient wetness method, with variation of the MgO content. X-ray diffraction (XRD), BET surface area and H2-temperature programmed reduction (TPR) have been used to characterise the prepared catalysts. From this, it has been concluded that the incorporation of MgO results in the formation of MgAl2O4 spinel, which modifies the acid-base properties of the catalysts. The formation of Ni-Sn alloys after the reductive pre-treatment has also been evidenced. The influence of the temperature of reaction and of the MgO loading on the hydrogen production by reforming of methanol has been established. Moreover, tests of catalytic stability have been carried out for more than 20 h. The carbonaceous deposits have been examined by temperature-programmed oxidation (TPO). The analysis of the catalysts after reaction has confirmed the low level of carbon formation on these catalysts. In no case, carbon nanotubes have been detected on the solids.
Enero, 2011 | DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2010.11.016
2010
2010
Materiales de Diseño para la Energía y Medioambiente
Illization of kaolinite: The effect of pressure on the reaction rate
Mantovani, M; Becerro, AIClays and Clay Minerals, 58 (2010) 766-771
Show abstract ▽
Studies of the paragenesis of authigenic illite in arkosic sandstonesof various regions and ages have revealed that the illitizationof kaolinite is an important reaction accounting for the formationof authigenic illite in sandstones during burial diagenesis.The illitization of kaolinite takes place at an intermediateburial depth of 3–4 km, where pressure can reach valuesof 100 MPa ( 1000 bars). The purpose of the present study wasto analyze the effect of pressure on the rate of kaolinite illitizationin alkaline conditions. Hydrothermal reactions were conductedon KGa-1b kaolinite in KOH solution at 300°C and under pressuresof 500, 1000, and 3000 bars for 1 to 24 h. The visual examinationof the X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns indicated a notableinfluence of pressure on the reaction rate. Molar percentagesof muscovite/illite formed at each time interval were calculatedfrom the analysis of two diagnostic XRD peaks, representingthe 060 reflections of kaolinite and muscovite/illite. The datawere modeled to obtain the initial rate of conversion at eachpressure. The results indicated that the initial rate of kaoliniteto muscovite/illite conversion is one order of magnitude greaterat 3000 bars than at 500 or 1000 bars. Comparison of these datawith those in the literature show a faster conversion rate (severalorders of magnitude) in an initially high-alkaline solutionthan in a near-neutral solution.
1000 bars). The purpose of the present study wasto analyze the effect of pressure on the rate of kaolinite illitizationin alkaline conditions. Hydrothermal reactions were conductedon KGa-1b kaolinite in KOH solution at 300°C and under pressuresof 500, 1000, and 3000 bars for 1 to 24 h. The visual examinationof the X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns indicated a notableinfluence of pressure on the reaction rate. Molar percentagesof muscovite/illite formed at each time interval were calculatedfrom the analysis of two diagnostic XRD peaks, representingthe 060 reflections of kaolinite and muscovite/illite. The datawere modeled to obtain the initial rate of conversion at eachpressure. The results indicated that the initial rate of kaoliniteto muscovite/illite conversion is one order of magnitude greaterat 3000 bars than at 500 or 1000 bars. Comparison of these datawith those in the literature show a faster conversion rate (severalorders of magnitude) in an initially high-alkaline solutionthan in a near-neutral solution.
Diciembre, 2010 | DOI: 10.1346/CCMN.2010.0580604
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Study of the stabilization of zinc phthalocyanine in sol-gel TiO2 for photodynamic therapy applications
Lopez, T; Ortiz, E; Alvarez, M; Navarrete, J; Odriozola, JA; Martinez-Ortega, F; Paez-Mozo, EA; Escobar, P; Espinoza, KA; Rivero, IANanomedicine-Nanotechnology Biology and Medicine, 6 (2010) 777-785
Show abstract ▽
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) has emerged as an alternative and promising noninvasive treatment for cancer. It is a two-step procedure that uses a combination of molecular oxygen, visible light, and photosensitizer (PS) agents; phthalocyanine (Pc) was supported over titanium oxide but has not yet been used for cell inactivation. Zinc phthalocyanine (ZnPc) molecules were incorporated into the porous network of titanium dioxide (TiO2) using the sol-gel method. It was prepared from stock solutions of ZnPc and TiO2. ZnPc-TiO2 was tested with four cancer cell lines. The characterization of supported ZnPc showed that phthalocyanine is linked by the N-pyrrole to the support and is stable up to 250 degrees C, leading to testing for PDT. The preferential localization in target organelles such as mitochondria or lysosomes could determine the cell death mechanism after PDT. The results suggest that nanoparticulated TiO2 sensitized with ZnPc is an excellent candidate as sensitizer in PDT against cancer and infectious diseases. From the Clinical Editor: Photodynamic therapy is a two-step procedure that uses a combination of molecular oxygen, visible light and photosensitizer agents as an alternative and promising non-invasive treatment for cancer. The results of this study suggest that nanoparticulated TiO2 sensitized with ZnPc is an excellent photosensitizer candidate against cancer and infectious diseases.
Diciembre, 2010 | DOI: 10.1016/j.nano.2010.04.007
- ‹ anterior
- 364 of 422
- siguiente ›














