Artículos SCI
2010
2010
Nanotecnología en Superficies y Plasma
Improved Non-Covalent Biofunctionalization of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Using Carbohydrate Amphiphiles with a Butterfly-Like Polyaromatic Tail
Assali, M; Leal, MP; Fernandez, I; Romero-Gomez, P; Baati, R; Khiar, NNano Research, 3 (2010) 764-778
Show abstract ▽
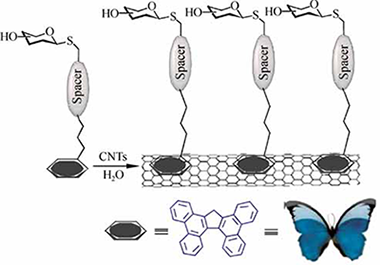
We have developed an efficient strategy for the non-covalent functionalization of multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) which allows a biomimetic presentation of carbohydrates on their surface by pi-pi stacking interactions. The strategy is based on the use of sugar-based amphiphiles functionalized with tetrabenzo[a,c,g,i] fluorene (Tbf), a polyaromatic compound with a topology that resembles a butterfly with open wings. The new carbohydrate-tethered Tbf amphiphiles have been synthesized in a straightforward manner using click chemistry. The reported method has been developed in order to improve the rather low ability of pyrene-based systems to exfoliate MWCNTs in water. By means of thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), ultraviolet (UV), infrared (IR), and fluorescence spectroscopies the interaction between MWCNTs and the Tbf group has been found to be stronger than those involving pyrene-based amphiphilic carbohydrates. The resulting aggregates with a multivalent sugar exposition on their surface are able to engage in specific ligand-lectin interactions similar to glycoconjugates on a cell membrane.
Noviembre, 2010 | DOI: 10.1007/s12274-010-0044-2
Propiedades mecánicas, modelización y caracterización de cerámicos avanzados
Segregation-induced grain boundary electrical potential in ionic oxide materials: A first principles model
D. Gómez-García, Juan J. Meléndez, Robert L. González-Romero, A. Domínguez-RodríguezActa Materialia, 58 (2010) 6404-6410
Show abstract ▽
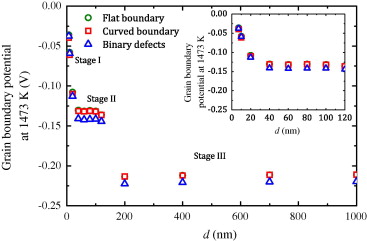
A first principles continuum analytical model for cationic segregation to the grain boundaries in complex ceramic oxides is presented. The model permits one to determine the electric charge density and the segregation-induced electric potential profiles through the grain and can be extrapolated to the range of nanostructured grain sizes. The theoretical predictions are compared with existing data for yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystals. The implications for physical properties (mainly high temperature plasticity and hardening behaviour) are then discussed.
Noviembre, 2010 | DOI: 10.1016/j.actamat.2010.08.002
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Iron-modified ceria and Au/ceria catalysts for Total and Preferential Oxidation of CO (TOX and PROX)
Laguna, OH; Centeno, MA; Arzamendi, G; Gandia, LM; Romero-Sarria, F; Odriozola, JACatalysis Today, 157 (2010) 155-159
Show abstract ▽
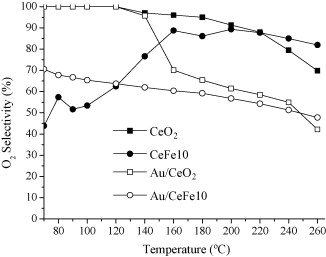
Iron-modified ceria supports containing different molar percentages of Fe (0% 10% 25% and 50%) were synthesized by thermal decomposition of the metal propionates The formation of a Ce-Fe oxide solid solution is evidenced through XRF XRD BET and Raman spectroscopy For Iron contents above 25% the formation of alpha-Fe2O3 was detected pointing out the formation of the isolated oxides The catalytic activity of the Fe-modified catalysts in the Total Oxidation of CO reaction (TOX) is higher than for the bare CeO2 material The synergy between Ce and Fe shows a maximum for 10% Fe content (CeFe10) catalyst that shows the highest CO conversion per atom of Fe incorporated Gold catalyst was also prepared on CeFe10 and its catalytic activity compared with Au/CeO2 catalyst The addition of iron to the gold catalyst resulted in an enhancement of the catalytic activity for CO oxidation especially at low temperature This Au/CeFe10 catalyst was also active and selective with excellent stability in the Preferential Oxidation of CO (PROX) showing a higher CO conversion than the Au/CeO2 catalyst at temperatures below 150 C being hardly affected by the presence of CO2 and H2O in the gas stream.
Noviembre, 2010 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2010.04.011
Química de Superficies y Catálisis
Modified cryptomelane-type manganese dioxide nanomaterials for preferential oxidation of CO in the presence of hydrogen
Hernandez, WY; Centeno, MA; Romero-Sarria, F; Ivanova, S; Montes, M; Odriozola, JACatalysis Today, 157 (2010) 160-165
Show abstract ▽
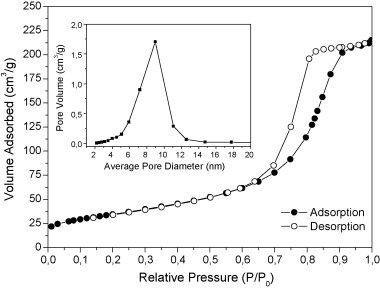
Transition metal (Cu Co Ni and Zn)-modified cryptomelane-type manganese dioxide nanomaterials were synthesized by the milling method The obtained solids have been characterized by means of Xray diffraction (XRD) scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy (SEM and TEM) N-2 adsorption-desorption measurements at 77 K Raman spectroscopy and temperature programmed reduction (TPR-H-2) showing similar structural and textural properties All the solids were active in the preferential oxidation of CO in the presence of hydrogen (PROX) being the modified with copper the most active The catalytic activity correlates fairly well with the TPR results finding higher CO conversion for the material with higher reducibility (OMS-Cu) The O-2 selectivity measured as ([CO](in)-[CO](out)/2[O-2](in)-[O-2](out)) x 100 is very similar for all synthesized materials.
Noviembre, 2010 | DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2010.03.010
Reactividad de Sólidos
Quantitative Characterization of Multicomponent Polymers by Sample-Controlled Thermal Analysis
Sanchez-Jimenez, PE; Perez-Maqueda, LA; Crespo-Amoros, JE; Lopez, J; Perejon, A; Criado, JMAnalytical Chemistry, 82 (2010) 8875-8880
Show abstract ▽
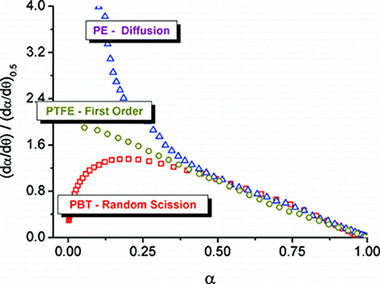
This paper explores the potential of sample-controlled thermal analysis (SCTA) in order to perform compositional analysis of multicomponent polymeric materials by means of thermogravimetric experiments. In SCTA experiments, the response of the sample to the temperature determines the evolution of the temperature by means of a feedback system; thus, what is controlled is not the temperature time profile, as in conventional analysis, but rather the evolution of the reaction rate with time. The higher resolving power provided by the technique has been used for determining the composition of polymer blends composed of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and different commercial plasticizers, a system where the individual components have very similar thermal stabilities, thereby rendering useless thermogravimetric experiments run under conventional conditions. Different SCTA procedures, such as constant rate thermal analysis (CRTA), which has received special attention, and high-resolution and stepwise isothermal analysis have been tested, and the results obtained have been compared with linear heating rate technique. It has been proven that CRTA can be used to effectively determine the exact composition of the blend.
Noviembre, 2010 | DOI: 10.1021/ac101651g
- ‹ anterior
- 367 of 422
- siguiente ›














