Artículos SCI
2010
2010
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Physicochemical Characterization and Use of Wastes from Stainless Steel Mill
Dominguez, MI; Romero-Sarria, F; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAEnvironmental Progress & Sustainable Energy, 29 (2010) 471-480
Show abstract ▽
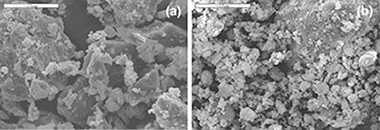
Several types of wastes are produced during the manufacture of stainless steel (slags, refractory bricks, and dust). Most of these wastes are not recycled but stored in security deposits or landfills depending on their environmental danger This article reports the study of the physicochemical and mineralogical properties of stainless steel wastes. Their possible uses are also discussed.
Diciembre, 2010 | DOI: 10.1002/ep.10435
Propiedades mecánicas, modelización y caracterización de cerámicos avanzados
A first study of the high-temperature plasticity of ceria-doped zirconia polycrystals
de Bernardi-Martin, S; Gomez-Garcia, D; Dominguez-Rodriguez, A; de Portu, GJournal of the European Ceramic Society, 30 (2010) 3357-3362
Show abstract ▽
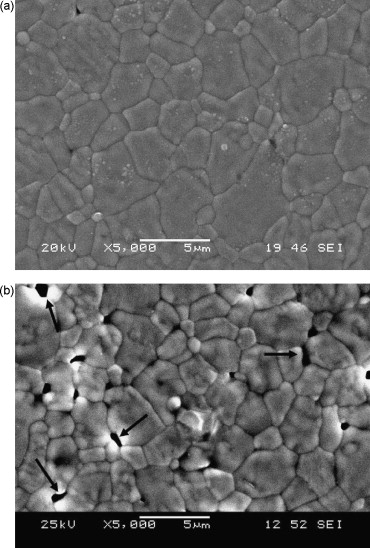
Ceria zirconia ceramic alloys were sintered by high-temperature annealing, considering several synthesis temperatures to obtain a full-dense ceria zirconia ceramic material using a temperature as low as possible. It was found that fully density is achieved at temperatures of 1450 degrees C. Monolithic specimens were crept under compression at high temperatures. The creep results fitted an empirical constitutive equation consistent with a classical Ratchinger mechanism for grain switching. This result was confirmed through microstructural characterization of as-received and post-mortem specimens. Since the conventional Ashby-Verrall model is contrary to the mechanism controlling creep in other zirconia alloys, the results are considered in the framework of a new grain boundary sliding model, with particular discussion of the validity of that model for the ceria zirconia case.
Diciembre, 2010 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2010.07.043
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Gold supported on metal-doped ceria catalysts (M = Zr, Zn and Fe) for the preferential oxidation of CO (PROX)
Laguna, OH; Sarria, FR; Centeno, MA; Odriozola, JAJournal of Catalysis, 276 (2010) 360-370
Show abstract ▽
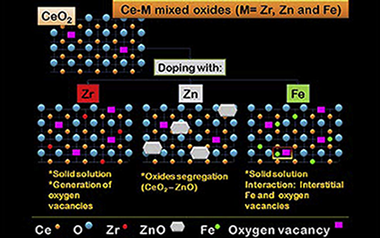
A series of ceria oxides doped with 10 mol % of Zr Zn and Fe have been prepared by a pseudo sol-gel method throughout the thermal decomposition of the corresponding metallic propionates With these supports 1 wt % gold catalysts were prepared by the deposition-precipitation method All the solids were characterized by means of XRF N-2 adsorption XRD Raman spectroscopy and SEM techniques and their catalytic activity toward preferential oxidation of CO (PROX) reaction tested The results showed solid solution when doping with Zr and Fe and ZnO surface segregation in the case of Zn We demonstrate that gold dispersion depends on not only the oxygen vacancy concentration but also the nature of the doping agent Finally the catalytic activity was highly promoted by gold in all cases being the doped gold catalysts more active than Au/CeO2 at low temperature.
Diciembre, 2010 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jcat.2010.09.027
Variscite source and source analysis: testing assumptions at Pico Centeno (Encinasola, Spain)
Odriozola, CP; Linares-Catela, JA; Hurtado-Perez, VJournal of Archaeological Science, 37 (2010) 3146-3157
Show abstract ▽
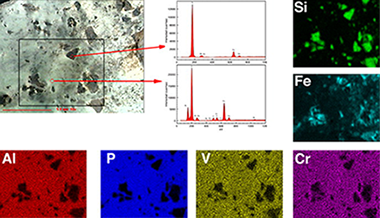
The analysis of trade and their implications for understanding social interaction is a major research question of prehistoric research in Europe. Variscite is a rare mineral that offers an excellent opportunity to study trade and exchange patterns in prehistoric Europe through proveniencing of source material. In this paper we discuss the exploitation and exchange of variscite at Pico Centeno mining district during the Copper Age. XRF, XRD, and FTIR analyses of the mineral recovered at Pico Centeno mining district during archaeological survey provides a baseline mineral signature for the source and sub-sources, which were then compared to other Iberian sources and to 44 green beads from 8 megalithic tombs from two different regions, in order to test ‘provenance postulate’ and distribution models. Mineral sampled during survey at Pico Centeno mining district turned out to be pure variscite phases, while extremely varied for the studied green beads: variscite, muscovite, talc or chlorite. On testing ‘provenance postulate’ we have focused on compositional comparison of Pico Centeno’s variscite with reference from various geological sources of Western Europe. We found that the concentrations of trace elements do not allow us to establish the origin of the beads, as traditionally claimed, due to the strong natural variability on minor and trace elements of the sources. Instead we found after FTIR analysis, that different proportions of phosphate species, which results in P/Al ratios higher than 1, arose during the genesis of the variscite deposits and resulted from the associated pH and nature of the host-rocks, modifying the concentrations of PO43−, H2PO4− and HPO42−. Thus, the P/Al atomic ratio should be an indication of provenance as it is established during mineral genesis. This issue has not been addressed in any of the other studied sources where this ratio seems to be ≈1.
Diciembre, 2010 | DOI: 10.1016/j.jas.2010.07.016
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Band Gap Narrowing versus Formation of Electronic States in the Gap in N-TiO2 Thin Films
Romero-Gomez, P; Hamad, S; Gonzalez, JC; Barranco, A; Espinos, JP; Cotrino, J; Gonzalez-Elipe, ARJournal of Physical Chemistry C, 114 (2010) 22546-22557
Show abstract ▽
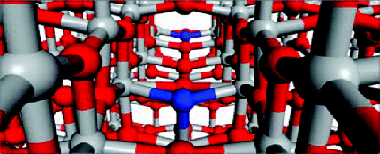
N-containing TiO2 thin films with different amounts of nitrogen have been prepared by plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) by using different titanium precursors without (titanium isopropoxide, TTIP) and with (tetrakis diethylamino titanium, TDEAT and tetrakis dimethylamino titanium, TDMAT) nitrogen in their structures and different N-2/O-2 ratios as plasma gas. For low/high content of nitrogen, Ti-NO- and/or Ti-N-like species have been detected in the films by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). Their optical behavior is characterized by a red shift of their absorption edge when Ti-N species are a majority, and by an unmodified edge with localized absorption states in the gap when only Ti-NO-like species are present in the film. The experimental results have been interpreted by calculating the density of states of model systems consisting of a 2 x 2 x 3 repetition of the anatase unit cell. This basic structure incorporates nitrogen defects in either substitutional or interstitial lattice positions that are considered equivalent to the Ti-N- and Ti-NO-like species detected by XPS. To simulate the effect of, respectively, a low or a high concentration of nitrogen, calculations have been carried out by placing two nitrogen defects either in separated or in nearby positions of the anatase structure. The computational analysis reveals that the defects have different stabilization energies and confirm that an edge shift of the valence band is induced by the substitutional nitrogen centers, as observed when a high concentration of Ti-N species becomes incorporated into the films. In agreement with the experimental results, when only Ti-NO-like species are detected by XPS, no band gap narrowing is obtained by the calculations that predict the appearance of localized electronic states in the gap. The fact that only these latter films present water wetting angle photoactivity when irradiated with visible light supports that the presence of Ti-NO-like species is a required condition for visible light photoactivity.
Diciembre, 2010 | DOI: 10.1021/jp104634j
- ‹ anterior
- 365 of 422
- siguiente ›














